Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment Help services.
The present assignment aims to explain the business objectives that are affected by the ethical considerations and their implications to the stakeholders. A variety of ideas and theories are implemented in the chosen organisation Tesco such as CSR Carroll's pyramid, Ethical Dimensions theories, Elkington's Triple Bottom Line (TBL), or stakeholder management theory. The consequences of sustainable business on the external environment are evaluated using appropriate ideas, models, and research findings, and discover how leaders may effectively preserve a competitive edge utilising these strategies throughout the assessment with applicable ideas and concepts, such as Elkington's TBL, Ethical Dimensions, the Circular Economy, and selective use of PESTLE analysis. Also, the current methods of communication and working habits in the present scenario of the Covid19 pandemic corporate climate are examined in this report, and a viable approach for leading the organisation Tesco ethically has been discussed. An effective leadership approach is examined applying the VUCA concept to the post-COVID-19 pandemic business climate. Recent COP26 results may serve to enlighten the perspective on the difficulties ahead.
CRS Carrol’s Pyramid:
Tesco company cares more about people, including their overall workforces, the existing customers, as well as the targeting customers in different ways, through a potentially healthy living, as well as such education persuasive, several charities support, providing such healthful working environments, promoting comprehensive, and at the same time, proceeding human rights in the supply chain Lee et al. (2019). In contrast, Carroll's four domains regarding Corporate Social Responsibilities, or even CSR, comprise one of the primary approaches in the areas of systemising the main concept of CSR. The main purpose of these dour domains lies in the factor that this framework classifies the overall responsibilities that the society expects the organisations to simulate. The probabilities regarding the movement within these domains, mainly argued by Carroll, as suggested by Kusyk (2021), is a basic function of the entire concept. However, there lies such suggestion that focused on the areas of the fact that this is considered an oversimplification, according to the arguments of Carroll related to the fact that 10 focus mainly from an aspect of the CSR would be potentially focusing on the entire pyramid as such a unified whole. It, in contrast, is better focused on the areas of assessing the way the organisation may involve in actions that further fulfil the entire elementary phases. According to Carroll's pyramid, Tesco has focused on the areas of fulfilling different responsibilities at four levels (Ayalew, 2018).
Figure 1: CRS Carrol’s Pyramid
(Source: Kusyk, 2021)
Economic responsibility: It is considered as the lowest level of the pyramid, representing the initial responsibilities of the organisation that is further to be profitable. Being profitable is referred to as the sole way for the company to be capable enough for surviving long run, and at the same time, convenience society.
Legal Responsibility: It is referred to as the second level of the pyramid, and at the same time, the legal obligation of the company is mainly to obey the law, as well as regulation Lee et al. (2019). There are different factors, including employment laws, competition along with other companies, tax-related regulations, as well as both the health and safety of the overall workforce are considered as examples of legal responsibilities Tesco should adhere to.
Ethical Responsibility: The ethical phase regarding the pyramid is potentially described as performing the appropriate thing, being fair in every condition, as well as further avoiding harm.
Philanthropic Responsibility: Situated at the top of the pyramid, occupied the tiny space, philanthropic responsibility focused on the areas the businesses of the company have long been categorised for their carbon footprint. At the same time, their phase in pollution, utilising such resources that are considered natural, and even more.
TBL or Triple Bottom Line Theory is considered as such a concept that has potentially come up with three factors that a company should strongly follow in terms of becoming sustainable that further includes people, planet, as well as profit Shim et al. (2021). In this present era, different companies, including Tesco, are adequately aware of the fact of running their business in the long run. The reason behind this lies as people currently believe that for big enterprises for becoming successful, they must try to become more sustainable. In such case of Tesco, it seems that there are some negative aspects regarding their sustainability. At present, as stated by Liang et al. (2018), again, the company has enhanced to at least over 11 countries across the globe, and there are closely 35K stores in the U.K. It focused on the areas of making such a huge amount of profits for decades Kar et al. (2021). Tesco, added to this, has done different things in the areas of appearing people as such public services, as well as tried in terms of balancing along with several factors for maintaining such ideas of sustainabilities. It, however, seems the factor that they are not performing adequately to be claimed potentially as such a sustainable company. There lie several arguments from different people regarding the sustainability of Tesco. This is because several people in the U.K. believe that Tesco has caused different negative outcomes on both the environment, as well as society. According to Tesco, there are gnarly about 40% of Apples that are dumped into the trash every year that is considered as overall 28K tonnes Kar et al. (2021). Added to this, the company is further trying in the areas of finding different solutions for its leftovers products. Tesco, on the other hand, creates one of its solutions by providing different awareness campaigns that include advertising to raise different awareness to the community regarding this issue. As per the report of Tesco, as it has studied the living accommodation of the people in Europe referee to as EMCC, as stated by Kar et al. (2018), the company is better responsible for about 5.4 million tonnes of CO2 emissions in the U.K. that is referred to as the central cause. In addition, this is mainly due to the high electricity consumption. The company, therefore, has come up along with such a strategy regarding decreasing their overall consumption.
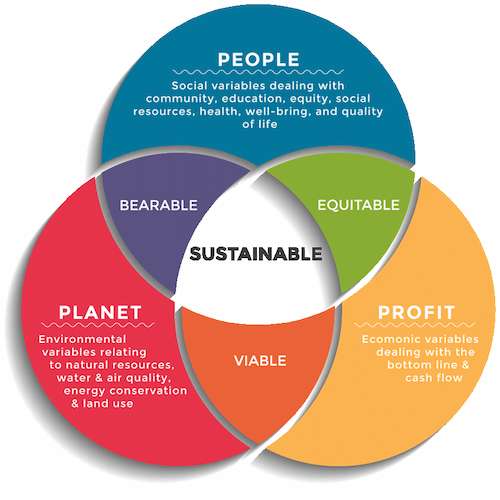
Figure 2: Triple Bottom Line theory
(Source: Kar et al., 2018)
Ethical Dimensions theories:
Both ethical theories, as well as guidelines regarding this, are referred to as such foundations regarding such moral investigation. In addition, there is such a way that the companies are the aspects from which constellations could be potentially gained with such a pathway to such a decision (De Bakker et al., 2019). There are different theories that Tesco focused on the areas of developing their overall ethical dimensions within the company. The following discussion is focused on the concept of Utilitarianism in Tesco.
Utilitarianism: It is considered as such a factor a morally overwhelming performance that could provide such a remarkable estimate with some connection to the counting of people. However, the entire improvement is further essential to such outcome in this specific institution, again being accessible. At the time, such noteworthy speculations stress different common principles, as well as the absence of prejudice; in such cases, the moral of consideration better underlines such importance associated with the reaction. Utilitarianism added to this, as suggested by López-Fernández (2020), judges the moral value regarding the moral value of performance by such utilities regarding their outcomes, especially for the people who were affected by a particular set of functions. Tesco aims in terms of responding in both their trading as well as commercial actions. The company, in contrast, has been a member of the ethical trade initiatives since it was established. The company sells as well as promotes different fairtrade productions. There lie several reasons for the way the company utilises the Utilitarianism theory Anshari (2020). First of all, Tesco wishes to create such a potential relationship with both their customers as well as suppliers in the areas of maintaining their reputation within the market industry. It further helps the company to have such a sustainable supply for both its goods as well as services.
The circular economy
The main concept regarding the circular economy is focused on the areas of gaining such momentum in both the political as well as business thinking. This is specifically about such a transition to a more sustainable future. According to both EuroCommerce, as well as the European RRT, or Retail Round Table, the ultimate findings disclose the fact that approx 50% of the conducting European retailers pointed such a commitment to this circular economy Hashim et al. (2021). At the same time, to such ethics that are potentially underpinning it, as well as an amount of them looked forward in terms of evidence their commitment between such operation regarding their retails. Within a circular economy, on the other hand, waste management is considered as no longer seen as an issue but, at the same time, rather as a scope in terms of returning as much waste as possible return back into such productive utilisation. The central focus, in contrast, is specifically on the protection, utilisation, as well as recycling of the waste components better than their disposals Lazell et al. (2018). In such cases, waste can not be potentially prevented, reutilised, as well as recycled at the time of recovering the energy consistent is further seen as preferable to landfill, and at the same time, waste to such solution associated with the energy which is further seen to be more integral to the overall circular economy. In the areas of Tesco, the pooling system helps the company to save both money as well as the planet. Added to this, by utilising, as well as sharing trays as circular logistic carriers, Tesco at their Euro Pool System supports their customers in terms of making limitations their environmental footprints on the way. For decades, Tesco has been involved in different initiatives that further limited both its carbon footprint, as well as fighting for the wastage of food Suresh (, 2020). The company, as the retail trade associations, looked forward in the areas of developing the overall performance regarding the environment to the retail industry of the economy and further involves the entire of the supply chain.
The PESTEL analysis of Tesco examines the different types of external factors, including political, economic, social, technological, environmental, as well as legal factors. This analysis will be focused on the areas of highlighting the distinguish extrinsic scenario that better affect the overall business of the brand.
Tesco is conducting in about 11 countries such as Asia, as well as Europe. It is, in contrast, exposed to different political factors that can better be affected the overall performance associated with Tesco Woohyoung et al. (2020). The factors include current as well as impending legislation, rates of tax, instability in politics, the rate of unemployment, the current economic conditions regarding the country in which the company is operating. Britain has a very stable environment, but at the same time, Tesco follows such safety regulations in several countries to provide such safe products.
Labour cost is considered as the most significant economic factor that can potentially affect the supermarkets in the U.K., including Tesco. For instance, the yearly wage is strongly amounting to about GBP 4.5 billion. In addition, both diversifications, as well as the presence in the global market, are referred to as such significant strategies in the last few years Tirawatnapong (, 2018). It is worth mentioning the fact that the company is still dependent on the market in the U.K. along with such an approx 27.7% share in the U.K. market of grocery.
Social Factors
The shopping trends of their consumers are continuously transforming over time. People prefer one-stop shopping. Tesco, on the other hand, is relying on the customers in the U.K., and at the same time, should better understand, as well as offer such services in terms of meeting different issues Kim et al. (2019). The entire demand for its goods, as well as services, in addition, is associated with its customer's loyalty and attitudes that are referred to as such another significant issue.
Technological Factor
Technological advancement, in contrast, brought different advancement opportunities to Tesco in the areas of regaining their loyalty to the customer. Tesco, added to this, focused in terms of embracing such advancement in technological as scope specifically by adopting obtainable retail technologies. The company introduced RFID technology in the areas of enhancing their in-store experience for their customers Rosnizam et al. (2020). This counts stock, as well as focused in terms of removing it after a product is sold.
Environmental Issues
There are different companies that are facing immense pressure from several government agencies in terms of addressing the issues related to the environment. In such cases, Tesco, in contrast, encourages its consumers to shop online at tesco.com. The van of Tesco will not solely utilise fuel-saving routes, but at the same time, further gather excessive plastics bags from the customers, as well as recycle them. Tesco, as suggested by Keiningham et al. (2020), is committed to the fact of using renewable sources, as well as generating 100% of its entire electricity by 2030.
In every business legal environment, do not underestimate the central areas where regulations transform that can better impact the overall business performance for accomplishing the objectives of the company. In the year 2016, 17 workers of Tesco took such legal actions against their employers on the basis of both ages, as well as gender discrimination Michalakopoulou et al. (2021). Tesco further faced such legal activity in the areas of accounting fraud, as well as misleading their investors, and ultimately agreed to pay GBP about 12 million for settling such legal actions.
Five forces analysis of Tesco
The following discussion is a detailed analysis of Porter's five forces regarding Tesco. It, in contrast, focused on the areas of examining the effect of the five forces, including competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, the threat of substitutes, as well as the threat of new entrants on Tesco that on the other hand, further operates in the supermarket sector. Tesco is the market leader in the U.K., and at the same time, drives in different countries.
Bargaining power of the purchasers of Tesco
Tesco, in general, serves a huge number of its customers both in its stores as well as on digital platforms (Tesco, 2020). According to Beke Lisányi (2018), the bargaining power of the customers or the purchasers in the U.K. is adequately low. This is because they are considered as not organised, as well as it is unlikely to factor that they can be further better off in such cases; they mainly focused in terms of switching to their competitors such as Asda and Sainsbury's. This establishes the overall sector as attractive for Tesco.
Bargaining power of the suppliers of Tesco
Tesco performs along with about 2,500 suppliers in the U.K., as well as more thousands in the rest of the world Alford et al. (2021). However, these specific suppliers cannot exert any kind of significant power on the company as there are so many of them out there. The company, in addition, negotiates very difficulties along with such suppliers to enhance its profit margins.
Figure 3: Porter’s five forces law
(Source: Alford et al., 2021)
The threat of advance entrants affecting Tesco
The threat of advanced entrants is better focused on such areas of coming into the supermarket of the U.K. industry is considered as very low specifically because of the capital needs Woohyoung et al. (2020). The company does not require to worry about different advanced entrants as it enjoys economies of measure, as well as has its own focused competencies.
The threat of substitute products and services affecting Tesco
Tesco provides its customers along with a broad range of products. It further sells substitutes for the majority of its products. For instance, it sells both jars of butter, as well as margarine Keiningham et al. (2020). Therefore, it is get-at-able to argue the fact that the threat of substitute products, as well as services for Tesco, is mostly incoherent.
Rivalry amongst the companies existing competitors
Tesco has a huge number of potential competitors in the U.K. These competitors, added to this, spend lavishly on advertising, as well as different marketing methods Byun et al. (2020). Though Tesco is considered the market leader, the pressure from the nearest competitors remains the same.
Several firms have had early success in reducing COVID-19 infection rates, while others have been overwhelmed. The causes for the disparities are complicated, but response efficacy has been influenced by the timeliness and scope of government engagement, as well as how communities have received, interpreted, and acted on government and other agency information. The COVID-19 epidemic has caused a catastrophe of a magnitude and with social, economic, and environmental consequences that have never been seen before. For most organisations, the effects of this crisis in the most impacted nations are many and of unparalleled intensity.
VUCA concept to the post-COVID-19 pandemic business environment
The military invented the term VUCA, which stands for volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity, in the 1990s to define the ever-shifting geopolitical terrain in which it had to operate. VUCA currently represents the climate in which corporate executives must fight the COVID-19 epidemic. Business leadership abilities are essential in a VUCA world. As they traverse new seas in a context of volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity, business executives face enormous hurdles. How effectively they perform might determine whether or not their firm survives. Tesco is dealing with an economic crisis unlike any other in our history, as unemployment has surged. Consumers, particularly those who have lost their employment, may think twice about spending on non-essential items. Businesses are facing difficult circumstances, but they also have the chance to test new business strategies. Businesses like Tesco who provide components required in the fight against Covid-19, have noticed a huge surge in demand for their goods. Entrepreneurial company executives saw an opportunity to adapt their manufacturing facilities to make these items. Some restaurants have switched to curbside takeout and delivery services after being ordered to close their dining rooms. Many other firms may be forced to pivot in order to stay afloat. Sadly, many of the businesses that were forced to close may never reopen (Silverman, 2020).
Empathy is required of business executives not only for individuals who are laid off or furloughed but also for those who are crucial to the company's running and are requested to work many longer hours than usual. This will take its toll over time, and their additional work must be appreciated. Business leaders will need to analyse and adapt their business models to accommodate social distance until a vaccine is produced and rapid-result Covid-19 testing is widely available as governors around the country reopen their economies. This is a moment of tenacity, perseverance, and creativity. Business executives and their teams should use what they are learning as a result of the pandemic's developments to their advantage. Disrupt long-held beliefs. Volatility, ambiguity, and complexity all bring opportunities for the betterment of the organisation. When certain corporate executives gaze down into the deep, black abyss, it is their best hour, and their companies emerge stronger than before (Hyland-Wood et al., 2021).
Volatility
Tesco has grown more unpredictable than ever before due to economic ups and downs, changing consumer spending power, changing consumer demographic patterns, changing attitude of the rapidly increasing, youthful urban middle class, and changing consumer taste and p
Get Better Grades In Every Subject
Submit Your Assignments On Time
Trust Academic Experts Based in UK
Your Privacy is Our Topmost Concern
offer valid for limited time only*
