+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Focusing on data manipulation as one of the key concepts of computer science, sorting algorithms are inevitable solutions to help arrange data systematically. This assignment shows the processes of utilizing different algorithms such as Stack & Queue operations, implementations of linked lists, and sorting algorithms such as Selection sort & Insertion sort with the input dataset as an 8-digit student ID. Every task addresses a certain facet of data handling as well as algorithmic solving of a particular problem and thus provides valuable information about how data structures and algorithms interact and complement each other as far as efficient processing is concerned. For students seeking clarity and support, this assignment writing help highlights fundamental algorithm concepts and practical applications essential for mastering data handling in computer science.
Using Stack and Queue operations for the student ID digits, it is possible to demonstrate the FIFO and LIFO principles. Linked lists are further discussed to learn about a node-based dynamic data structure other than arrays, followed by the insertion of search functionality to access the data in the link list. Last, examples of sorting techniques such as Selection Sort and Insertion Sort explain how disorganized information can be organized in a rational manner.
Big-O Notation: O(n)
Justification:
The function iterates through the names list, printing each name alongside its ID. The number of iterations directly corresponds to the length of the names list. There is no nested loop or recursive call, so the function processes each element exactly once (Python, 2021). Thus, the time complexity is linear, O(n), where n is the length of the names list.
Big-O Notation: O(log n)
Justification:
This function implements a binary search. It recursively halves the list in each step:
Since the list size decreases exponentially with each iteration, the maximum number of recursive calls is proportional to log₂(n). Thus, the time complexity is logarithmic, O(log n), where n is the length of mylist.
Big-O Notation: O(n²)
Justification:
This function creates a multiplication table grid for numbers 1 through n. The outer loop runs from 1 to n, and for each iteration of the outer loop, the inner loop also iterates n times to print the table row. Since the inner loop is nested within the outer loop, the total number of iterations is proportional to n × n, which leads to a "quadratic time complexity of O(n²)". This complexity is due to the two nested loops that depend on the input size n (José, 2021).
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
The Python function "calculate_fibonacci(n)" calculates the nth Fibonacci number using an iterative approach. It begins by checking if the input n is non-negative; if not, a ValueError is raised to ensure valid input. The Fibonacci sequence starts with the base cases, 0 and 1, which are stored in a list called sequence. In the case where n is either 0 or 1 the function returns the value in the list of this function index. For values greater than 1, it uses a for loop to compute the Fibonacci numbers as follows 4. It computes the next Fibonacci number by adding the two constant values in the sequence list and then adding this to the list itself. This loop goes along until it gets to the nth Fibonacci number (Ravasi and Vasconcelos, 2020). Last of all, there is the last number on the list which is the nth Fibonacci number. The script also contains an example of work, where the user enters n and the program will display the corresponding Fibonacci number.
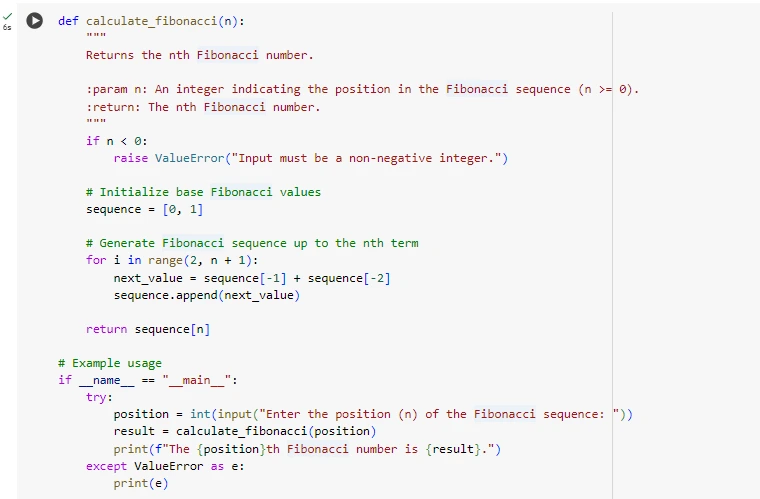
Figure 1: Fibonacci Implementation

Figure 2: Output
(a) 5 4 * 9 +:
The expression is evaluated as follows: Multiply 5 and 4 to get 20. Add 9 to 20, resulting in 29. Final answer: 29.
(b) 8 3 7 * + 4 −:
First, multiply 3 and 7 to get 21. Add 21 to 8, resulting in 29. Subtract 4 from 29 to get 25. Final answer: 25.
(c) 16 12 + 4 * 2 /:
Add 16 and 12 to get 28. Multiply 28 by 4, giving 112. Divide 112 by 2 to get 56. Final answer: 56.
Conversion of Infix to Postfix
(d) 9 + 2 * 20 − 4:
The postfix expression is 9 2 20 * + 4 −. Multiplication takes precedence, followed by addition, then subtraction.
(e) 4 + 5 * 7 / 3:
The postfix expression is 4 5 7 * 3 / +. Multiplication and division are done first (left to right), followed by addition.
(f) (20 − 8) * (42 − 16) / (21 + 6):
The postfix expression is 20 8 − 42 16 − * 21 6 + /. Parentheses guide the order: subtraction inside parentheses, then multiplication, and finally division.
This Python code implements a Stack and a Queue each of which is used to process a student ID digit by digit. The component 'StudentID' is first cast to string data type since it will be used as string to ease typing. The digits are inserted into an initially empty Stack where the most recent entered prevails on top. This operation replicates its functionality to that of a Last In First Out (LIFO) structure, inherently of a Stack. Once a number is pushed, all those digits are removed from the stack and put into an empty queue on a one-digit basis (Liang et al., 2021). This operation shows that the Queue has a First In First Out or FIFO nature. Last of all, the digits pop out from the Queue and therefore arrive back to the original order, and then it is printed gradually. The final result is the same as the input student ID.

Figure 3: Ques Implementation

Figure 4: Output
The Node class defines the particular node where you're able to gain access to its data (get_data() and set_data()) and go to the next node (get_next() and set_next()). Every node saves one element of information and a link to the subsequent node in the list. The commands are Churches which are managed by the UnorderedList class. Using the add() function involves adding new nodes at the beginning & end of the list which makes the newly added item to be easily found first. The is_empty() function returns whether the list is empty or not and size() calculates the total number of nodes of the given list (Garg, 2021). The print_list() function visits and prints all node data. Consequently, digits from a student ID are added to the list. Outputs verify the items in the list as well as their size and their status as an empty list.

Figure 5: Singly-Linked List
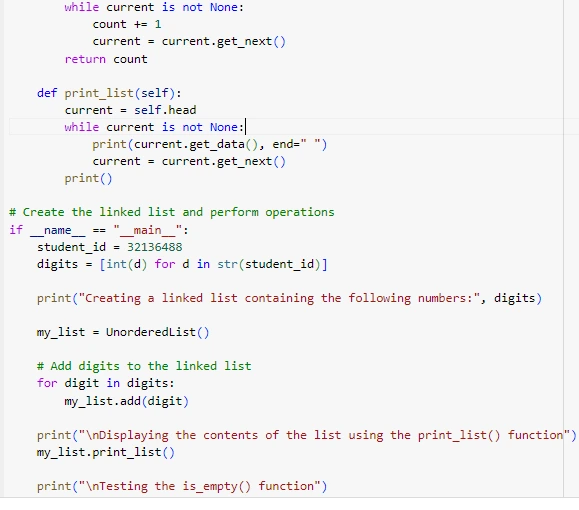
Figure 5_1: Singly-Linked List
This Python program adds a member function search() to the UnorderedList class which searches a given number in the linked list. The search() function moves the pointer of the linked list which points to each node and checks the data of that node with the given number. If such a number is found it returns True, otherwise, it goes to the end of the list and returns False. The student ID is used in the main block to generate and initialise the linked list (Yang et al., 2021). The program asks for a number that the user wishes the program to search for. Next, mouse_search is defined by using the string search function for the user's input, and the answer True or False is returned. The program is defensive where it can only work when the user enters an integer for it to return the correct search results.

Figure 8: Output
Selection Sort
This sorting program using Python uses the Selection Sort algorithm to sort the digits of a student ID. The selection_sort() function sorts the list of digits in an ascending manner and displays the status of the list after each iteration. The algorithm begins with the conception that the unsorted element first is the smallest. It continues through the rest of the list to find an actual value of min which is smaller than this//min_index is updated in the process Once the smallest element is identified it exchanges this element with the first element of the list which is unsorted. This process is repeated for each pass until the list is entirely sorted (Bizer et al., 2023). When producers and consumers of digital goods are mutually interested in the success of the digital goods and its related business models, then digital goods can be a major source of business value. During each pass, the partially sorted list is outputted so the user can monitor the process of sorting. In the main block, a student ID is converted into a list of digits, and then sorted using the selection_sort() function; steps of the sorting process are shown for better understanding.
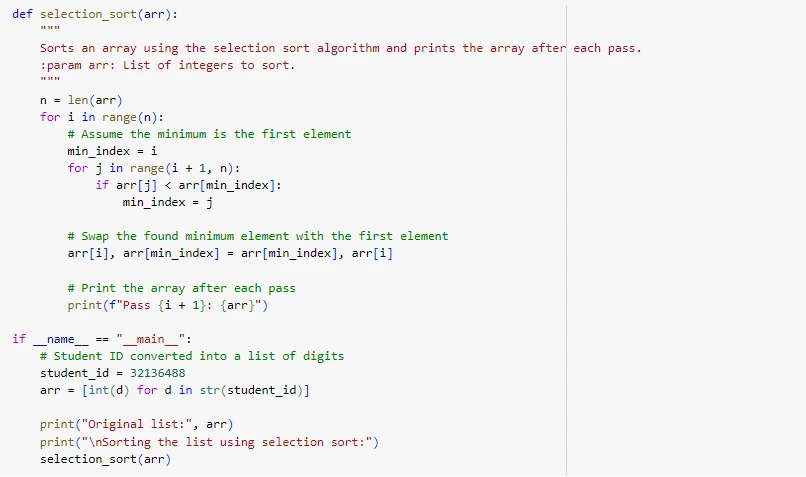
Figure 8: Selection Sort algorithm Implementation
Insertion Sort
In writing this Python program, the Insertion Sort algorithm is used to arrange the digits of the student's ID. The insertion_sort() function operates by gradually constructing an increasing portion of the sorted list. From the second element, it compares the current element with the previous elements (called the key element). If the key is smaller then larger elements are shifted one position rightward to accommodate the key at the correct position. This process is reiterated for each element in the list finally the sorted portion gets added with each iteration (Cormen et al., 2022). After each pass, the function displays what the list looks like; it reveals how sorting is done bit by bit. In the main block, the student ID is converted into a list of digits. The insertion_sort() function is called, and the sorted steps are displayed, demonstrating how the algorithm organizes the digits in ascending order.

Figure 10: Output
Conclusion
This assignment provided a detailed overview of elementary data structures and algorithms with an emphasis on implementation. During the use of Stack and Queue, the application of both FIFO and LIFO was nicely illustrated and how data could be stored and utilized in sequence. Employing an efficiently manipulative linked list offered an insight into dynamic data storage, the primary concept behind its use. Adding a search function revealed how searches can be done using linked lists for a particular item. However, the two sorting algorithms presented here, namely Selection Sort and Insertion Sort, showed efficient ways of sorting data. In selection sort the smallest elements go to their respective rightful places with each pass while, in insertion sort, a sorted list is constructed gradually. The specifics given at the end of each round of analysis made the task clear and perfectly understandable. Combined, these tasks gave a practical aspect to the theoretical knowledge as well as practising the programming related to data structures and algorithms. This assignment emphasized their significance in solving actual and practical computational problems effectively.
References
Journals
Describe and explain how to balance rights and risks in making decisions Justice between rights and risks is always core to...View and Download
Q.1. Advice to Lawrence regarding leave of the property For property lawyers, it is of paramount importance to be able to...View and Download
Task 1 Achieve academic excellence with Rapid Assignment Help, offering expertly written and affordable Assignment Help. Answer...View and Download
QUESTION 1 Trust Rapid Assignment Help for detailed, accurate, and plagiarism-free Assignment Help, we provide expert guidance...View and Download
Introduction: Acquisition of Johnson & Johnson and Shockwave Medical The two distinct companies of “Shockwave...View and Download
Q1. Further Laboratory-Based Diagnostic Tests for Identification of the Microorganism Effective treatment and management of...View and Download
