+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Struggling to meet deadlines? Get back on track with RapidAssignmentHelp your go-to solution for assignment help that's fast, reliable, and affordable. Stay ahead without breaking the bank!
The global maritime industry, an imperative course of international trade, is winding up investigating bizarre waters amidst the ongoing Russia and Ukraine conflict. As geopolitical strains rise, the repercussions on international shipping routes have become dynamically expressed. This assessment project dives into the astounding snare of challenges faced by the maritime region, focusing on the resilience strategies and risk management practices sent considering the geopolitical aggravation. Against the foundation of this dynamic and complex environment, the place of this study is to dismantle and analyse how shipping associations travel through the weaknesses introduced by the Russia and Ukraine wars. The objectives are triple: first, to analyse the unquestionable impact of the conflict on international shipping routes; second, to recognize and survey the resilience strategies implemented by shipping components; and third, to assess the ampleness of risk management gauges concerning the constant geopolitical trouble.
This proposal synthesizes structural and strategic insights from the above literature to build the Integrative Strategic Agility model tailored for shipping resilience. Extensive industry data analysis will further verify strengths and limitations while exploring progressive enhancements to the model. The field evidence aggregated holds currency for both academia and policymakers when reforming maritime regulations.
The thinking for undertaking this investigation lies in the fundamental meaning of understanding how the maritime region acclimates to geopolitical disruptions. By loosening up the layers of resilience and risk management, this study contributes significant encounters that can enlighten industry practices and procedure decisions. As we leave on this examination, the point is to understand the continuous challenges as well as to outfit the industry with data that energizes status for future weaknesses.
The foundation of this research wraps up the multifaceted challenges faced by the global maritime industry straightforwardly following the Russia and Ukraine conflict. As geopolitical strains uplift, international shipping routes, usually considered courses of smooth trade stream, are by and by reliant upon exceptional disruptions (Chunsheng et al. 2020). The persistent conflict has set off a flowing sort of impact, undulating through supply chains and demanding a careful understanding of its impact on the maritime region. The trade routes through the Black Sea were blocked, causing shipping companies to lose billions in revenue each year (Lloyd, 2022). With major grain export terminals blocked due to crop shortages, the conflict has also raised fears of global food shortages (Financial Times, 2022). Analyzing maritime sustainability strategies is therefore crucial as governments quickly find alternative cargo solutions before the dispute can further exacerbate supply chain instability globally (UNCTAD, 2022).
This research aims to create an Integrated Strategic Agility (ISA) model that synthesizes proactive, adaptive and flexible capabilities to improve maritime resilience during regional conflicts. The model is validated with evidence collected from global shipping networks affected by the Russian-Ukrainian war. The findings promise to inform policy reforms that balance conventional crisis management practices with the emerging realities of today's systemic risks. In addition to being useful to national regulatory authorities, the ISA framework provides a model of adaptation for shipping companies struggling to remain profitable in the face of conflict-related operational constraints and rising costs. By examining current risk practices against recent failures, this study ultimately aims to provide a nuanced and contemporary perspective on protecting maritime supply chains from geopolitical vulnerability.
The research structure is intended to unravel the intricacies of the maritime industry amidst the Russia-Ukraine conflict, aligning with the objectives. The introduction sets the stage, framing the geopolitical setting. The research overview conclusively dismantles careful investigations, literature review, and models, laying a foundation for understanding resilience strategies. The method, utilizing a total data collection approach, ensures a nuanced investigation of industry responses.
Maritime transport accounts for 90 percent of global freight (UNCTAD 2022). Thus, transport channel shocks cause systemic ripples globally. Due to the crisis in Russia and Ukraine, container costs have quadrupled and shipping delays have tripled since 2019 (McKinsey 2022). Such acute economic and operational stress highlights structural deficiencies in supply chain sustainability worldwide (Krason 2022). It is clear that traditional risk models have failed to assess and insure maritime logistics against regional conflicts. Current strategies falter even in slow crisis situations, showing an over-reliance on myopic, proactive systems that fail in times of radical uncertainty (Nilsen 2022). These blind spots urgently need to be supported by incremental robust frameworks that combine predictive and adaptive functions with market volatility scenarios (Ivanov 2022). This research project develops an Integrated Strategic Intelligence (ISA) model for the sustainable development of the maritime industry. By combining predictive analytics, system diversification and operational flexibility, the ISA framework aims to better cushion periods of turbulence. A field analysis of post-Russia and Ukraine provides an empirical understanding of the structure of the ISA model and assesses its viability as a policy. In summary, this proposal develops and tests the latest sustainability theory that reflects the new reality of global shipping.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
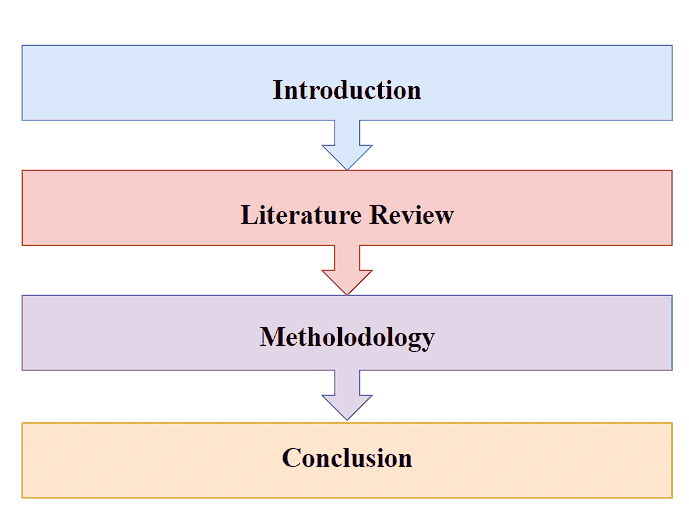
Figure 1: Research Framework
According to Nguyen et al., 2022, The key transit corridors face a spiralling blockade of energy and commodity prices, waves of trade instability threaten post-pandemic recoveries (Nguyen et al., 2022). The quantification of specific bottlenecks and risk lines is therefore essential, especially with regard to political reforms that increase the sustainability of international logistics frameworks. Nguyen et al. emphasizes the extent of the disorder. (2022) emphasize the almost complete cessation of shipping in the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov. Capacity utilization is falling, although 70% of Ukraine and typical exports are still domestic, the study warns of an explosion of cargo prices and deficits in the coming months. It notes Ukraine's important position as a supplier of almost half of the world's neon gas, which is essential for semiconductor value chains. The ban on Russian and SWIFT payment channels also jeopardizes the wages of merchant fleet crews, who make up nearly 15% of the maritime workforce.
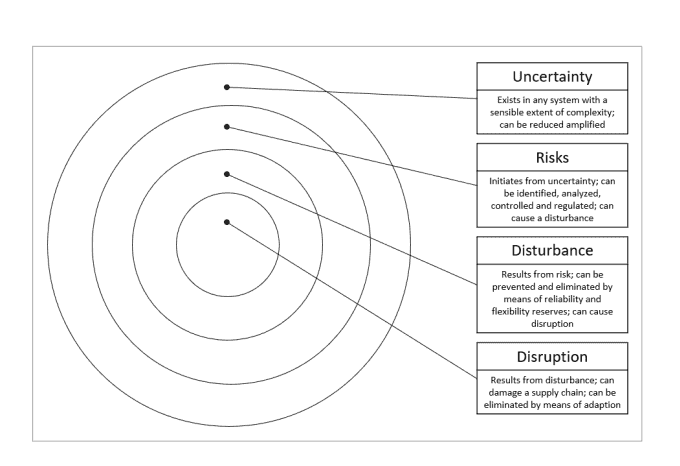
Figure 2: Interrelations of uncertainty, risks, disturbance, and disruption
Echoing these results, Suszynski (2022) estimates that more than 60% of conventional shipping volumes are forced to be diverted due to conflict. In particular, he describes the harmful reflections between Russian energy, Ukrainian and Western European production, and intercontinental distribution networks. The analysis shows the risks associated with plant closures when critical material supplies in both countries are depressed. It also warns of a war in Ukraine that could exacerbate already existing supply chain bottlenecks caused by the pandemic. However, there are limitations to predicting long-term trade distortions due to the inherent uncertainty of an incipient war. Special flexible tactics of logistics companies were also unstudied. In addition to diagnosing the challenges, specific strategy proposals to mitigate future crisis effects need more detailed consideration. Together, the articles provide a strong framework for examining the effects of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict on international trade. But further research is needed to crystallize the response mechanisms to improve the supply chain and its resilience and resilience to geopolitical disruptions.
According to Ngoc 2022, as exacerbated by the COVID pandemic, modern supply networks are vulnerable to disruptions ranging from localized events to global shock events. The invasion of Russia and Ukraine in 2022 represents the latter, and extensive trade and financial sanctions led to the freezing of material and financial flows regionally and internationally (Waters, 2022). Therefore, building resilience against such fractures is imperative, as it requires modern risk management protocols adapted for an era of evolving uncertainty.
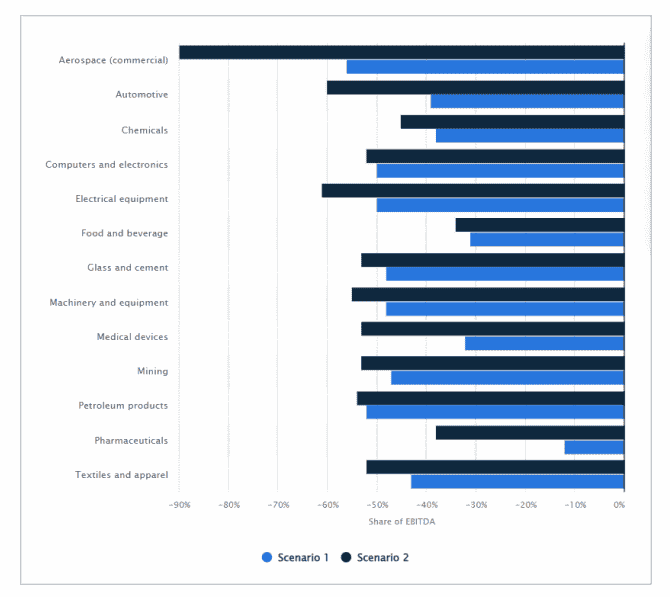
Figure 3: Impact of a 100-day supply chain disruption worldwide on companies
Underscoring this reality, argues that traditional identification-based risk management frameworks falter during unpredictable fluctuations that exceed forecasting systems. It signals a shift to creative flexibility that emphasizes quick recovery and minimal downtime regardless of the cause of the disruption. Ivanov and Sokolov (2010) support this view by distinguishing "stability" as a key measure for supply chain service level optimization along with costs. To increase resilience, specific capabilities are needed that increase resilience through coordination between multiple partners.
Boost your grades with expert Operations Management Assignment Help tailored to your academic needs. Get clear, step-by-step solutions to master key operational concepts and frameworks.
The article also identifies. Acquisitions and procurement as priority areas that require urgent sustainability improvements due to declines in recent years. It notes Ukraine's past status as a major global supplier of key industrial components such as rare earths and neon gas. The breakdown of energy availability and logistics networks crippled production hubs, necessitating advance planning to reroute pipelines and develop alternative procurement protocols. Therefore, the aim of the work is to prepare a practical guide that provides managers of various economic sectors with the principles of risk management applicable during geopolitical crises. However, the current scope is limited to cutting-edge research in resilient construction, where detailed mitigation strategies need to be learned. The paper highlights the struggles of traditional supply chain structures during extreme volatility events and suggests progressive, stability-oriented models that synthesize predictability and flexibility. A detailed plan for reforming the procurement and supply chain to repair the fractures caused by conflicts would further enrich the literature on the subject.
The attack by Russia and Ukraine severely disrupted global shipping networks and exacerbated the supply chain chaos caused by the pandemic. The sea routes through the Black Sea are blocked, which prevents the transportation of grain and oil (Li 2022). Shipping companies reported record losses from ship management (Lavender 2022). As wheat exports declined, the conflict also raised food security issues worldwide (Farley 2022). This complex crisis highlights the systemic vulnerability of maritime logistics to regional instability. As maritime trade underpins international trade, building resilience against such shocks becomes imperative in an unpredictable geopolitical climate. Recent events have exposed drastic flaws in laid out approaches and chance techniques (Bansal 2022). Current systems are being reexamined towards future stockpile chains (World Monetary Discussion 2022). This examination has quick importance as state run administrations and industry explore the unknown regions of contention prompted unsteadiness. The findings call for alterations to policy in order to enhance emergency preparedness and adapt regulatory standards to shifting circumstances. For experts, it gives an essential model to building versatility without excessively receptive protective strategies. In the end, ensuring the stability of logistics promises to benefit sustainable trade and global markets.
The inquire about of theories and models supporting stock association quality is basic to disentangle the bewildered components of the sea commerce in the midst of around the world pressures. Interior this space, a stack of theories includes to how we might decipher versatility. Striking among them are Complexity Hypothesis, Asset See (RBV), and Energetic Capacities Hypothesis, each advertising verifiable viewpoints on conclusive flexibility (Wieland et al. 2021). Capriciousness Hypothesis states that affiliations exist in assorted conditions, requiring versatile strategies for versatility. RBV asserts that organizations with exceptional and critical resources are superior arranged to investigate unsettling influences and puts an complement on the fundamental assignment of resources. Energetic Limits Hypothesis highlights an affiliation's capacity to organize, structure, and reconfigure interior and outside capacities successfully.
The inventory network versatility writing distinguishes responsiveness, flexibility, and Flexibility as key elements. Versatility licenses the relationship to adjust to unforeseen changes, adaptability incorporates changing techniques to new circumstances, and responsiveness demonstrates the ability to answer quickly to unsettling influences. The exchange of these components approaches the supporting of serious areas of strength for an organization, enabling fast changes and key responses even with worldwide challenges.
Despite the overflow of assessment, openings keep valuing the convoluted associations between flexibility, adaptability, and responsiveness for the creation of network adaptability (Shekarian et al. 2021). The composition, while simultaneously perceiving the significance of these components, much of the time comes up short in giving a sweeping appreciation of their trade.
The writing emphasizes the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between adaptability, versatility, and responsiveness. A nuanced view of how these factors cooperate or battle inside the marvellous snare of stock organization components is essential for convincing bet the board. Businesses looking into international vulnerabilities can learn a lot from future research by digging deeper into these connections.
The existing writing on the Russia-Ukraine struggle and its effect on worldwide supply chains and obtainment hazard administration methodologies gives profitable data, but contains imperative holes that require assist examination. To begin with, there's a have to be look at the long-term effects of struggle to decide how firms adjust their supply chain techniques within the long term. Second, the up to this point unexplored adaptable strategies utilized by coordination’s firms amid the emergency require encourage inquire about to supply practical guidance for progressing strength. Third, source-source chance administration procedures are not exact; Techniques such as broadening and innovation appropriation got to be investigated in detail. Fourth, the part of innovation in building adaptable supply chains requires in-depth examination. At last, the writing centers primarily on the endeavors of person companies, clearing out a hole within the understanding of cross-sector participation and government activities, conceivable impact. Bridging these crevices can offer assistance make successful procedures for companies to bargain with geopolitical disturbance.
The research uses a qualitative approach, collecting qualitative data to provide a comprehensive analysis of international maritime resilience strategies during the Russia-Ukraine conflict. Qualitative data will be collected through 12-15 semi-structured interviews with industry experts, including shippers, port authorities and maritime policy makers. Shipping industry reports collect Qualitative information on indicators such as global container volumes, vessel volumes, port congestion and vessel capacity utilization before and during the Russian-Ukrainian war. Statistical analysis measures supply chain disruptions and tests relationships between sustainability strategies and supplies. Qualitative discoveries are combined to evaluate the viability of flexibility strategies in keeping up trade coherence and recuperation in universal shipping amid geopolitical flimsiness.
The proposed research methodology embraces a thorough examination of discretionary data sources to plunge into the maritime industry's response amidst the Russia-Ukraine conflict. The project is going to be conducted as a secondary research. The proposed inquire about strategy incorporates an in-depth consider of subjective information sources on the sea industry and operations amid the struggle between Russia and Ukraine. The utilize of scholastic databases, industry reports and news diaries guarantees cautious assessment. By looking at existing information and definitive assets, the investigate points to pick up critical bits of knowledge into how the oceanic industry is reacting to the challenges of worldwide disturbance. This strategy employments a alter system from inquire about articles and industry reports and points to supply nuanced points of view on adjustment procedures and hazard administration in a changing strife scene.
The investigate approach combines deductive thinking to guarantee add up to investigation of the sea industry's reaction amid the Russia-Ukraine struggle. At the same time, deductive thinking permits for adaptability, empowering the review to reveal modern models and experiences inside the particular information. This approach works with a sensible investigation, leveraging laid out speculations whereas remaining open to rising topics and unexplored highlights. The collaboration among deductive strategies works on the research's significance and flexibility in understanding the complexities of strength and chance administration in worldwide supply chains amid geopolitical disturbances.
The investigate methodology for this think about may be a combined approach, coordination qualitative strategies. Subjective methodologies, counting substance investigation of instructive articles and media sources, allow a nuanced investigation of the oceanic industry's reactions amid the Russia-Ukraine strife. Complementing this, Qualitative parts, for occasion, quantifiable information from industry reports offer a more wide point of see and endorse subjective discoveries. This combined technique points to utilize the characteristics of the two approaches, guaranteeing a wide and strong examination of the strength and hazard administration techniques utilized by the oceanic industry in exploring the challenges presented by geopolitical disturbances.
Within the testing and information collection arrangement, an correct approach has been utilized, entering inquire about papers and industry reports. The show incorporates thoroughly picked articles from great databases like Elsevier, Springer, and JSTOR, guaranteeing an interchange degree of focuses of see. Industry reports from respected organisations just like the Baltic and Universal Sea Gathering (BIMCO) and the International Chamber of Shipping (ICS) contribute vital experiences into common sense applications. This crucial choice certifications a solid and appoint dataset, adjusting with the inquire about targets to completely analyse the sea industry's techniques amid the Russia-Ukraine strife.
The data analysis methodology utilises a qualitative approach. Qualitative substance analysis is applied to take apart printed information from scholarly articles, industry reports, and media sources, extracting nuanced insights into resilience strategies and risk management rehearses. Simultaneously, Qualitative methods involve the orderly categorization and evaluation of key themes and examples distinguished in the data.
Other References List
Journals
The Boy with the Top Knot The Boy with the Topknot is the memoir of the secrets, love as well as lies in Wolverhampton and is...View and Download
Introduction Nursing plays an important role in healthcare for improving the health conditions of patients by educating and...View and Download
Introduction: Exploring Lidl's People Management Strategies on Becoming the UK’s Highest-Paying Supermarket Get free...View and Download
1. Balance Sheet Observations Sources of Funding: Equity (89,288M USD in 2023, 95,916M USD in 2022) and long-term debt (61,538M...View and Download
1. Organisation Introduction Trust Rapid Assignment Help for fast, efficient, and accurate Assignment Help delivered on time,...View and Download
Understanding Contemporary Mental Health: Sonia's Struggles Explored Contemporary mental health reflects the state of knowledge...View and Download
