+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
AHS205 The Australian Healthcare System within a Global Context examines Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), a progressive airway illness that poses a growing global health challenge. COPD is a long-standing progressive illness involving the airways that has become a significant global health concern annually. You have long-standing irritating and obstinate respiratory complaints, which mainly involve chronic bronchitis and emphysema, responsible for impaired airflow. COPD is prevalent and deadly and likely to exacerbate in the coming years due to its close link to smoking and the unfavorable current and projected increases in environmental conditions. The World Health Organisation stated in 2021 that COPD was the third leading cause of death in the world. This also points to the considerable pressure it creates on the healthcare systems and the welfare of people. For students seeking Assignment Writing Help in UK on health sciences topics, understanding COPD’s burden and management is essential. The morbidity of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is normally measured using frequent admissions to the hospital and increased health costs due to recurrent conditions of the disease.
AHS205 The Australian Healthcare System within a Global Context examines Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), a progressive airway illness that poses a growing global health challenge. You experience persistent respiratory symptoms from chronic bronchitis and emphysema, impairing airflow and quality of life. As the World Health Organization noted, COPD ranks third in global mortality, burdening healthcare systems and patients alike.
Definition and Causes
AHS205 The Australian Healthcare System within a Global Context defines COPD as a long-term, progressive lung disease marked by airflow obstruction. Major causes include tobacco smoke, air pollution, and occupational dust exposure (Mallah et al. 2023), which induce chronic bronchial inflammation and alveolar destruction.
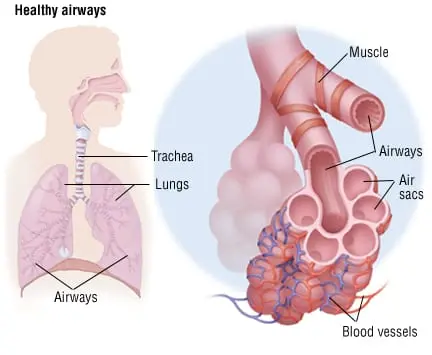
Figure 1: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
These irritants cause chronic inflammation of the bronchi of the lungs and lead to the destruction of the lung tissue and reduced lung capacity.
Symptoms and Impact on Lung Function
COPD encompasses two main conditions: such diseases as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Chronic bronchitis is described as a person having a cough accompanied by sputum for at least three months in two consecutive years. On the other hand, emphysema is a condition where there is a destruction of the alveoli and the efficiency of the exchange of gases also gets to be affected (Cao et al. 2022). These diseases cause dyspnoea, persistent cough, and excessive sputum production which are key determinants of lung function.
Effects on Quality of Life
COPD has lengthy, progressive effects on the patient with numerous ways that the symptoms alter the quality of life. Patients with COPD often experience limitations in their mobility and daily functioning due to shortness of breath and fatigue (Ribeiro et al. 2023). With the progression of the illness, acute exacerbations come more frequently, thereby leading to hospitalization and severe deterioration. Another argument is that COPD also aggravates the level of psychological distress since many patients suffer from anxiety and depression owing to their reduced ability to engage in physical or social activities.
Global Prevalence and Mortality
According to medical literature, COPD is a significant worldwide health concern with the increased tendencies of its frequency and mortality in particular in LMIC nations. Epidemiology: it is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity, and is swiftly becoming a more dire issue due to the aging of the population, and continued vulnerability to risk factors such as tobacco use and environmental pollution.
Healthcare System and Government Support
AHS205 The Australian Healthcare System within a Global Context details Australia’s COPD care, integrating Medicare-subsidized medications and pulmonary rehabilitation. Government-funded programs improve patient access to bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and comprehensive non-pharmacological support like exercise and smoking cessation.
Treatment Strategies
Australia’s strategy for the treatment of COPD is comprehensive since it encompasses the pharmaceutical and non-pharmacological management of the disease. The management options that are considered pharmacological include bronchodilators that cause the relaxation of muscles around the airways and inhaled corticosteroids that reduce inflammation in the lungs (Bereda et al. 2022). Beta-agonists such as long-acting bronchodilators are prescribed for mild to severe COPD and these are often administered along with corticosteroids. Moreover, the medication may also be prescribed to address infections that may exacerbate COPD.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
COPD is managed through non-pharmacological measures which are critical in its management. Pulmonary rehabilitation is available in Australia and involves individualized exercise prescriptions, management education, and psychosocial support for the patients. These programs aim to increase the muscular endurance of the patient, decrease the level of dyspnoea, and increase the patient’s overall life satisfaction. A final salient aspect of COPD care is smoking cessation. There are a couple of reasons why healthcare providers consider smoking cessation as one of the primary strategies: first and foremost, smoking is the leading cause of COPD. Smoking cessation programs, aided by nicotine replacement medicines and counseling are widely promoted and funded and are primary in retarding the progression of diseases.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
COPD requires timely and efficient management and healthcare workers particularly nurses have a significant responsibility for the management of COPD in Australia. Nurses are involved in various aspects of care including initial evaluation of the patient and constant follow up and counseling of the patient. These help the patients to come up with self-management plans, track the patient’s signs and symptoms, and also ensure that they adhere to the recommended treatment regimens (Valaas et al. 2022). The nurses are often involved in the management of the care coordination of different healthcare professionals thus ensuring that patients are administered comprehensive care plans.
Healthcare Policies in Australia and the UK
The management of COPD in Australia and the United Kingdom is, therefore, dependent on the respective healthcare policies of Australia and the United Kingdom. Most health care for COPD in Australia is accessed through Medicare which provides Australians with subsidized access to drugs, medical consultations, and rehabilitation programs. On the other hand, the National Health Service (NHS) in the UK plays a crucial role in providing equal access for all citizens to various healthcare facilities, including the management and prevention of chronic illnesses including COPD. With regards to the Guidelines for COPD, NICE guides the NHS and has given codes of practices that have to be followed in diagnosing and managing the illness.
The case is not the same when it comes to the implementation of these rules because there are disparities. However, the UK focuses on early intervention and rehabilitation and offers them through the National Health Service which is more centralized (O’connell et al. 2022). This means that COPD management treatments are always available for any patient and there are no charges at the time of treatment. On the other hand, Australians rely on Medicare and private health insurance, implying that they receive dissimilar services depending on their inadequate insurance.
Political Factors and Healthcare Funding
Healthcare political implication especially financing of COPD impacts airway disease management in Australia and the UK. The payments for Australian healthcare again include the payment made by federal and state Governments, out-of-pocket expenses, and private health insurance premiums. Australia devotes 9.3 percent of its gross domestic product to healthcare and the major portion is being spent on COPD. On the other hand, the UK awoke to the cold fact that it had been investing only 10. About 2 percent of its gross domestic product is to healthcare and they pay for their National Health Service through taxation. This relatively small budget difference makes a statement about the commitment to universal coverage and the treatment of COPD in the UK (Connolly et al. 2022). Political measures that aim at implementing equal standards regarding access to health care for all the inhabitants of the United Kingdom have an impact on the management of COPD.
Financial Influences and Subsidies
Treatment cost Issues and financial protection of affected individual in the Australian as well as UK context plays an important role in managing COPD. Medications used in treating COPD such as bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids are supplied at a subsidised cost through PBS in Australia. Most of these subsidies assist the patient in accessing necessary procedures, but other miscellaneous expenses may be incurred in line with the insurance policy of the patient (Etemadi et al. 2022). The medication for COPD and pulmonary rehabilitation courses in the UK are funded by the NHS. Most of the treatments in the NHS are funded by taxes, and as a result, most patients will not pay for the treatments. The problems of the NHS are financial, so essential rehabilitation often takes a long time because of budget constraints.
Role of International Agencies
AHS205 The Australian Healthcare System within a Global Context contrasts UK and Australian COPD policies, highlighting NHS-centered care in the UK versus Australia’s Medicare model. The NHS offers free treatment access, while Australians rely on a mix of Medicare subsidies and private insurance.
International agencies have the following important responsibilities related to COPD which include setting guidelines, of course, providing directions, and raising awareness about the disease through various programs globally. Two global agencies that are well-informed about COPD’s management and prevention include the World Health Organisation and the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease.
WHO has a central role in leading the global initiatives regarding COPD in the global arena. Essential guidelines developed by the WHO based on research for use in preventing and managing NCDs like COPD are attributed through this paper. Furthermore, it helps to raise the awareness of COPD patients, especially from low and middle-income countries since the prevalence rate of COPD is high in these regions health-wise due to issues such as pollution and inadequate medical care. The World Health Organisation (WHO) advocates for the promotion of other measures than the ones highlighted above as they enhance the fight against tobacco-forced smoking being the main cause of COPD in the whole world. The organization supports initiatives that raise the quality of the air, to decrease the impact of hazardous substances on the population.
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD)
GOLD Instead, is a forum of healthcare professionals and healthcare organizations match aimed at COPD regulation. GOLD published for the first time the “Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of COPD” which is worldwide considered as the reference for COPD care. These guidelines are based on the scientific data that was published most recently and provide healthcare providers with complete reference material for diagnosing as well as managing COPD (Bhutani et al. 2022). All the recommendations Royal assigns to patients with the condition are updated to reflect the most recent advancements in the research of the condition. It also participates in raising public awareness through international initiatives including World COPD Day which enlightens not just the medical community and patients, but the general population about the importance of early detection and effective management of diseases.
Lung Foundation Australia’s Better Living with COPD Program
Better Living with COPD is an extraordinary community initiative developed by Lung Foundation Australia that aims at improving the quality of life of individuals affected by Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). It is a program that seeks to provide the patient with a package of support services in the form of education, self-management practices, and referred service delivery that meets their needs and expectations. The initiative offers a compendium of services including but not limited to fitness programs, information, education sessions, and support groups with an overall objective of enabling patients to effectively and efficiently manage the disease (Ezenwankwo et al. 2022). In a way, the program increases patient-centered practices of COPD management in that it addresses both the physiologic as well as psychosocial aspects of the illness at the community level.
AHS205 The Australian Healthcare System within a Global Context showcases Lung Foundation Australia’s Better Living with COPD program, where nurses deliver education, self‐management planning, and psychosocial support to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Role of Nurses in the Program
The “Better Living with COPD” mission involves nurses in a significant way in its execution. They are involved in several dimensions of patient care, including the delivery of disease information, helping the patients develop management plans, and providing routine emotional and psychosocial support. Therefore, nurses educate patients on COPD symptoms, the importance of adhering to prescribed medications, and the recommended exercise regime (Tian et al. 2022). These are the components of the program which is under implementation. They also help patients to recognize symptoms of worsening to encourage timely doctor visits and prevent admissions.
7.0 Conclusion
The study has presented the experience of COPD treatment in Australia, focusing on such aspects as subsidies and certain methods of administration as well as compared it to the NHS experience in the UK. During the discussion, it was deliberated how WHO and GOLD had set standards for treating COPD across the globe along with local contributions like the program provided by the Lung Foundation Australia. These endeavors demonstrate the importance of cooperative approaches in managing COPD. It is proposed that there could be future enhancements in COPD care including early diagnosis, increased access to rehabilitation, and bolus promotion of prevention measures across the world.
8.0 References
Introduction Struggling with deadlines or complex topics? Our tailored Assignment Help UK service delivers high-quality,...View and Download
P1 Assess own personality traits and attributes in terms of them having a positive or negative effect on management approaches...View and Download
CHAPTER 1: Importance of Organisational Well-being & ESG Get expert assignment help for college students to excel in...View and Download
Introduction: Project Management for LCCA Relocation: Key Strategies Project management is defined as the process with the help...View and Download
Part 1:Modern Marketing and Media in the 21st Century Definition of marketing in the 21st century In the 21st century, the face...View and Download
1. Aim Gain valuable insights into ethical research practices and get Assignment Help from experts to enhance the quality...View and Download
