+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Spherical vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers used as a versatile drug delivery system for hydrophilic drugs are liposomes (Nsairat et al., 2022). This unique structure enables the encapsulation of water-soluble drugs in their aqueous core to increase bioavailability as well as to provide targeted drug delivery to cancer cells, a topic often explored in Online Assignment Help UK academic discussions. The liposomal form is advantageous as it allows targeted delivery to the site of action, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while simultaneously limiting systemic toxicity (Hamad, Harb and Bustanji, 2024). Thereby, it improves the suitability of liposomes for oncological treatments. Furthermore, liposomes exhibit biocompatibility, biodegradability, and the ability to bypass biological barriers, making them widely used (Dymek and Sikora, 2022). However, despite these advantages, optimal formulation is not always achieved. Initial testing has revealed low drug encapsulation efficiency and the formation of aggregates in liposomal suspensions. These challenges compromise stability, delivery efficiency, and therapeutic potential, highlighting the need for further optimization to ensure safe, consistent, and effective drug delivery to cancer cells.
Learning Objectives are as follows-
Formulations of hydrophilic drugs within the liposomal form represent a major challenge. Especially in the situation of achieving high encapsulation drugs in the formulation as well as formulation stability (Liu, Chen and Zhang, 2022). In this case, the low encapsulation efficiency and aggregate formation observed in the initial tests may be attributed to several formulation and process-related factors. The aim is to identify these underneath causing components to enhance the liposomal system and evaluate its medicinal effectiveness.
Causes of Low Encapsulation Efficiency
Low drug encapsulation efficiency is one of the main reasons and that happens either when the lipid composition is inappropriate or when there is an imbalance between the drug and lipid. For liposomes to form a robust bilayer with a hydrophilic drug entrapped in the aqueous core, a carefully optimized phospholipid and stabilizing agent blend is required. Encapsulation may be compromised using lipids with low membrane stability or high drug load, which will result in drug leakage, and hence reduced efficiency.
Poor encapsulation can also be caused by ineffective hydration techniques employed while preparing. Hydration times, temperatures and agitation have to be controlled exactly in methods such as thin film hydration or reverse phase evaporation. At these conditions, the lipid bilayer may not fully swell, which leads to lower drug hydrophilic entrapment (Nikolova, Kumar and Chavali, 2022). The pH of the hydration medium also affects the solubility of the drug as well as its interaction with the liposomal membrane, which could prevent efficient encapsulation.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Drug leakage during preparation or storage is another factor. Liposomes lose their ability to protect hydrophilic drugs if defects on the bilayer exist or through osmotic pressure differences between the liposome and the external environment (Abbasi et al., 2022).
Figure: Schematic presentation of typical liposome structure loaded with hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs
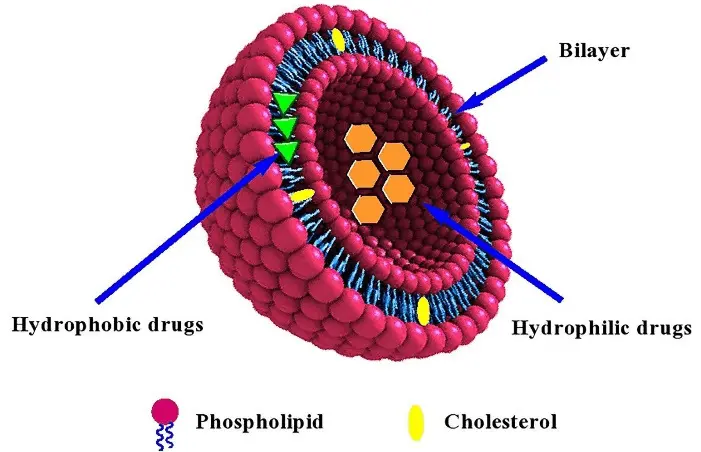
(Source: Abbasi et al., 2022)
This issue is exacerbated by factors such as temperature fluctuations and prolonged storage, and the drug load will slowly decrease.
Causes of Aggregate Formation
Electrostatic instability between individual liposomes is responsible for the formation of aggregates in liposomal formulations. The lipid composition and the surrounding medium may induce surface charges on the liposomes, thus resulting in repulsive or attractive forces (Lombardo and Kiselev, 2022). In such cases, liposomes may stick to each other to form aggregates that disturb the stability and homogeneity of the formulation.
The second reason is the high lipid concentration (or the increased ionic strength of the solution surrounding it. Overcrowding of liposomes due to elevated lipid content can also facilitate fusion or aggregation (Gbian and Omri, 2022). Similarly, repulsive electrostatic forces between liposomes can be shielded by high ionic strength, which promotes particle-particle interactions and aggregation.
In addition, aggregation is promoted by poor control over temperature and solvent conditions during preparation. Liposomes are more susceptible to fusion as a result of rapid temperature changes that can result in phase transitions of the lipid bilayer (Grażyna Neunert et al., 2021). Particularly during hydration or purification the lipid membrane can be destabilized by inappropriate solvent use, which increases the risk for aggregate formation.
Solutions and Action Plan
These formulation challenges need to be addressed by formulating a comprehensive action plan of how to optimize lipid composition, improve encapsulation efficiency and to reduce formulation instability.
Lipid Composition Optimization and Drug-to-Lipid Ratio
For improving encapsulation efficiency, appropriate lipids and stabilizing agents need to be selected. Cholesterol can improve membrane rigidity and reduce permeability to minimize drug leakage by incorporating cholesterol into the phospholipid bilayer (Giraldo-Lorza, Leidy and Manrique-Moreno, 2024).
Figure: Chemical structure of Cholesterol
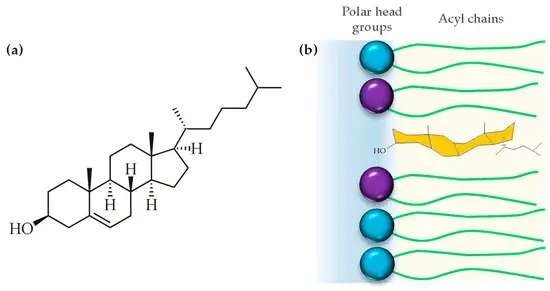
(Source: Giraldo-Lorza, Leidy and Manrique-Moreno, 2024)
Furthermore, the ratio of drug to lipid is adjusted so that the liposomal core can accommodate the hydrophilic drug without overloading the system and causing the bilayer to destabilize.
Included pH and Ionic Strength of the Hydration Medium
Maintaining the pH during liposome preparation is important to optimize drug solubility and interaction of the drug with the lipid bilayer. The drug-lipid affinity can be improved by slight acid or base pH, according to the properties of the drug (Liu, Chen and Zhang, 2022). Maintaining electrostatic balance is also important like ionic strength and the ionic strength of the medium can be managed similarly to prevent aggregation while supporting stable drug entrapment.
4. Conclusion
The development of a stable liposomal formulation for hydrophilic drugs in cancer therapy is a careful optimization of multiple factors. These observed challenges low drug encapsulation efficiency and aggregate formation. These are due to inappropriate lipid composition, ineffective hydration techniques, electrostatic instability, and poor storage conditions among others. These issues need to be tackled in a systematic way such as optimising lipid composition. That can help to balance membrane stability with cholesterol, optimising pH and thus ionic strength to maximise drug entrapment, as well as the use of PEGylation to prevent aggregation. Moreover, microfluidics can also be used to achieve uniform liposome size to enhance the overall stability and therapeutic efficacy of the formulation. These solutions enable the liposomal formulation to reach higher drug encapsulation efficiency, decrease aggregation, and improve stability. Overall it will ensure better effectiveness of the liposomal formulation as a cancer treatment targeted delivery system.
5. References
1.0 Introduction to Challenges In Pursuing Justice For Cases Assignment The “European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR)”...View and Download
Introduction - international human resource management Get ahead in your academic journey with Rapid Assignment Help, your...View and Download
Introduction - Impact of Staff Shortages on the Quality of Healthcare Delivery in NHS Understanding how staff shortages...View and Download
Introduction: BUS5013 Sales Management Sales management explicated as the process of hiring, training and motivating sales staff...View and Download
Introduction This assignment showcases how detailed research and critical analysis create a strong academic piece focused on...View and Download
Part A Part A presents the overall network design and explains why each connection, configuration, and addressing method was...View and Download
