+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking Assignment Help Online services in the UK.
“Metabolic Syndrome (MetS)” belongs to metabolic disorders that can lead to a number of physiological risks, which include diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, and impaired renal functions along with some neoplasia. Various pathological conditions associated with increased risk of MetS include higher blood glucose levels, higher abdominal fat, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Studies indicated that MetS have become a major clinical issue around the world with around 40% of the western population suffering with at least two clinical issues related to MetS. Unhealthy food habits increased physical inactivity and high levels of stress have effectively contributed to the prognosis of Mets. Molecular studies have revealed studies on several biomolecules regarding the pathogenesis and significant treatment of MetS.
“Metabolic Syndrome (MetS)” is a metabolic disorder leading to several major clinical ailments.
Various risk factors as a result of modern lifestyle especially type 2 diabetes Miletus and higher obesity have contributed to higher risk factors for MetS. In highly obese people there occurs an increased deposition of adipose tissue layers leading to increased chronic inflammation. The liver and intestines were also seen to contribute actively to increased inflammation seen in MetS. Adipose tissues secrete a large number of cytokines known as adipokines which are seen as dysregulated in obese people (Wang et al. 2020). The dysregulated pro and anti-inflammatory adipokines lead to insulin resistance, hypertension, inflammation, and hyperlipidemia as seen in MetS. Specific adipokines like leptin and “adiponectin” were seen involved with the pathophysiology of MetS where the levels of leptin were found to increase almost double in patients infected with type 2 diabetes Miletus while the levels of “adiponectin” were found to decrease in diabetes Miletus affected patients.
Again Insulin resistance (IR) also plays a key role in the development of MetS where IR leads to the increase of serum glucose levels leading to the development of diabetes mellitus and “Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)”. Triglycerides deposition has also contributed significantly to the formation of MetS. Deposition of triglycerides leads to disruption, regarding glucose as well as insulin metabolism that leads to several clinical complications including cardiovascular effects. According to the reports presented by the “International Diabetes Federation (IDF)”, India was considered as the main center of Diabetes Miletus with over 70 million infected individuals where the numbers stand just next to the Chinese population. Studies conducted by The “Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)” also suggest a significant increase of about 10% was seen in hyperlipidemia cases for urban populations compared with that rural cases.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
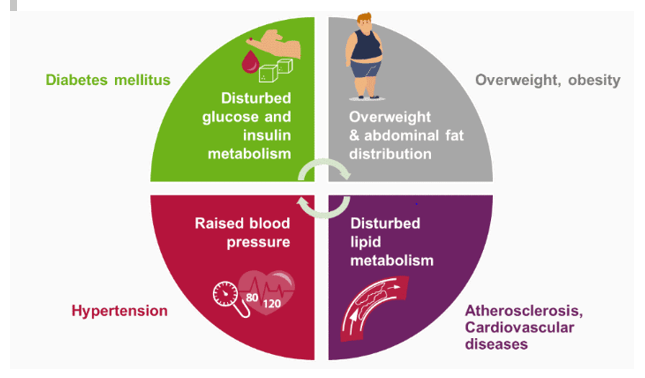
Figure 1: Various risks associated with MetS
On deciphering various biochemical pathways involved in MetS, some of which are mentioned, several attempts were made for early detection of altered metabolic pathways involved in MetS along with the formation of effective biochemical treatments that can be applied.
Metabolism of Polyamines, which are cationic compounds that are found associated with a number of cellular activities like differentiation, secretions of insulin, programmed cell death, etc. and having antioxidants properties were seen dysregulated in a number of Mets cases which provides disease prognosis studies (Ajith et al. 2022). Studies using natural polyamine derivatives showed to have a positive impact on inflammatory conditions, glucose metabolisms, and biological stresses. Feeding relative doses of natural polyamine derivatives on obese mouse models have shown their improved glycemic status, also intaking high amounts of these derivatives provided positive cardiovascular conditions along with decreased death rates as seen in the case of humans. Apart from Polyamines, several natural phytochemicals were seen effective regarding treatments of MetS (Francini-Pesenti et al. 2019). Phytochemicals obtained from green tea, berries, pomegranate, and Olive oil have shown decreased inflammatory actions along with improved diabetic conditions and levels of antioxidants helping to regulate biological stress.
Studies regarding the several pathways of MetS identified several protein biomolecules such as the “xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR)” to be positively correlated with MetS clinical manifestations (Battelli et al. 2019). Impaired XOR activities during Mets lead to increased activity of these enzymes involved in purine biosynthesis leading to higher levels of oxidative stress and inflammations within the body that leads to clinical manifestations of MetS. Therefore therapeutic blockage of XOR can provide better diagnostic measures regarding MetS.
Several reports also suggested endothelial dysfunctions as a leading cause of diabetic and cardiovascular effects of MetS (Marzoog, 2022). On deciphering their molecular linkage with MetS, possible therapeutical drugs for type 2 diabetic and cardiac ailment patients can be designed to reduce the clinical effects of MetS.
Conclusion
MetS has emerged as a medical hazard with serious clinical complications for over decades and researchers are continuously trying to decipher various biochemical pathways, cellular systems, and specific biomolecules that can be linked with the various clinical ailments observed for these groups of metabolic disorders. Biomolecules ranging from proteins and polyamines have been identified and mentioned here with potential abilities to reduce the clinical complexities of the several disorders that are associated with MetS. Thus Biomolecular sciences are helping actively to decipher the reasons associated with and providing effective treatments for MetS.
Reference
Journals
Introduction to Social Isolation And Stigmatization Assignment Analysis of current issues in health care There have been...View and Download
Introduction: Unit 4: Leadership And Management University Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction to Endocrine, nervous and Excretory Systems Assignment Sample Part A The brain, situated at the core of this...View and Download
Introduction: Academic Skills and Studying With Confidence Enhance your academic skills with Assignment Help UK on managing...View and Download
1.1 Introduction to Analysis of Heat Exchangers in Engineering Applications Heat exchangers are essential equipment in thermal...View and Download
