+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
This assessment is totally based on the Economics of International Trade which critically analyzes the effect of the EU as a trade-creating customs union on its members and the rest of the world. In this question one, critically discussed about Trade creation, eliminating tariffs for union members, developing trade barriers for other countries, focusing on developing products, Reducing the import cost for union members, and UN trade creation for other countries. The Trade creation refers, it’s the process of creating new trade opportunities and economic welfare between countries or regions. question two critically Evaluates the dynamic benefits the nations forming a customs union are likely to receive and, in this part, significantly discusses, Economic assimilation, Increased economic welfare, Reduced trade deflection, and Enhanced trade flows. In question three clearly explain how the theory of customs union is an example of the theory of the second best.
This section provides an in-depth evaluation of how the European Union functions as a trade-creating customs union, focusing on its impact on member nations and global trade relations. It explores trade creation, tariff elimination, trade barriers, product development, and reduced import costs with supporting research insights. Expert guidance from an Assignment Helper can further enhance understanding of these economic dynamics.
Trade creation is the process of creating new trade opportunities and economic welfare between countries or regions. As per the argument of Bindi, (2022), the European Union is an impactful example of trade creation. The EU removed trade barriers between its collaborating or member countries leading to enhanced trade and economic benefits. The trade creation occurs when trade barriers, such as tariffs or quotas, are reduced which can lead to higher real incomes and increased competition. As stated by Das et al. (2024), the EU customs union has created trade creation benefits by allowing products from countries with lower production costs to compete with products from countries with higher production costs.
In order to manage the trade creation, it follows several steps
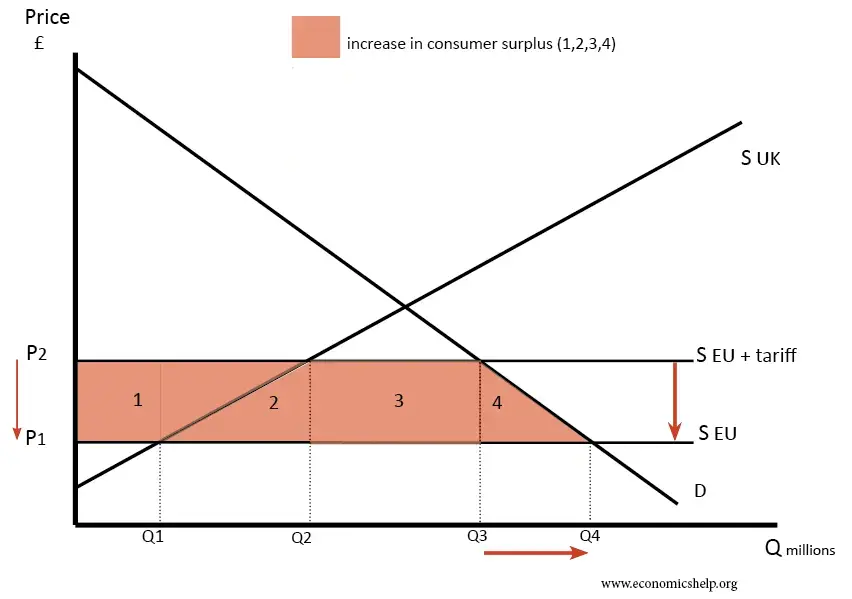
Figure 1: trade creation
(Source: economicshelp.org, 2024)
A customs union is a special trading arrangement, and it reduces or eliminates the tariffs between the member countries which increases economic and trade activity. The specific elimination of tariffs for union members includes the elimination of tariffs, increased trade, greater revenues, common external tariffs, and lower prices. all member countries eliminate tariffs among themselves on trade times (rieti.go.jp, 2020). Good relationships between all member countries enhance trading activity always and the reduction in tariffs and other barriers regarding trade always leads to an increase in the activity of trade and also economic activity.
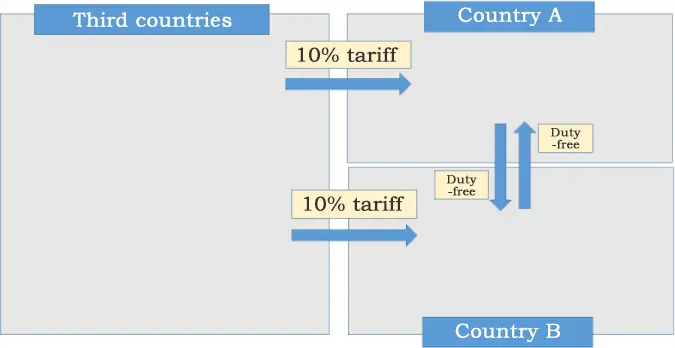
Figure 2: adjustment between the member of UN countries
(Source: rieti.go.jp, 2020)
The member countries of the customs union make a common external tariff-related trading, and all member countries accept a common external trade policy with nonmember countries. It's also connected with greater revenues and lower prices. As argued by Arndt et al. (2023), the increase in trade causes greater revenues for all member countries or nations and countries can obtain goods at a lower price. The other benefits of a customs union include protection for domestic industries and revenue sharing. All members create a common policy regarding trading to protect their members' industries from outsiders and they also agree to share revenue from common tariffs imposed on outsiders.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Trade barriers are a type of restriction on trading internationally that any country's government imposes to protect their domestic economy. According to Yu et al. (2021), it can have many bad or negative impacts including raising processes, reducing employment, limiting the choice of products, lowering net income, and lowering economic output. To develop the trade barriers against other or non-member countries a government can focus and implement some key measures like setting quotas on import quantities, providing subsidies to domestic industries, and establishing technical standards that are difficult for the foreign goods to meet. Some important key methods for developing trade barriers include tariffs, non-tariff barriers, government subsidies, embargoes, import quotas, technical standards, and export restrictions. Most countries have agreements with the WTO regarding international trade and These agreements limit the types and increase some trade barriers.
When countries focus on developing products in the face of trade barriers, the countries mainly prioritize specializing in niche markets, identifying their comparative advantage, and improving product quality and standards to meet the requirements of international markets. As stated by Azeem et al. (2021), they need to identify a comparative advantage and critically analyze which specific products or goods they can produce more efficiently than others. They need to focus more on production in those areas and maximize export potential. As argued by Eum et al. (2024), they always need to focus on quality improvement and ensuring goods meet international quality standards and certifications. It helps to overcome non-tariff barriers related to reliability and safety.
The simple meaning of reducing the import cost for union members was lowering the price that union members pay for products or goods imported from other countries. According to Tian et al. (2022), the countries mainly achieve this by collaborating and negotiating trade agreements that reduce trade tariffs on those products or goods. It also helps to allow all union members to purchase imported products at a lower cost. Some important key points about decreasing and reducing import costs for all union members include trade agreements, impact on price, and domestic industry concerns. Hare provides some examples of scenarios regarding reducing costs for union members. As stated by Juust et al. (2021), if a trade agreement reduces trade tariffs on imported types of car parts, the union members have the chance to purchase vehicles or their parts at a lower price due to the cheaper cost of components. Another example was about textile workers, if trade tariffs on imported clothing are lowered, the union members have a chance to buy clothes at a lower price. It could potentially impact the jobs of domestic textile workers.
Trade creation is sometimes beneficial for the countries in terms of national welfare. The trade creation is when trade between countries increases due to the formation of a free trade area or customs union. According to Peltola et al. (2022), the United Nations Trade and Development (UNCTAD) organization helps developing countries to improve their access to global markets. This UNCTAD includes helping countries to improve their national trade policies and diversify their economies. It mainly researches and publishes findings to improve the economic prospects of developing countries. As stated by ESCAP et al. (2024), UNCTAD helps countries draft and implement regional agreements, and increase access to digital technologies.
all member countries of CU can receive economic assimilation due to trading agreements. all member countries can enhance their resources and their overall business efficiency. As argued by Ababouch et al. (2023), some important key benefits a customs union country can get, include increased trade flow, enhanced economic growth, improved market access, economies of scale, greater efficiency, and technological transfer. Those all are contributing to a degree of economic assimilation between the participating nations. Increased trade flow is an important benefit of customers union countries, it eliminates trade tariffs and any types of trade barriers within the union. all countries can freely trade goods across international borders, and this leads to a higher volume of trade between all member countries. According to Ishfaq et al. (2024), it also enhanced economic growth when countries increased their trading. It also boosts investments and promotes specialization within member countries. Another benefit was technological transfer, technology, and sharing of knowledge can be facilitated within the customer union, and it promotes innovation and development of an economy.
all member countries of the customs union can receive Increased economic welfare Benefits due to trading agreements. The member countries can thrive through trade creation and trade diversion. As stated by Bazaluk et al. (2022), all nations that form the customer union are likely to benefit from increased economic welfare including lower prices for consumers, investment attraction, enhanced market access, and trade creation. When tariffs regarding trading are removed within the union member countries, they can be more flexible and freely trade with each other. It also leads to increased production and consumption of products and goods where each member's country has a comparative advantage. As stated by Cakranegara et al. (2022), another benefit like lower prices for the consumers, when increased competition within the larger and more competitive market can lead to lower prices for consumers as businesses strive to remain competitive.
The customer union (CU) of all member countries can receive Reduced trade deflection Benefits due to trading agreements. The CU can effectively deal with trade deflection, and it also can lead to trade distortion. According to Chawarika et al. (2024), they earned many benefits due to CU members including economic integration, revenue sharing, large market effect, trade creation, and trade diversion and revenue sharing. The customs unions create a common trade policy regarding trading including tariffs and quotes which protect member industries from outsiders. The customs union always encourages their member countries to trade with each other and discourages trading with non-members.
The customer union (CU) of all member countries can receive Enhanced trade flow Benefits due to trading agreements. Some important key points about the trade flow enhancement in a customs union include trade creation, economies of scale, simplified customer procedures, and greater consumer choice. As argued by Sanguinet et al. (2022), when establishing the customs union trading was created between all member countries because they traded goods to each other at lower prices due to the removal of trading tariffs. It always leads to increased market access and potential for higher sales. The economy of scale refers to accessing a larger market and businesses can produce larger quantities of products or goods. Leading to lower production costs per unit and potentially more competitive prices. all consumers within the CU can access a wider variety of products from different CU member countries at potentially lower prices due to increased competition.
of the second-best. The theory of CU is an example of the theory of the second best because it exemplifies how interventions in other sectors of the economy can enhance the outcomes when some sectors are deformed.
The theory of customs unions: the theory of customs unions is the conceptual idea that customs unions can increase world welfare even if they don't maximize it. As stated by Clark, (2022), a customs union is a trade regulating authorization that reduces trade-related tariffs and always establishes a common external tariff. The theory is based on the idea that a customer union reduces tariffs regarding trade and moves toward free trade, and free trade maximizes world welfare. It can help to avoid trade deformity that can occur when a nonmember country sells goods to a low-tariff country, which then resells them to a high-tariff country.
Theory of the second best: the concept of the theory of the second best was established by economists Richard Lipsey and Kelvin Lancaster. According to Lin et al. (2024), this theory refers to when a market has distortions, it may be more efficient to let those distortions cancel each other out instead of trying to fix them. Some important key points about the theory of the second best include first best vs. second best, and market distortions.
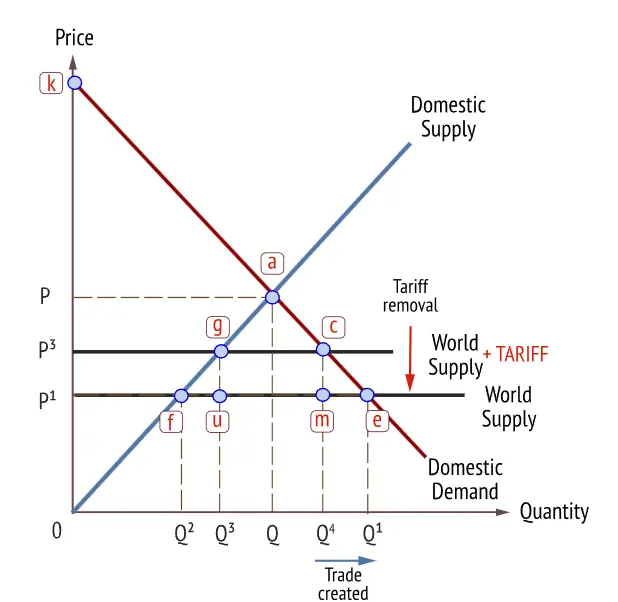
Figure 3: Custom unions
(Source: learn-economics.co.uk, 2024)
Conclusion
In conclusion, this discussion is basically based on the Economics of International Trade which critically analyzes the effect of the EU as a trade-creating customs union on its members and the rest of the world. In this assessment, different questions represent different aspects of the customs union knowledge, and features of CU. share provides the Trade creation, eliminating tariffs for union members, developing trade barriers for other countries, focusing on developing products, Reducing the import cost for union members, and UN trade creation for other countries. In this part also critically Evaluates the dynamic benefits the nations forming a customs union are likely to receive. This part also evaluates how the theory of customs union is an example of the theory of the second best and how its impact on members' countries.
Reference
Chapter 1 - Introduction Assignment samples are offered to assist students in understanding coursework structure and key...View and Download
1. Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction Master patent race concepts and innovation management with Assignment Help UK, exploring how R&D investment and...View and Download
Task 1- Organisational Behaviour Assignment This focuses on organisational behaviour assignment, which is really the study of...View and Download
Task 1: If you're struggling with complex healthcare topics, our College Assignment Help services offer expert support for...View and Download
Introduction to Report on Personal Development Assignment Personal development plays an important role in helping students build...View and Download
