+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Sustainable construction has become a vital focus in the modern building industry, aiming to reduce environmental impact while enhancing efficiency and innovation. This assignment explores sustainable construction through the case study of The Crystal building in London, a pioneering example of green architecture and smart technology integration. For students struggling to analyze such complex topics, professional Assignment writing Help can provide valuable guidance in understanding key concepts and delivering well-structured reports that meet academic standards.
The Crystal is situated in the Royal Victoria Docks area of London. It was inaugurated in 2012 and was designed by Wilkinson Eyre Architects and was developed by Siemens as the hub for urban sustainability. It is a temporary exhibition space and a conference venue as well as an institute on smart cities and technologies(KNXtoday,August 2024). Due to it captivating structure that features like exterior and crystal like architecture the building has become easily recognizable in East London. The Crystal was designed to showcase several features of energy efficiency and environmentalism and the building was built with many sustainable features and systems.

Figure 1: The Crystal , London
This report uses The Crystal facilty as a case study in sustainable construction and innovation. It will assess the building’s major sustainability parameters and design and construction and operation innovations. The report will focus on two main innovative elements: the type and quality of products utilized in the construction process and the the types of digital technologies that are incorporated in the structure at some stage in its life cycle. Further, it will look at how these innovations align itself with the sustainability objective of The Crystal. At the end of the study, there will also be made suggestions for the additional improvements of the sustainable performance of the building.
The Crystal is selected to be the object of this case study because it is one of the world’s leading examples of sustainable architecture and embraces the latest technologies. It is one of the world's most sustainable structures, and it is thus useful to describe how it is possible to design and build structures with as little pollution as possible in the process. The concept behind the Crystal, its own exhibition on urban sustainability, aligns with the organisation’s transparent positioning, therefore making it relevant for inspection(www.inawe.in, 2024). London also enables facilities to be considered from the perspective of sustainability in a big city environment. It has been in use for many years; therefore, its constant functioning and open Gates afford the researcher with all the data and material they could need.

Figure 2: LEED and BREEAM certification of The Crystal
The objectives of this case study are as follows:The objectives are the following:
This case study utilised a method known as the literature review as the secondary approach to research. Academic as well as professional literature was used while collecting information on The Crystal. Google Scholar has been utilized as the main search engine for the collection of the articles. Scholarly articles related to the topic were searched using keywords like; The Crystal London, sustainable architecture, modern building technology.
Emphasis was placed on the scholarly articles in the area of green construction, architecture and city planning published in refereed journals(Hossain et al. 2020). These included research journals Building and Environment ,Energy and Buildings, and Sustainable Cities and Society. Information from the technical reports and case studies developed by Siemens Company, the building development Company was also considered.
Self-sources consisting of official website of ‘The Crystal’ and other sustainability reports offered most recent information about the characteristics of the building and its efficiency. Further information was obtained from reliable websites, and professional associations in sustainable construction(Solaimani and Sedighi 2020). Only the information which appeared in the sources in the last ten years was chosen. If older sources were employed, their applicability were properly assessed. To ensure credibility, all the collected data was checked and compared on the basis of different sources.
Energy efficiency: Energy efficiency was one of the first thoughts that were given while planning the Crystal. The building employs many strategies because it uses tested designs for efficient energy saving. In the light of such an advance design with appropriate positioning of this building. The maximum natural lighting was incorporated in the interior so as to reduce on use of artificial lighting(Shinoda et al. 2024). It also reduces highly the energy required for lighting and controlling of temperature to a very great extent. Besides, The Crystal does not feature conventional lighting installations and very often employs LED that helps to minimize the consumption of electricity.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.

Figure 3: Smart energy efficiency
Renewable energy systems: The following are some of the innovations used at The Crystal that as an addition also helps to reduce carbon emissions which is Renewable energy systems. Solar panels are arranged at the top of the building to generate a reasonable amount of electrical energy used in the building. Heating and cooling systems make use of ground source heat pumps when the temperatures of the ground below the surface are stable.
Water conservation: Another area that can be said to be forming part of the sustainability plan for The Crystal is water. A sustainable aspect of the building is the rain water harvesting system where water is harvested and stored in this case for use in washing of utensils, clothes and for watering of plants among others(Fathalizadeh et al. 2022). The wash water from the hand basins is collected treated, and used for toilet flushing purposes.

Figure 4: Smart Water system
Sustainable materials: The selection of the materials used in construction of The Crystal also had consideration to green building principles. To advise environmental friendly supplies and transportation; recycled paper and other locally available materials were used in construction where possible(Solaimani and Sedighi 2020). Recycled content steel and concrete were used in the construction of the structural frame of the building. The final obtained trimmings with interior finishing were chosen with special attention paid to choosing finishing that had least effects on the environment and supported good quality indoor air.
Waste management: In constructing the building as well as in its operations, waste management is given great attention at The Crystal. Throughout the construction phase waste was segregated and where possible was recycled instead of being disposed. Concerning the ongoing operation of the building, there are facilities for the recycling of wastes profusely available, as well as a forced waste segregation policy(Bulakh et al. 2020). Coffee grounds and other organic waste produced by the café are disposed of through compost bin provided in the building, to enhance our environmental footprint.
Smart building management: The Crystal has a state-of-the-art building management system (BMS) that includes use of KNX technology. This system governs and regulates diverse operations within the building, such as lighting, heating, cooling as well as fresh air supply. It controls the usage of energy by causing changes to the systems as regards to the occupancy of the rooms, time and even weather conditions. It also supplies actual-time data regarding utilization of energy that helps in constant reinforcement of the building performance.
Biodiversity and green spaces: Despite the fact the that The Crystal is situated in an urban area, the design contains aspects that would help support wildlife. Around the building certain species of local plants have been planted as a way of providing habitats for the animals. Solar-panel covered parts of the building’s exterior are supplemented by green roofs that also support the local population of plants and insects and control the flow of stormwater. These green areas also reduce the phenomena of the urban heat island and create comfortable territories for visitors and staff.
The use Of Building Management System is one of the best strategies that The Crystal has adopted as part of its sustainability strategy. Central to this system is the incorporation of KNX technology a bus based open standard for buildings. KNX system implemented in The Crystal consists of the interconnection of numerous operating facilities such as lighting, heating, ventilating, air conditioning and provides for energy metering.
System Overview: More than 3,500 KNX devices have been integrated in The Crystal; making it one of the biggest KNX projects globally(KNXtoday,August 2024). These devices are dais connected through a single bus wire on which all of the devices are connected and therefore can be controlled and monitored. The system is also planned to be quite open and extensible in terms of technologies it might use, so updates and integration of new concepts could be performed easily.
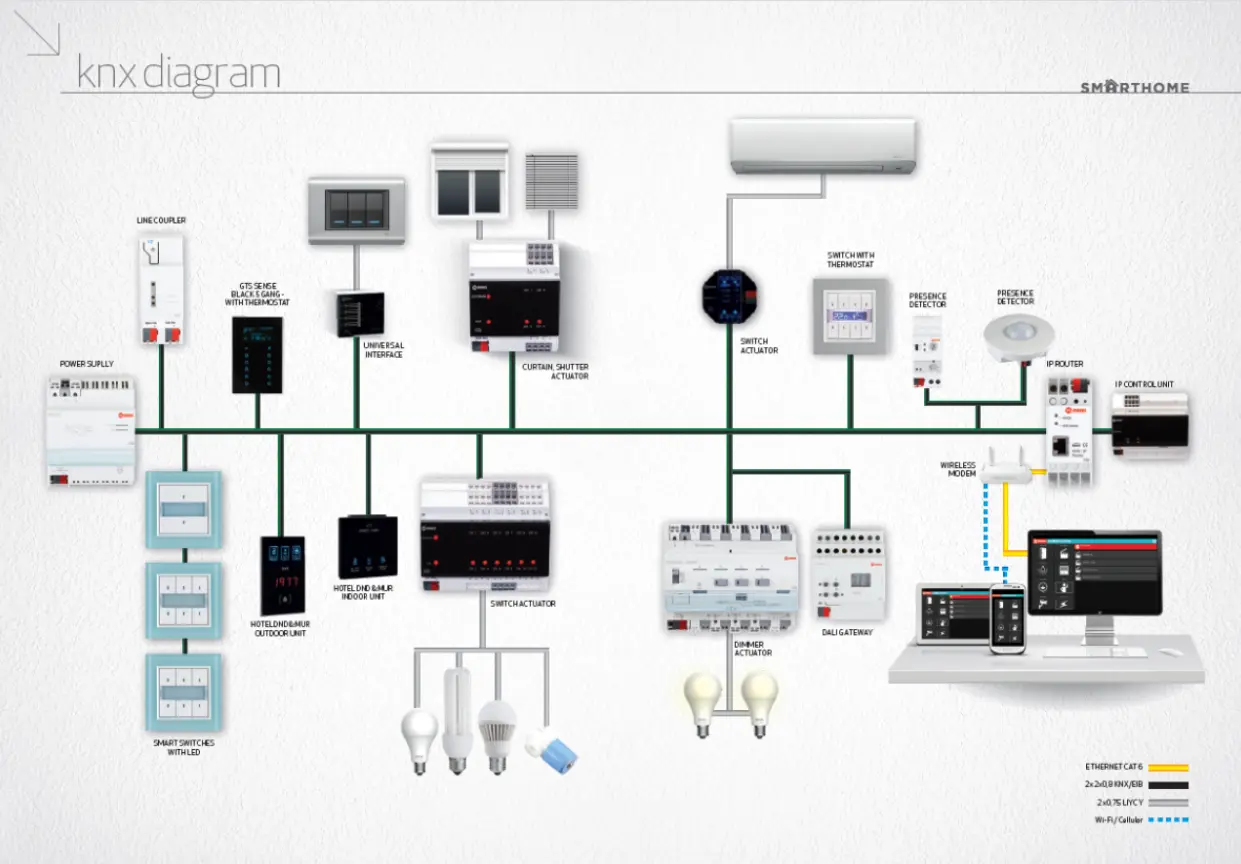
Figure 5: KNX-controlled Electricity
Energy Efficiency: The KNX system is compatible with signal cost since one of the major advantages of the KNX system installation is energy saving. It controls the lighting also by natural light available and occupation of areas such that energy will not be wasted where there are no people(Murtagh et al. 2020). The same applies with the HVAC systems, where they are regulated depending on the set comfort levels but with special emphasis on power use. This intelligent control has gone a long way in ensuring that The Crystal cuts on energy consumption leading to it being regarded as one of the sustainable buildings in the world.

Figure 6: LED with KNX control
Data-Driven Decision Making: The BMS integrates the live properties in terms of energy use and functionality of the edifice(KNXtoday,August 2024). From this amount of information, the facility managers can easily make decisions on matters relating to the building/ facility and note down areas that need improvement. Its application of detailed data of energy consumption of different systems and zones of the building is useful for continuous fine-tuning of the power consumption.
Critical Evaluation: In the present research, a KNX-based BMS is proposed and implemented and, despite the fact that it presents several advantages, it is also known that it can introduce some disadvantages(Awad et al. 2021). The nature of such a system is complex, and the first approach means that only experts should maintain it and solve various problems; hence the maintenance costs may be significantly higher. Also new is the fact that having one system that serves multiple functions in a building exposes this system to the function of acting as a single point of failure in case it develops some problems.
System Design: The GSHP system at The Crystal are pipes which are laid in borehole beneath the building(The crystal / Wilkinson Eyre. 2024 ). These pipes contain a water glycol solution which is used to heats the ground in winter and cools it in summer. Heat pumps then use this energy to either discharge it within the building or take it out of the building as required.
Figure 7: Heating and Cooling systems
Energy Efficiency: It can assume that a great amount of energy is consumed is used to operate the pumps and the compressors that this system uses. The United States Environmental Protection Agency has estimated that GSHPs may use up to 44% less energy compared to air-source heat pump systems and up to 72% less energy compared to electric resistance heat.
Critical Evaluation: Despite the multiplicity of advantages associated with the use of the GSHP system, there are still unique disadvantages. There are initial installation costs which are considerably higher than a normal HVAC system, which can act as a disadvantage(Ogunmakinde et al. 2022). Another factor is the capacity of the system which is reduced by soil conditions as well as available space that could be a problem in many urban locations.
The Crystal project incorporated Building Information Modelling (BIM) to a great extent in the course of its design and construction. With the help of BIM technology it is possible to create the most detailed 3D model of the building including not only architectural, but also structural, mechanical and electrical and plumblng and facets(www.building.co.August 2024). This integrated model provided a common database for all project information and was used to support the flow of information between the various functional specialisms. BIM helped with making the design work more effective as clash detection between several systems of construction could now be detected during design phase only. I have found that this greatly helped to minimize the number of problems as well as temporaneous delays on-site that are associated with giving and redoing work(Ferdosi et al. 2023).
Figure 8: BIM design of The Crystal
The Crystal has an IoT installation which forms a critical component within the building management infrastructure. Such devices include those for occupancy, temperature, humidity, and lighting levels at different areas of the building. The sensors deployed gather data which is inputted into the BMS so that the control of lighting, heated, and cooling may be done in real-time depending on the range founded(www.building.co.August 2024). IoT also can be used in Predictive Maintenance for the building systems. Thus, regular assessments of the appliances used entail that any complications are detected early enough and rectified to prevent abrupt breakdowns or low functioning of the equipment.
Figure 9: BMS of The Crystal with IoT
During the design design stage, Virtual Reality (VR) may have been employed in order to generate virtual walkthrough of The Crystal so that design and other interested parties could get the feel of the intended environment prior to its construction. It would have been especially helpful in terms of adjusting some of the arrangements of the exhibition halls and the movement of visitors. Information collected in the operational phase show that, Augmented Reality could be used in the building of an institution that seeks to further education(www.building.co.August 2024). Using smart phones and tablets, visitors can get more details about the sustainable aspects of the building as they are taken round the facility through the use of AR applications.
The Crystal could potentially be made more efficient by installing an adaptive façade system. Smart windows in form of electrochromic glazing could allow a user to set the degree of tinting according to the amount of light and the required control of indoors environment(Awad et al. 2021).
A large battery storage system integration allows The Crystal to store real power generated by the photovoltaic panels in the large battery storage for use particularly in the evening or on a cloudy day.
New forms of AI chatbots and virtual guides can be incorporated within the building for contactless provision of services(El-Sayegh et al. 2021). The provision of guided tours and instant answers to queries on sustainability aspects of the structure.
Figure 10: Sustainability approach of The Crystal
The application of the elements of biophilic design such as green walls or indoor plants can improve the quality of the air in the enclosed premises(Mistri et al. 2020).These affect the well-being of the people, and provide evidence of nature’s integration into cities’ constructions.
Implementing the system would enable The Crystal to transact in P2P electricity trading with surrounding structures. Energy usage in the community can thus be optimized; development of a mini-grid can also be pursued.
Conclusion
Summary of Main Themes
London possesses one of the most outstanding icons of architecture that supports sustainability, especially in the technologies used in construction-known as the Crystal. Thus, in the course of this case study, an attempt has been made to critically discuss the sustainable perspective of this structure, together with its design, construction, and occupancy. This for effectiveness of energy, usage of water, and disposal of waste is evidence to the observation that Crystal has a holistic approach to sustainable development. Application of information technology including the Building Management System and Ground Source Heat Pump System that has been implemented on the basis of KNX shows that innovations are a way of increasing the performance of buildings and sustainability.
Key Outcomes
The work on the structure of The Crystal as applied for the research on innovation presented the following main findings: The Building Management System and primarily the extensive Building Automation for according to the KNX standard has become very efficient in energy management as well as in the acquisition of fundamental data required for its constant further development. However, this complexity creates problems in respect of maintainability and can generate further problems with reference to systemic risks and problems. When it comes to energy consumption and the usage of the fossil fuel, the ground source heat pump system is excellent but there are some point which includes the following points: The initial cost of the system is higher and some of the processes concerned are not so friendly to the environment in the long run.
Conclusion Based on Evidance
As The Crystal demonstrates, ‘green buildings’ can be put into practice with the assistance of modern design and engineering. The other aspect is the indices of energy consumption and water usage and this indicates that it is indeed possible for the modern urban structure to make a difference on the environment on a big way. Digital integration of the buildings also enhances the performance and productivity of the buildings and in addition there is enhanced public outreach and awareness on sustainability.
Reference List
Journals
Awad, T., Guardiola, J. and Fraíz, D., 2021. Sustainable construction: Improving productivity through lean construction. Sustainability, 13(24), p.13877.
Bulakh, Iryna & Didichenko, Margaryta & Kozakova, Olena & Chala, Olena. (2020). Sustainable futures in the context of architectural design of hospitals. E3S Web of Conferences. 166. 08001. 10.1051/e3sconf/202016608001.
El-Sayegh, S.M., Manjikian, S., Ibrahim, A., Abouelyousr, A. and Jabbour, R., 2021. Risk identification and assessment in sustainable construction projects in the UAE. International Journal of Construction Management, 21(4), pp.327-336.
Fathalizadeh, A., Hosseini, M.R., Vaezzadeh, S.S., Edwards, D.J., Martek, I. and Shooshtarian, S., 2022. Barriers to sustainable construction project management: the case of Iran. Smart and Sustainable Built Environment, 11(3), pp.717-739.
Ferdosi, H., Abbasianjahromi, H., Banihashemi, S. and Ravanshadnia, M., 2023. BIM applications in sustainable construction: scientometric and state-of-the-art review. International Journal of Construction Management, 23(12), pp.1969-1981.
Hossain, M.U., Ng, S.T., Antwi-Afari, P. and Amor, B., 2020. Circular economy and the construction industry: Existing trends, challenges and prospective framework for sustainable construction. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 130, p.109948.
Mistri, A., Bhattacharyya, S.K., Dhami, N., Mukherjee, A. and Barai, S.V., 2020. A review on different treatment methods for enhancing the properties of recycled aggregates for sustainable construction materials. Construction and Building Materials, 233, p.117894.
Murtagh, N., Scott, L. and Fan, J., 2020. Sustainable and resilient construction: Current status and future challenges. Journal of Cleaner Production, 268, p.122264.
Ogunmakinde, O.E., Egbelakin, T. and Sher, W., 2022. Contributions of the circular economy to the UN sustainable development goals through sustainable construction. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 178, p.106023.
Omopariola, E.D., Olanrewaju, O.I., Albert, I., Oke, A.E. and Ibiyemi, S.B., 2024. Sustainable construction in the Nigerian construction industry: unsustainable practices, barriers and strategies. Journal of Engineering, Design and Technology, 22(4), pp.1158-1184.
Sadeghi, M., Mahmoudi, A. and Deng, X., 2022. Adopting distributed ledger technology for the sustainable construction industry: evaluating the barriers using Ordinal Priority Approach. Environmental science and pollution research, 29(7), pp.10495-10520.
Shinoda, Tabata & Meirelles, Célia. (2024). The Crystal Building: Sustainable performance and technologies. 10.56238/sevened2024.003-001
Solaimani, S. and Sedighi, M., 2020. Toward a holistic view on lean sustainable construction: A literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 248, p.119213.
Tokbolat, S., Karaca, F., Durdyev, S. and Calay, R.K., 2020. Construction professionals’ perspectives on drivers and barriers of sustainable construction. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22, pp.4361-4378.
Website
Case study: The crystal – a Siemens Sustainable Cities initiative featuring KNX (no date) KNXtoday. Available at: https://www.knxtoday.com/2013/11/2605/case-study-the-crystal-a-siemens-sustainable-cities-initiative-featuring-knx.html (Accessed: 17 August 2024).
The crystal: One of the most sustainable buildings in the world. Available at: https://www.inawe.in/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/The-Crystal-Sustainability-Features.pdf (Accessed: 17 August 2024).
Sánchez, D. (2012) The crystal / Wilkinson Eyre Architects, ArchDaily. Available at: https://www.archdaily.com/275111/the-crystal-wilkinson-eyre-architects (Accessed: 17 August 2024).
Ijeh2012-09-19T13:30:00+01:00, I. (2012) Case study: Siemens Crystal, Building. Available at: https://www.building.co.uk/focus/case-study-siemens-crystal/5042760.article (Accessed: 17 August 2024).
Introduction: Unit 12 - Organisational Behaviour Assignment A major part of this paper is devoted to organizational...View and Download
1.1 Food & Beverage Marketing for Product Success Assignment Get top-quality Assignment Help Online for topics in strategic...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction to Finance Assignment Sample Financial analysis refers to the process of evaluating business, budget, project and...View and Download
Accounting for Business Essay Investment analysis may be defined as a tool which investors undertake for examining, assessing...View and Download
Introduction - International Trade Assignment Sample International trade means the exchange of goods, services and capital...View and Download
