+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
The objective of this research study is to examine the effects of IFRS 16 implementation on the financial statements and basic ratios of chosen airline enterprises. The data collected for the purpose of this study is financial information of the selected airlines for both 2018 before the implementation of IFRS 16 and for 2019 after the implementation of IFRS 16. This has been effective from January 2019 reclassifies most of lease obligations onto the balance sheet and have notably affected reported total assets, liabilities and expenses figures. Students grappling with these complex IFRS 16 financial analyses can seek help with assignment writing to master ratio computations and research methodology effectively.
The airline sector has been selected for analysis because it is receptive to leasing for its aircrafts and infrastructures and hence it will be easy to see the impact of IFRS 16. Through the examination of Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM, as airline companies, this research intends to reflect on how changes in lease accounting have affected financial reporting.
This research mostly involves the computation of financial data and the use of financial ratios, so quantitative data will be used. The objective is to investigate the effect of IFRS 16 implementation on the balance sheets of two chosen airlines. Pre-IFRS 16 analysis has been based on 2018 data while post-IFRS 16 analysis using data from 2019 (Mathew 2023). Analyse data that was collected from secondary sources that consist of financial statements and lease related disclosures of selected airlines and key ratios.
The scope of this research focuses on two airline companies Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM. These companies were selected because of their financial openness, relative industry and the availability of information. As both airlines have a considerable number of leased assets, they allow investigating the impact of IFRS 16, as the standard mainly relates to lease accounting. For this purpose, the study will adopt financial data from two financial periods 2018 representing the pre-IFRS 16 period and 2019 as the post-IFRS 16 period. This is in line with the government’s move to adopt IFRS 16 in January 2019 as a global accounting standard.
This research will compare the financial statements of the two years in order to draw differences. Leases will be considered in relation to disclosure requirements while ratios concerning debts to equity, return on assets, and interest cover will also be included together with overall company performance. Furthermore, historical financial figures shall be used for descriptive purposes, while inferential analysis through multiple regressions shall determine the effect of IFRS 16 leading financial indicators.
The main data collection tools will be the annual reports of the selected airlines containing the basic financial statements: balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements etc. For historical data, Investing.com will be used as an additional source to provide information about the financial data and key performance indicators during the period (Dong 2022). This information is very useful in the evaluation of main performance indicators, including profitability, liquidity, and solvency based on the computation of the airlines’ major financial ratios before and after implementation of IFRS 16.
To analyse lease related disclosures data will be pulled from the annual reports as companies always give further details of their leases there. Prior to IFRS 16, airlines reported on operating leases and finance leases separately In doing so, the details are provided in the notes to the financial statements (Afsari 2022). Subsequent to the implementation of this standard, the airlines report lease liabilities and ROU assets. These will be carefully extracted from the 2019 financial reports in order to evaluate the effect of the new lease accounting standard.
The two companies have been chosen for this research and are Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM. Such firms were selected because of their huge participation in the airline business, high levels of disclosure and access to financial reports. The proposed solution for increasing the reliability of the comparative analysis is a selection of airlines that operate from different locations and have different financial characteristics.
For this study, the time frame will be restricted to 2018 as the pre IFRS 16 period and 2019 as the IFRS 16 period. As it will be observed, the company adopted IFRS 16 with effect from January 1, 2019. Therefore the financial statements ending December 31, 2018 will be prepared before implementation of the new standard while those to December 2019 will be prepared in compliance with IFRS 16.
In this research, the Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM organisations’ analysis of the IFRS 16 changes will be based on the financial statement. The first annual report under consideration includes Balance Sheet, Income statement and Cash flow statement containing significant information about the financial situation and results of airline companies.
Key Ratios
These ratios are chosen because they are key measures of a firm’s financial condition and performance, and will offer insight as to the effects of implementing the IFRS 16 standard in the airlines’ capital and business models.
Lease-Related Disclosures
Pre-IFRS 16 (2018): Before the adoption of IFRS 16, even the operating lease and the finance lease were presented separately by the airlines (Lopes 2023). Whereas operating leases were originally listed as off B/S items, lease payments were recognized as expenses in the I/S. On the other hand, finance leases were recorded on the B/S as assets and liabilities.
Post-IFRS 16 (2019): According to IFRS 16 concerned with leases, all airlines are required to recognise lease obligations alongside the right of use assets. These changes will occur at the BS and affect the industry and the competing company’s financial construction and benchmarks (Luhtaniemi 2023). As a result lease liabilities and ROU assets will have a significant role to provide an understanding regarding the nature of the new lease accounting treatment from the perspective of financial reporting.
Accounting Ratio Analysis
The comparative analysis of the selected companies’ financial statements will be done for the 2018 (before implementing IFRS 16) and 2019 (after implementing IFRS 16). This entails examination of Balance Sheets, Income Statements and Cash Flow Statements) for the period before and after implementation IFRS 16 (Velioglu and Demirkol, 2024). The analysis will be put on how the capitalising of leases influences these statements and the activity-related essential financial ratios.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Prior to the adoption of IFRS 16, operating leases were considered to be off-balance sheet items, where the lease obligations were recognised as an expense on the income statement. IFRS 16 after which operating lease is recognized on the Balance Sheet as right-of-use (ROU) asset and lease obligation. Moreover, lease cost is from operating lease cost to depreciation (on the ROU assets) and interest (on the lease liabilities) (Melchionda 2022). In addition, as part of operations cash flows, payment of lease will now be separated into financing and operations cash flows in the statement of Cash Flow. In order to improve the quality of data presentation, the application of a variety of tables, charts, and graphs will be done. These are figures, which will help to show the comparison of the periods before and after the leasing standards IFRS 16.
Statistical Analysis
To analyze the impact of the transition to IFRS 16 on the main financial ratios, descriptive statistics analysis and multiple regression analysis will be used with EViews. The business financial performance for the year 2018 and 2019 will be assessed descriptively to establish the varying key financial performance indicators. This will unveil patterns and movements of these statements before and after the IFRS 16 transition (Belesis et al. 2021). However, to get a more sophisticated form of the evaluation, multiple regression analysis will be used in order to determine the impact of the adoption of IFRS 16 on the organisation. Multiple linear regression will be applied in an effort to establish the relationship between these ratios and the IFRS 16 using historical information.
A possible drawback of this study is data variables and their accessibility and comparability across different regions. It should be noted that the main data collection is based on Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM annual reports. However, some difficulties can be encountered in comparing the data of different years and ensuring the comparability of lease disclosures (Jakobsen and Fugllien, 2022). Hence, it is agreed that, sometimes the airlines may not disclose some information about their lease terms or use different reporting methods and influence the reliability and comparability of information. Also in this study, there is a possibility of some missing data at some particular period in the time frame of study.
The last limitation is an extension of the previous point and concerns the generalization of the results. This study involves only the two airlines, and the results cannot be generalized to all the airlines or other industries (Kljajić and Mizdraković, 2024). Each airline may have the factors, for example, leasing practices or financial structures, which influence the consequences of IFRS 16 implementation on their financial results.
3.7 Conclusion
The research approach that will be used for the purposes of comparing the consequences of Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM’s IFRS 16 implementations. They are based on the comparative analysis of financial statements from 2018 and 2019 with respect to certain ratios and lease information. For users such as investors, managers and analysts, it is therefore important to understand the effect of IFRS 16. The details and analysis of the empirical data will be given in the next chapter developed based on the presented methodology.
This chapter discusses the results stemming from the financial analysis of Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM in the light of IFRS 16. The purpose is to analyze changes in trends in financial performance indicators and key ratios that occurred within the transition from the previous leasing standard to IFRS 16 and in the period after its implementation (2018 and 2019). Comparison of profit and loss account and balance sheet, ratio calculations and statistical tools are used to determine the impact of recognizing lease liabilities and right-of-use assets. Gain understanding on how this study reveals the effects of IFRS 16 on financial reporting and performance of the airline industry.
4.2.1 Financial Overview
The financial structure and reporting analysis concentrates on the main shifts to the balance sheets of Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM consolidated financial statements upon the transition to IFRS 16 in the financial year ended 2019. This paper aims to demonstrate specific changes in balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements by including lease liabilities and right-of-use (ROU) assets (Velioğlu and Demirkol 2024). For Aegean Airlines, the recognition of ROU assets enhanced the total assets due to enhanced capitalization on the prior off-balance sheet operating leases. Altogether, lease liabilities resulted in the significant increase in total liabilities, and thus the growth of the debt-to-equity coefficient.
4.2.2 Descriptive Analysis

Figure 1: Descriptive Statistics for Pre IFRS 16
The first group of quantitative results – the pre-IFRS 16 descriptive statistics – present the companies’ financial metrics prior to the changes brought about by the new regulation. For Aegean Airlines, the evaluated key financial variable has a mean value of 7.485749, and the standard deviation coefficient is 0.744608, which characterize moderate stability in this set of values. These two statistics suggest that the distribution is quite near normal, but not perfect (Kljajić and Mizdraković 2024). The mean of Air France KLM was higher (44.17713) also the standard deviation was again higher (6.363272) indicating more spread in the data. The stock volume for Air France KLM shows a high level of activity with a mean value of 481.1581 and has high volatility levels considering a high standard deviation of 340.8472.
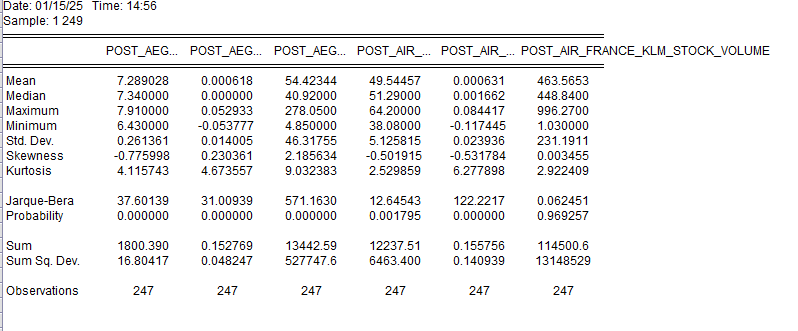
Figure 2: Descriptive Statistics for Post IFRS 16
The following statistical differences present essential changes in financial data after the implementation of the IFRS 16 lease accounting standard. There was a minor shift of mean value to 7.289028 for Aegean Airlines and a significant drop in variability which shows a little more stability in reported data (Standard deviations 0.261361). Likewise, the mean of Air France KLM was triggered to 49.54457 while the variability was reduced through a small standard deviation of 5.125815 indicating enhanced reliability (Utami et al. 2024). For both the airlines, the skewness and kurtosis indicates some shift in data distribution further with Air France KLM presenting less variability in terms of stock volume (mean 463.5653). It is remarkable that these changes evidence the effects of IFRS 16 on the qualitative characteristics of reporting products with a specific reference to the elements of standardization and comparability of accounts in the airlines’ business environment.
4.3.1 Debt to Equity Ratio
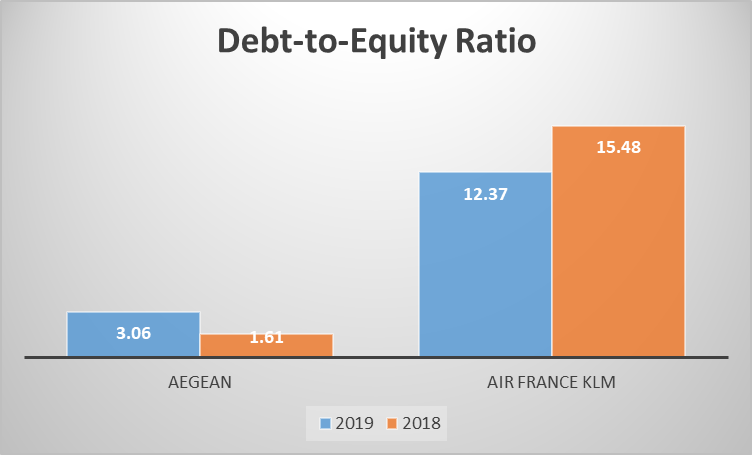
Figure 3: Debt to Equity Ratio
Debt to equity ratio shows the proportion of total debt against total equity of the company. In particular, the airline’s debt-to-equity ratio that in 2018 remained 1.61x, remarkably jumped to 3.06x in 2019 as a result of IFRS 16 implementation. In case of lease liabilities, this rise clearly suggests that liabilities which are newly capitalized assets in the balance sheet increased the level of the company's debt. Analysing the current ratio for Air France KLM, the figure declined from 15.48 in 2018 to 12.37 in 2019. These savings might have been effected through debt management or equity rebalancing. These results support the fact that the effects of IFRS 16 are not the same from airline to airline or year to year because of the possible differences in leasing structure and financial management (Slater et al. 2024).
4.3.2 Current Ratio
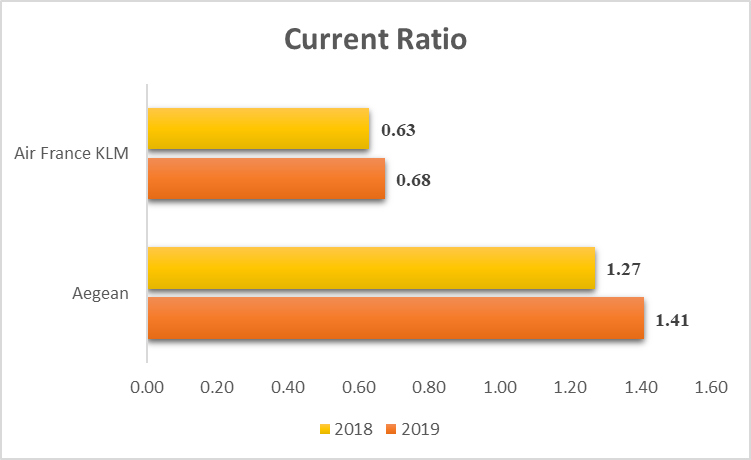
Figure 4: Current Ratio
For Aegean Airlines, the ratio increased from 1.27 in 2018 to 1.41 in 2019 to underscore improved short term liquidity even with the implementation of IFRS 16 in the recognition of lease liabilities (van Wyk and Enslin 2025). This improvement can, therefore, be due to an increase in the current assets or better management of liquidities. The current ratio of Air France KLM which shows the extent of liquidity of the firm also edged slightly up from 0.63 in 2018 to 0.68 in 2019. Although the ratio of Air France KLM remains less than 1, this marginal up move shows an enhanced efficiency to handle the short term liabilities after implementation of IFRS 16.
4.3.3 Return on Assets

Figure 5: Return on Assets (ROA)
Return on Asset (ROA) measures the effectiveness in management of assets in generating return or profit. The performance of Aegean Airlines was also high, where the ROA of the company was enhanced from 0.77 in 2018 to 1.63 in 2019. This much improved position indicates that there must have been improved utilization of assets or higher profitability than before though the total assets have gone up due to IFRS 16. However, Air France KLM recorded a slightly lower figure of ROA, which declined from 0.60 in the year 2018 to 0.58 in 2019. This decline could be attributed to a combined total assets figure with a significant element of ROU assets which has resulted in a total asset base diluting the efficiency of asset utilization (Balasem 2024).
4.3.4 Interest Coverage Ratio
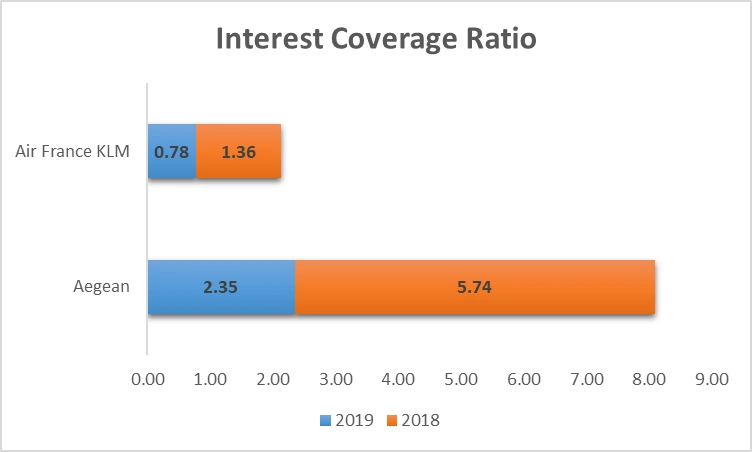
Figure 6: Interest Coverage Ratio
Interest coverage ratio gives information regarding the strength of such companies in covering up the interest expenses by operating income. Aegean Airlines had a decrease in its ratio from 5.74 in the year 2018 to 2.35 in the year 2019 meaning that the airline has the ability to generate the required interest to meet interest obligations lowered due to high interest expenses on lease liabilities. In the same manner, the interest coverage ratio has a reduction from 1.36 in 2018 to 0.78 in 2019 on the part of Air France KLM which shows a decreased capacity in the servicing of interest. The above two ratios reduced in both airlines and this was due to the cost of lease which in IFRS 16 has been reclassified and opens a new line of interest expense (Aladwan 2025).
4.4.1 Pre IFRS 16 Multiple Linear Regression of Aegean
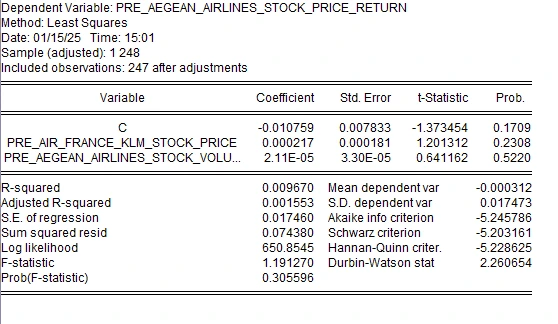
Figure 7: Multiple Linear Regression for Pre IFRS 16
For Aegean Airlines, the pre-IFRS 16 regression model gave an extremely low R-squared of 0.00967; this means that the independent variables namely, stock price of Air France KLM and stock volume of Aegean Airlines together account for just 0.967% of the Aegean Airlines stock price returns. The coefficients for the variables present only a modest impact on the dependent variable where coefficient for Air France KLM’s stock price is 0.000217 and coefficient for Aegean Airlines stock volume is 2.11E-05. However, both the variables examined in the are significant at p>0.05 hence suggesting that the results are statistically insignificant. Based on these results, it is safe to conclude that prior to the adoption of IFRS 16 standard the selected variables carry a low sensitivity score regarding the SRR of Aegean Airlines (Iwata 2024).
4.4.2 Post IFRS 16 Multiple Linear Regression of Aegean
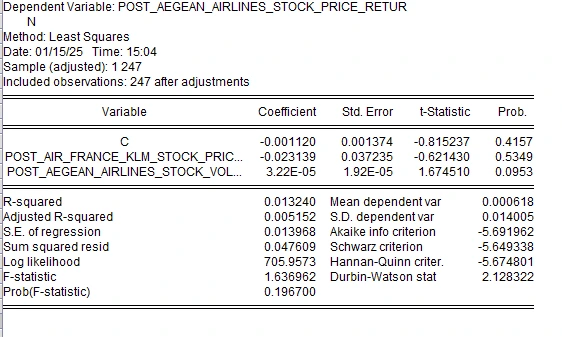
Figure 8: Multiple Linear Regression for Post IFRS 16
For Aegean Airlines, after applying IFRS 16 changes the R-squared rises to a meager 0.01324, indicating the explanatory power of the model has improved to a trivial degree after post IFRS changes. The coefficient for stock price changes reduces to -0.023139 for Air France KLM and becomes negative while for stock volume, the coefficient rises to 3.22E-05 for Aegean Airlines and it is positive. However, the two have become insignificant when it comes to its p-value since it’s greater than 0.05 for all models. The adjusted R-squared value is still less than zero, which supports the low of the tested model. Non Freundlich autocorrelation also known as the Durbin Watson statistic of 2.128322 shows no evidence of autocorrelation (Sura and Di Ventura 2024). Comparing the chosen variables and Aegean Airlines’ stock price returns, these results reveal that IFRS 16 implementation did not significantly affect the observed correlation.
4.4.3 Pre IFRS 16 Multiple Linear Regression of Air France KLM
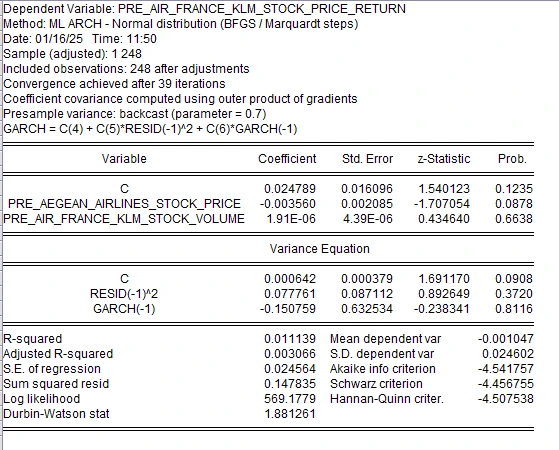
Figure 9: Multiple Linear Regression with Arch for Pre IFRS 16
From the regression model applied prior to the implementation of IFRS 16, namely the GARCH (1,1), the Air France KLM model embeds an R-squared of 0.011139, which is an indicator of a poor explanatory capability of the variables that form the independent dataset, namely the Aegean Airlines stock price and Air France KLM stock volume. The results show that Aegean Airlines’ stock price has a negative effect as its coefficient is equal to -0.00356 for Aegean while the coefficient for stock volume of Air France KLM is 1.91E-06 proving a very slight positive effect. Here, both these coefficients look statistically insignificant as their p-values tend to be high. The variance equation focuses on residual variance ( RESID(-1)^2 ) which has a positive significant coefficient of 0.077761 ,signifying that there is volatility cloning. This conclusion arises from the fact that Durbin-Watson statistic of 1.881261 may slightly suggest that the residuals were possibly affected by mild levels of autocorrelation (Sun 2024).
4.4.4 Post IFRS 16 Multiple Linear Regression of Air France KLM
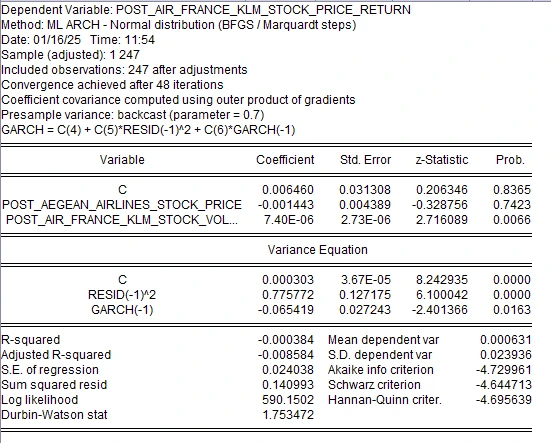
Figure 10: Multiple Linear Regression with Arch for Post IFRS 16
After adopting IFRS 16, the regression model of Air France KLM exhibits the negative R-squared of -0.000384 confirming very low predictive ability of endogenous variables. The coefficient for Aegean Airlines’ β for stock price changes falls to -0.001443, although it remains statistically insignificant, and is still overall negative in sign while that for Air France KLM’s, for stock volume, rises to 7.40E-06, a value that is statistically significant (p-value < 0.05). The equation for variance produced results supportive of RESID(-1)^2 as it produced positivity of the value of 0.775772 with respect to coefficient stressing on the continual volatility impact over the stock price returns. The Durbin-Watson statistic of 1.753472 indicates no significant problem of autocorrelation within the residuals. The study reveals that while IFRS 16 implementation affected the explanation of the results to a negligible level, it affected the coefficient of some variables including the stock volume of Air France KLM
4.5.1 Discussion of Descriptive and Accounting Ratios
Descriptive Analysis
The descriptive analysis of the pre and post IFRS 16 displays the changes in the financial variables as a result of the new lease accounting standard. In the same respect, for Aegean Airlines, post IFRS 16 period was characterized by less fluctuation in the financial information as evidenced by lower stock return standard deviation (Aliya and Nasiru 2024). This therefore imply that IFRS 16 improved on the stability of financial reports for the company. However, we observe a similar form of volatility convergence in case of Air France KLM, although a dip in the standard deviations for the stock price returns as well as stock volumes can also be noted. Nevertheless, the mean values of Air France KLM’s financial ratios rose after IFRS 16 implementation, which may indicate its market acceptance of the company’s adjusted set of accounting standards.
The values of skewness and kurtosis for both airlines indicate that IFRS 16 affected the distribution of the analysed data. According to the above tables, Aegean Airlines had a submission of skewness and kurtosis behind IFRS 16, as the coefficient of skewness reduced and kurtosis rose. In case of Air France KLM, after the implementation of IFRS 16 kurtosis was slightly lower down as a result of less variation in the financial ratio values as shown in figure 9. These changes remain the area where IFRS 16 is targeted to ensure that companies provided standardized and less volatile financial information disclosures (Li and Venkatachalam 2024).
Accounting Ratios
For Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM, the debt to equity was inclined in opposite directions post adoption of IFRS 16. Aegean Airlines’ ratio increased from 1.61 in 2018 to 3.06 in 2019, it shows that the company capitalized lease liabilities had a significant effect on financial leverage. It also demonstrates the cost of placing operating leases on the balance sheet as liabilities. On the other hand, the AIR FRANCE KLM ‘s debt-equity ratio reduced from 15.48 in 2018 to 12.37 in 2019, while employing SE analyses or better liabilities post IFRS 16. These variations support that cost differences of implementing IFRS 16 due to leasing structures and plans are firm-specific (Xue and Huang 2024).
Aegean Airlines’ ratio increased from 1.27 to 1.41, due to the efficient handling of current assets than current liabilities. Actual demonstrated liquidity remained below 1 and even though it marginally increased from 0.63 to 0.68 the situation at Air France KLM remained stretched. These findings imply that IFRS 16 could have led to enhancing the liquidity profile to address the lease liabilities among airlines.
Return on Assets (ROA) offers information about how the organisation management utilises the assets. The company enjoyed a remarkable BOOST in its ROA where the figure was 0.77 in 2018 but rose to 1.63 in 2019. This growth also revealed the ability of the company to achieve better returns from the new asset base, including ROU assets recognized under IFRS 16. On the other hand, total asset turnover marginally rose from 0.18 to 0.19 while Air France KLM’s ROA slightly declined from 0.60 to 0.58 as seen below By increasing asset base while at the same time searching for higher profitability is not very easy. These two trends show opposite effects of IFRS 16 on asset efficiency based on revenue generation capability and cost control mechanisms of the firm (Mardiani et al. 2024).
As seen in the working capital analysis, using the interest coverage ratio there were declines for both airlines after implementation of the IFRS 16. Aegean Airlines saw its ratio decrease from 5.74 to 2.35 suggesting the company has less ability to offset interest costs due to the reclassification of operating leases to interest expenses. Like most players in the industry, theums ratio has reduced from 1.36 to 0.78 indicating financial pressure on the company. These conclusion clearly show that IFRS 16 has posed new financial burden especially in the interest rates obligation.
4.5.2 Discussion of Multiple Linear Regression
Pre-IFRS 16 Findings:
The pre-IFRS 16 regression model for Aegean Airlines with stock price returns gave the least R-squared value of 0.00967 as stocks of Air France KLM and stock volume of Aegean Airlines had the least impact on Aegean share price. The coefficients in both independent variables were statistically insignificant having adjusted p-values greater than 0.05. From these outcomes, one can assert that prior to IFRS 16 implementation such outside factors or something related to the market choice of variables affected Aegean Airlines’ stock price.
In the same vain, in result, exploration of Air France KLM’s pre-IFRS 16 regression using the GARCH model displayed an R-squared of 0. 011139, signifying low predictive abilities. Coefficient of Aegean Airline proved to be statistically insignificant as for Stock Price while the coefficient of Air France KLM proved to be statistically insignificant as for Stock Volume. In the variance equation, the role of residual variance was also emphasized implying the existence of volatility effects (Farinelli 2024). These results suggest that until the implementation of IFRS 16, the stock price returns of Air France KLM were being determined by a few other factors as seen in the selected variables.
Post-IFRS 16 Findings:
After the implementation of IFRS 16, the regression output for Aegean Airlines degraded a bit and showed an R-squared value of 0.01324 for the model which is a slightly better number. Interestingly, the coefficient of Air France KLM stock price remained insignificant at - 0.023139 while Aegean Airlines stock volume coefficient equal to 3.22E-05 was also insignificant. The findings derived from this study imply that the application of IFRS 16 did not alter significantly the pattern of the correlation between the chosen variables and Aegean Airlines’ stock price returns. Continuity of low explanatory power informs the fact that there might be several factors that influences stock price such as macro-economic factors, market feeling and company performance (Putra and Khaddafi 2024).
Analyzing the same after the transition using GARCH model at Air France KLM resulted in an R Sqaure of - 0.000384, a model with almost zero efficiency. Nonetheless, the coefficient for Air France KLM’s stock volume (7.40E-06) changed its value to be statistically significant with the p<0.05. This implies that IFRS 16 affected investors’ perceptions making stock volume even more important factor determining stock price returns. The variance equation again pointed towards the residual variance and the constant fluctuations observed in stock price.
4.6 Conclusion
The discussion of descriptive statistics, accounting ratios, and regression findings shows the extensive but diverse influence of IFRS 16 on financial reporting and Stock price indicators of Aegean Airlines and Air France KLM. Although the new standard improved transparency and comparability of financial reports, its impact on stock prices and the subsequent changes of financial ratios show that the transition to the new framework is a process full of difficulties. To these ends, the following quantum of unreserved insights is imperative for the stakeholders in determining the broader ramifications of IFRS 16.
Reference List
Journals
Rationale: Water-Based Learning Experiences These learning experiences focus on engaging children with water as a science...View and Download
Introduction to Strategic Analysis Of Apple Inc. Assignment Sample 1. Apple Inc. Apple Inc. is a multinational technology...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction to Professional Relationship In Nursing Effective professional relationships in health and care are based on key...View and Download
Introduction A Business plan refers to a document that demonstrates goals, objectives and strategies of company cater as a...View and Download
Introduction to Psychological Factors Assignment Background The spinal cord injury is defined as an injury that includes damage...View and Download
