+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
In understanding the key and important functions of various body systems, it is crucial to organize and present information clearly, much like how an assignment helper in UK would assist students in structuring complex topics effectively. For example, in the skeletal system, the key function is to provide a firm structure to the body through compact and spongy bones, supporting overall body shape and protecting vital organs. Additional important functions include working with the musculoskeletal system to facilitate movement and producing blood cells through haemopoiesis. Similarly, the muscular system’s primary role is enabling contraction and relaxation that drives body movements, while also maintaining posture and generating heat to regulate body temperature. The circulatory system plays a vital role in delivering oxygen, hormones, and nutrients to cells and in regulating body temperature and immunity. Clear presentation of these functions is essential for comprehensive understanding, and seeking support from an assignment helper in UK can be valuable in mastering how to explain such scientific concepts with accuracy and clarity.
| Body system | Key function | Important function | Important function |
| Skeletal | The skeletal system can give the firm structure to the body which can make the bones spongy and compact. This can support the body in maintaining the proper body shape. | This can work with the musculoskeletal system which helps in running, walking and various types of movements. | Haemopoiesis happens in the bone marrow which produces three types of blood cells such as red and white blood cells and platelets. |
| Muscular | This system enables the contraction and relaxation of the muscles for enabling the body movements. | This also maintains the body posture which can support the body in an appropriate position like in the upright position. This can help in the stabilisation of the joints with the prevention of falling of the body. | This can also generate the heat in the process of contraction with the maintenance of the body temperature and this process is also known as the process of thermogenesis. |
| Circulatory | The system of circulation can properly deliver the hormones, nutrients and oxygen to each of the cells in the body and this also helps in the removal of waste products including the carbon dioxide. | This also helps in the regulation of the body temperature. This system can distribute the heat properly throughout the whole body. | This can provide immunity with the protection through antibodies and WBC in the bloodstream. |
| Respiratory | The respiratory system helps in the gaseous exchange so that it can supply the proper oxygen into the bloodstream and excretes the carbon dioxide. | It also helps in the regulation of pH by maintaining acid base equilibrium by controlling the levels of Co2 in the body. | This also helps in the process of vocalisation. It can generate the sound when the human body can pass the air by the vocal cords. |
| Nervous | The nervous system helps in the coordination of the human body by controlling the body activities. This can transmit the body signals between the spinal cord and brain. It can also transmit the signal to the other body parts. | In sensory perception this is also helpful. It can detect and interpret the different types of stimuli such as the temperature, pain and touch (Shaffer et al. 2023). | It regulates the functions in the body automatically. This can manage the involuntary processes in the body properly. The various involuntary processes which are controlled by the nervous system are heartbeat, breathing and digestion. |
Skeletal System
The skeletal system is so designed in form, shape, and size that it serves as a frame work on which the body is built. It includes dense bone also known as compact bone and the other one is lighter bone known as spongy bone. The first layer of the compact bone matrix is composed of compact bone which provides the formation of rigidity and strength to oppose mechanical pressure. The cancellous bone or spongy bone is one which is mostly settled in the terminal of lengthy bones and is porous and full of bone marrow for making blood cells (haemopoiesis).
Muscular System
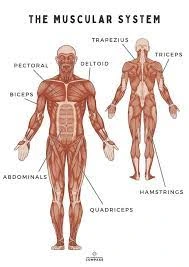
Figure : Muscular system
The muscular system consists of three types of muscles and the three categories of muscular tissues are the nervous, muscular and somatic. Voluntary muscles are those which are connected to the bones with the help of tendons and assisting in the various movements like running and walking. Due to the arrangements of layers or striae they possess capacity for manifesting distinct contractions. The involuntary ones include smooth muscles, for example in the stomach, or intestines, and cardiac muscles to make the heart continuously pump blood.
Circulatory System
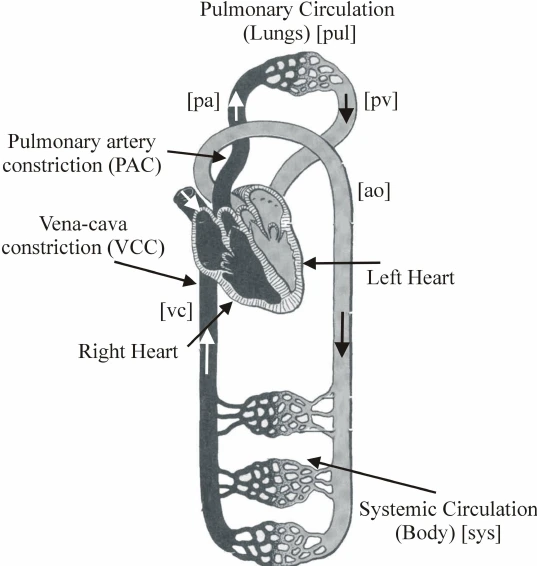
Figure : Circulatory system
The system of the circulation has revolved around the components of the circulatory system like blood, blood vessels and heart. The heart can be recognised as the muscular walls which are categorised into the four chambers that can help in the pumping of the blood efficiently. Arteries of the blood vessels are known as the thick wall which can bear the pressure as they can carry the oxygenated blood.
Respiratory System
The system of the respiration is categorised into the lungs, bronchi, bronchi and alveoli which can assist in the process of gaseous exchange in the body. Among these components the trachea and bronchi are aligned with the cartilages for maintaining the open air circulation (Dhar et al. 2021). On the other hand the other components like alveoli are known as the tiny air sacs that can enhance the surface area for diffusion of Co2 and O2. The muscles of diaphragm and intercostal region help in the facilitation of the breathing process by expansion and contraction of the chest cavity.
Nervous System
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
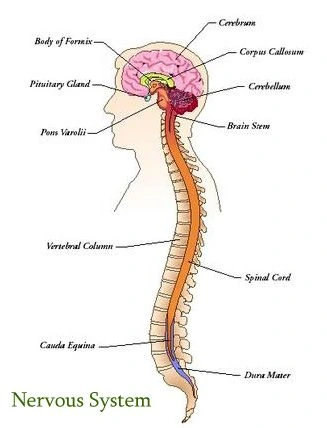
Figure: Nervous system
The structure of the nervous system is derived from specialized structures that are called neurons and that use electrical impulses. The principles consist of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The head contains the brain surrounded by the skull: the skull protects the brain which controls thought processes and reaction,and the vertebral column shields the spinal cord which transmits impulses between the brain and the rest of the body.
Skeletal System
The skeletal system which is part of the muscular system gives that framework on which Mr. Patel’s body is built when taking this run. The bones are used as keys while the joints offer the kind of flexibility needed for running movements. As it is with all iliopsoas athletes at this stage of the race, the lower limb bones comprising the femur, tibia, fibula and pelvis and muscles compress and expand as he transfers force from the ground. His joints are covered with cartilage which reduces over rubbing of the bones. His skeletal system also shields other vital organs such as lungs and heart which are struggling to provide oxygen and pump blood respectively. Stressing pressure on his bones constantly, helps in carrying out bone remodeling for six months of training to make his bones strong.
Muscular System
Mr. Patel’s muscular system provides the force to enhance his speed level in his muscular system. Some of the major muscles involved include the skeletal muscles, on his lower limbs, including; Quadriceps, hamstring, calves and Gluteus muscles. Muscle depots hold glycogen and oxygen bodies as a source of energy in muscle that is needed to run for longer periods. At 7K his muscles will develop more cross linkages that will take more ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Muscular movements become spirited through anaerobic as well as aerobic respiration to meet special energy needs. The extra contractions also produce heat and his body controls the heat by sweating.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system has one of the most crucial roles of supplying the working muscles of Mr. Patel with oxygen and nutrients. This is the reason it will raise his heart rate as he speeds up, this forces blood through the arteries at a faster place. Blood carrying oxygen and glucose and nutrients reaches tissues of his legs to help in production of energy. However, the blood that contains little oxygen that is formed from the metabolism of carbon dioxide and other products circulates in the lungs. In addition, they dilate (vasodilation) to ensure sufficiency in supply of oxygen just like the removal of wastes that would lead to muscle cramping.
Respiratory System
For the muscles to supply enough oxygen needed for running faster Mr. Patel’s respiratory system steps up to supply adequate levels. His breathing rate and depth will also increase for the purpose of effective endowment of oxygen in the alveoli. The oxygen is absorbed by Co2 and blood of each of the cells in the body and this is given by the process of cell respiration which is excreted by blood (Ayaz, and Ismail, 2022). His diaphragm and the muscles joined between the ribs work harder to expand his lungs and bring in more volumes of oxygen for his muscles. Proper integration and response between his respiratory and cardiovascular systems clears the built up lactic acid causing a delay in fatigue and keeping up a faster temperature.
Nervous System
The nervous system regulates all activities within the body to assist Mr. Patel in coping with the rising call for duties. His brain detects levels of fatigue and muscle stress and sends messages through the spinal cord to muscles to work harder. His somatic nervous system controls all the movements of his legs and his autonomic, is in charge of all the functions of his heart, blood pressure, respiration, etc. He may feel stiffness in his joints and muscles that tell him the position of his body which he corrects to improve his manner of walking.
Abstract
The following research assesses the effects of stair climbing and jump rope exercises on the body in comparison with complete inactivity. Some of the important parameters considered were the heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, their time recovery period. Data presented indicate that cardiovascular and respiratory requirements for performing jump rope were higher than for stair climbing with longer recovery time of 12.3 minutes as compared to 8.5 minutes respectively. The results demonstrate the relationship between activity type and intensity and physiological changes thus offering significant information on exercise prescriptions and individualized physical training.
[Keywords: Physical activity, heart rate, blood pressure, physiological response]
Introduction
This study looks at the impacts of a range of PA on various body system outcomes. Over the course of one day and through five trials, the study examines the differences of heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, and recovery for two types of physical activities, stair climbing and jump rope, when compared to a control resting state. Such understanding gives birth to how the skeletal, muscular, circulatory, respiratory and nervous systems interact with each other to supply the body with energy and oxygen when involved in physical activities.
Method and Materials
Materials
Method
Stair Climbing Activity
The participants ascended three floors of stairs at a steady rate which was reasonably close to moderate to high intensity exercise.
Jumping Rope
This exercise included skipping for 2 minutes in a high intensity that entailed working out many muscles and it raised the cardio level.
Resting state
Initial assessments were made during seated rythmometry after five minutes of rest to provide a base on which future comparisons could be held. These activities were chosen because they vary in the level of how much they require different parts of the body.
Procedure
In the data collection process, the study has adhered to a laid down procedure to make the study credible and accurate. Preoperative measurements were done five minutes after the participants settled in order to get their baseline. For both stair climbing and jump rope activities each activity was done to the specified sets and reps with post activity measurements done immediately. Further assessments were made at two minute intervals into recovery to determine how soon the physiological variables would return to their normal state. Ten minutes of resting was given in between the activities to reduce the chance of practicing effects (Zhao et al. 2021). To increase the reliability and to account for variation in the responses each of the activities was conducted three times.
Results
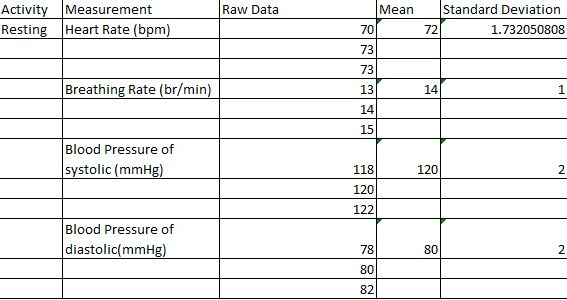
Table 1: The findings of the Resting period
In this study, essential differences in the physiological trends were observed under the three conditions. This yielded resting measurements whereby participants had a mean heart rate of 72 ± 1.73 bpm breathing rate of 14 ± 1 br/min, and mean blood pressure of 120/80 ± 2 mmHg.
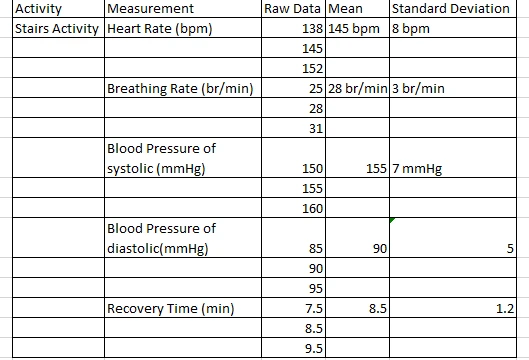
Table 2: The findings of the stairs activity
Stair climbing increased mild to moderate elicit, heart rate increase to an average of 145 ± 8 bpm, breathing rate to 28 ± 3 br/min, and blood pressure to 155/90 ± 7/5 mmHg and took an average of 8, 5 ± 1.2 minutes to recover.
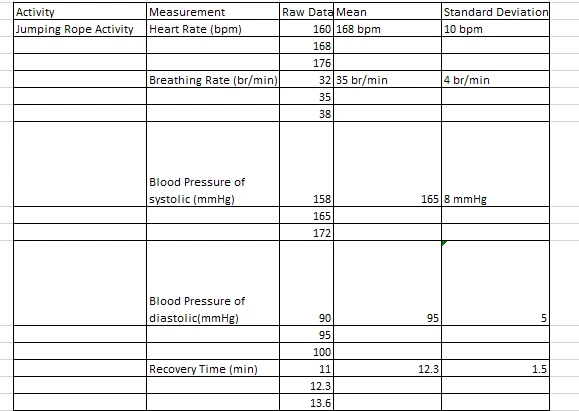
Table 3: The findings of the jumping rope activity
Among all exercises, the highest responses for heart rate were recorded at 168 ± 10 bpm, breathing rate 35 ± 4 t/min, BP 165/95 ± 8/5 mmHg and jump rope recovery time was 12.3 ± 1.5 min.
Discussion
The different results obtained in the activities can be explained by the differences in the strength and muscle activation (Xiao, 2024). As expected, the new exergonic activities revealed even greater physiological demands than stair climbing; jump rope did so especially clearly and more often than not because this kind of activity is continuous for the most part and involves the upper body as well. The high standard deviations in the data relating to jump rope highlight the fact that people’s response to high intensity exercise varies even more. The fact that jump rope has a considerably longer recovery time (12.3 minutes) compared with stairs (8.5 minutes) shows that this exercise increases cardiovascular and respiratory systems’ metabolic stress more significantly. These findings are consistent with current knowledge in exercise physiology in views of intensity-dependent cardiovascular adaptations and recovery.
Conclusion
This study provided a clear enunciation of how different types of physical activities affect bodily systems responses. Though the survey revealed the physical nature of the jump rope in terms of cardiovascular and respiratory effects as being much more pronounced compared to stair climbing and even the resting condition. This can be particularly insightful regarding system stress and individual variability, as reflected in the recovered jump rope numbers: recovery time was larger, while standard deviation was accordingly higher. These findings raise awareness of how activity intensity and type bear a very close relationship with the physiological outcomes. Knowledge of these relationships may be used to guide exercise prescriptions and physical activity interventions for the various fitness objectives and populace.
Reference List
Journals
Introduction Discover expert reflections on growth with this sample. With Assignment Help UK, develop tailored insights for...View and Download
Introduction: LJMU-7508-BEGP Leadership for Strategic Execution Leadership plays a major role in implementing and developing...View and Download
Introduction to Business and Tourism Management Assignment Sample Business and tourism management is a field which combines...View and Download
1. Introduction - Epidemiology of Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases Assignment Sample Tuberculosis (TB) is an...View and Download
Introduction: Values, Ethics And Working Collaboratively Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for...View and Download
Introduction: Innovation to Transformation in Nursing Practice This study will analyses the increase in poor cleanliness...View and Download
