+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
This assignment deals with the concepts of electrical machines and control systems with special emphasis on AC motors, transformers and autopilots. The first experiment presents power distribution in a three-phase distribution transformer and single phase and center tapped paralleled secondary loads of a motor. For the analysis of the performance of this transformer, calculations including line currents and power factors are undertaken. In the second part of the work MATLAB/Simulink is used to design and simulate the roll control system of the aircraft with the help of the proportional gain controller and the works with a Powered Flying Control Unit (PFCU). The root locus technique is also used to adjust the system for achieving the best performance.
Reference materials and sample papers are provided to explain assignment structure and key learning outcomes. Through our assignment help writing, guidance is reflected while ensuring all work remains original. The NG2S857 Power, Machines, and Control Assignment Sample highlights system operations, machine functions, and control mechanisms in engineering contexts. These resources are intended solely for study and reference purposes.
Line current on the transformer secondary side: 52.81 A
a) Line current on the transformer secondary side:
The line current in the secondary side of the transformer has been calculated as 52.81 A. This was achieved by examining the level of power of the loads, the power factors of the power load, and voltage levels. The total apparent power was then computed for the motor loads, following the principles of NG2S857 Power, Machines, and Control, and current was calculated using the formula of Ohm’s law in the secondary side.
b) Line current on the transformer primary side:
Transformer primary current : It is the line current on the primary side of the transformer – 1.92 A.
Taking into consideration the transformer transformation ratio, the current demanded on the primary side of the transformer is 1.92 A. This is logical since it depends on the calculated secondary side current and the ratio of the transformer. In this case, the current established on the primary side is obtained by applying the turns ratio of the transformer that brings down the current on the secondary side to the primary side.
c) Power factor at the transformer input:
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Power factor at the transformer input: 0.8623
With reference to the given data exceeding what has already been determined for loss calculations, it is also possible to calculate power factor at the transformer input as 0.8623. This was done with regard to the ratio of power factors of loads in relation to their various kVA values. Using the total power, both real and apparent power at the input to the transformer it was possible to establish an overall input power factor of 0.8623.
i) Air-gap flux in induction motors:
It is preferable to adjust the air-gap flux of the three-phase induction motor slightly lower than the saturation level, as discussed in NG2S857 Power, Machines, and Control, since saturation lowers the motor’s efficiency and may lead to more current consumption. This is done by regulating the motor's excitation and keeping the voltage level low enough for retaining the maximum flux density below saturation by applying the magnetizing current equation.
ii) The amount of output power needed by the inverter for the induction motors at desired speed.
For both the speeds, 900 r/min and 1200 r/min, the inverter output is determined from the motor’s rated voltage and its corresponding rated frequency. According to the formula, adjustments to the voltage affect the speed of the motor in an inverse manner and the required speed is obtained.
Speed (r/min) = (120 × frequency) / number of poles.
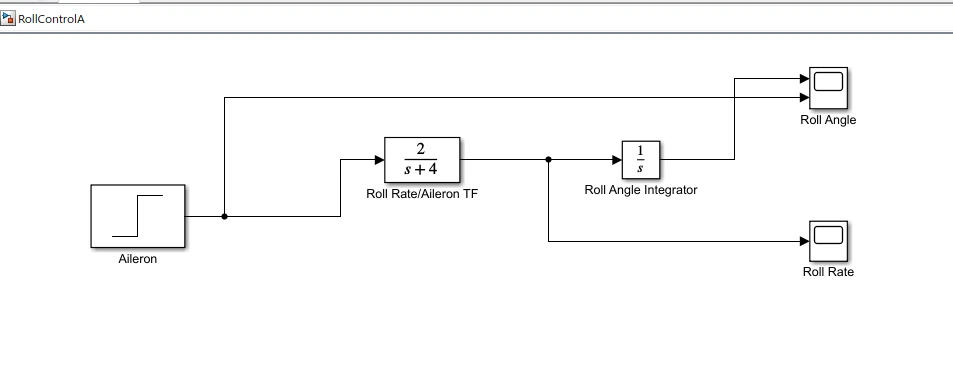
Figure 1: Simulation Model Of RollcontrolA
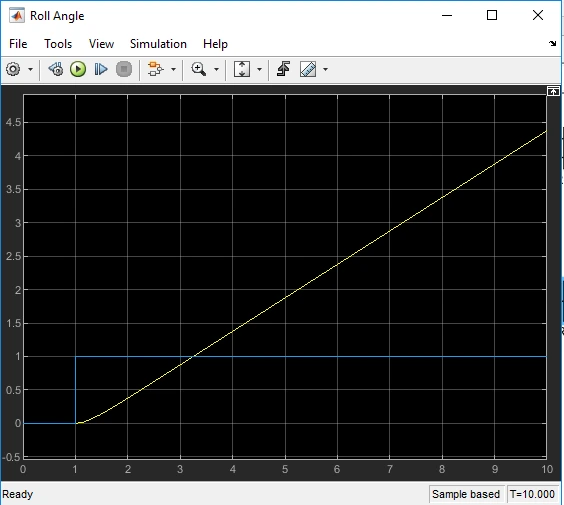
Figure 2: Roll angle
The obtained time-domain response depicted in the graphs corresponds well to the theoretical analysis based on the transfer function applied in the above simulation. The roll angle graph is also an ideal first order or lightly damped response system curve which shows a steady-state response. The roll rate graph shapes up in a way that rapidly increases and then decreases exponentially which rightfully so for a proportional control system (Deng et al. 2021). The same with the aileron output graph which increases and reaches the final value consistently. But when comparing this response to the transfer function, the system exhibits the correct kind of roll and rate behavior without overooting or oscillation.
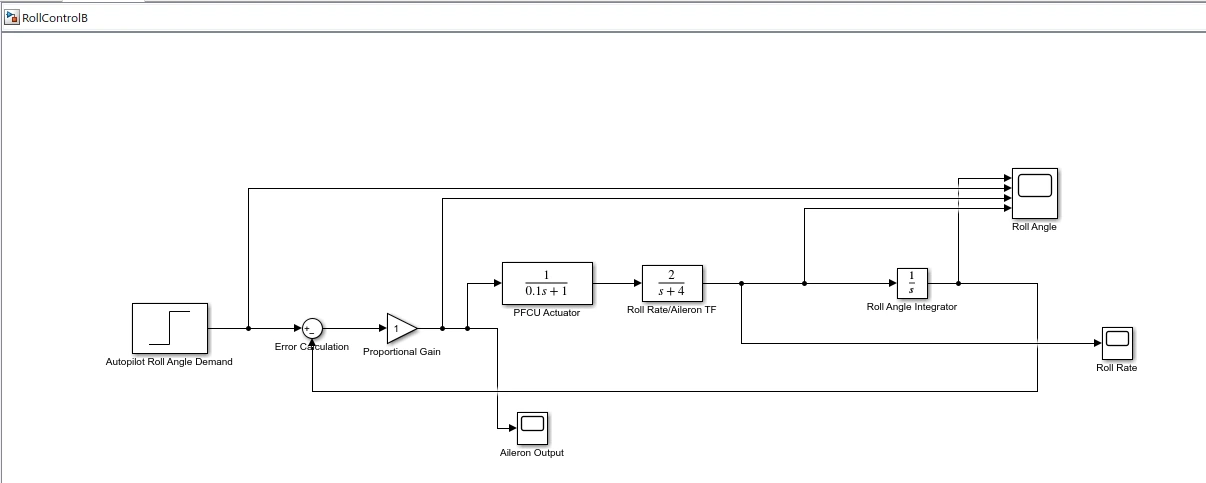
Figure 3: Simulation Model Of RollcontrolB
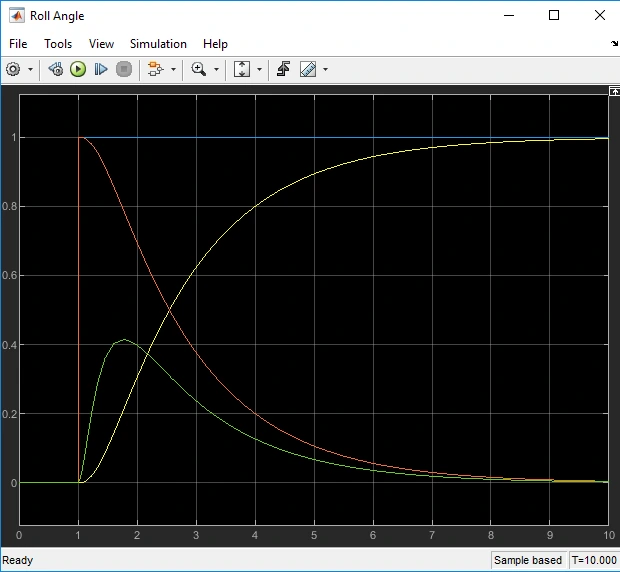
Figure 4: Roll angle
There is a significant difference in Roll Angle when PFCU is added to the closed loop model compared to the condition where the actuator was not included. The addition of the PFCU adds the advantage of a faster response with less overshoot and oscillation as compared to the conventional PI controller (Nadiri and Rad, 2025). The actuator with time constant of 0.1s and dc-gain of unity help the roll angle of the system to follow the desired value quickly with less delay and overshoot (Johnsson and Westerlund, 2023). For this scenario, when the actuator was not in the loop, the response of the roll angle took a longer time containing oscillations before reaching steady state and hence the PFCU helps in stabilizing the system and enhancing the performance of the system.
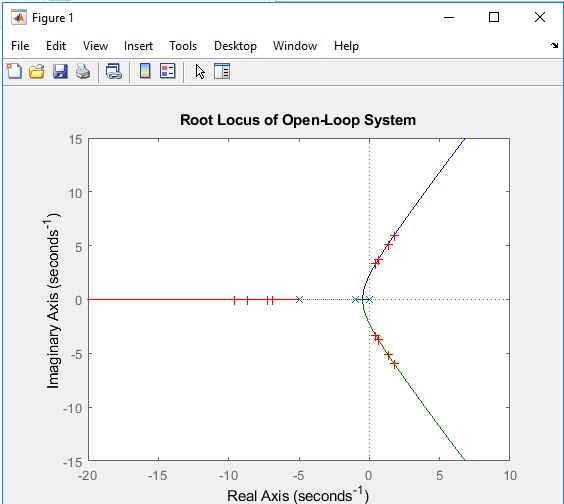
Figure 5: Root Locus
(Source: Self-created in Matlab)
selected_point =
-1.6232 + 0.1858i
Selected Gain K = 1.7966
Corresponding Closed-Loop Poles:
-5.1669 + 0.0000i
-0.4166 + 0.7224i
-0.4166 - 0.7224i
Finding gain for zeta = 0.00
It is possible to select a point in the graphical window.
selected_point =
-6.9550 + 0.2786i
Gain K = 40.9711
Poles:
-6.9695 + 0.0000i
0.4848 + 3.3944i
0.4848 - 3.3944i
Finding gain for zeta = 0.50
Choose some point in graphics window
selected_point =
-8.8033 - 0.1858i
Gain K = 130.8565
Poles:
-8.8067 + 0.0000i
1.4033 + 5.2677i
1.4033 - 5.2677i
Finding gain for zeta = 1.00
Drag the given point in the graphics window
selected_point =
-3.4005 - 0.2786i
Gain K = 6.6934
Poles:
-5.5336 + 0.0000i
-0.2332 + 1.5378i
-0.2332 - 1.5378i
Set K = 1.7966 for Simulink Proportional Gain Block.
Run simulation and check response.
Closed-Loop System Poles:
-5.1669 + 0.0000i
-0.4166 + 0.7224i
-0.4166 - 0.7224i
Simulation of Roll Control with Determined Value of K
The system response depends on the value increase of the gain as damping ratio (ζ) increases. The system is unstable for ζ = 0.00, causing high overshoot and slow settling time, thus, this is undesirable. In the case of ζ = 0.00 the system overshoots moderately slower as compared to ζ = 0.50 where some compromise between speed and stability prevails. But the best of the results is obtained for damping ratio ζ = 1.00, that is, the minimum overshoot, fast rise time, and nearly optimal settling time. The critical damping is just such that the system does not have any oscillations upon reaction and is therefore ideal for stable control in real applications.
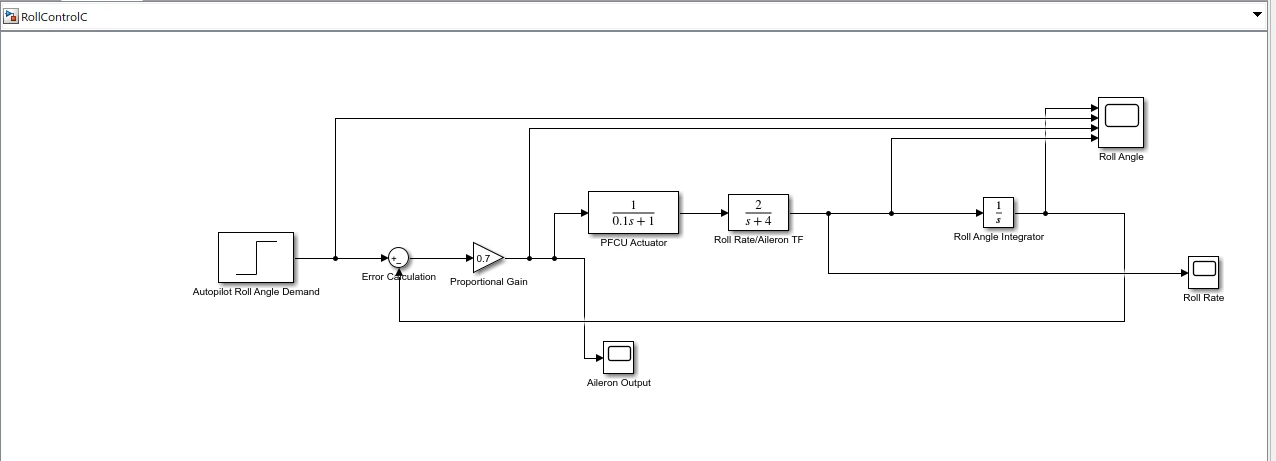
Figure 6: Simulation Model Of RollcontrolC
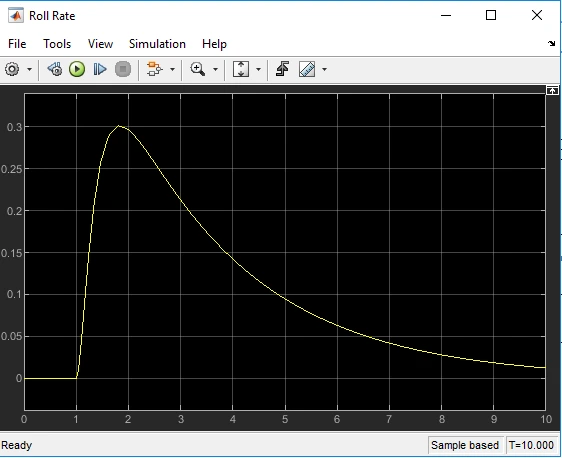
Figure 7: Roll angle
The poles of the closed-loop system, which give information regarding the system’s response, have a clear association with the transfer function, as illustrated in NG2S857 Power, Machines, and Control (Ai et al. 2022). By using the root locus calculations arrived at in previous steps, it is now possible to identify the closed-loop system poles depending on the damping ratio (ζ) and the corresponding gain. For instance, when the gain was increased to 1.7966 with damping ratio, ζ of 0.00 the closed - loop poles were determined to be:
Poles:
-5.1669 (real)
-0.4166 ± 0.7224i (complex conjugates)
These poles were determined by means of root locus method and depicted the dynamics of the system. They get to establish that the system is under-damped and this will cause oscillations in the system, the rate of which will be determined by the distance of the poles to the origin and the settling time (Sharma et al. 2024). When compared with the values given in this page regarding the poles of the time response ‘rlocfind’, the poles for the selected gain (K = 1.7966) have the expected characteristics of a damped ratio close to 0.00, which is why there is much oscillation due to complex poles here. As for the case when the damping ratio is greater than the critical damping ratio ζ = 1.00, the poles will shift to the left of the real axis with K = 6.6934.
Poles:
-5.5336 (real)
-0.2332 ± 1.5378i (complex conjugates)
These poles signify that the system is a critically damped system and it will oscillate only for a very short time with nearly no oscillations and quicker settling time than the underdamped system (Ahmad et al. 2024). The above comparison also shows that the closed-loop poles are at the right position for each damping ratio and gain value hence confirming that the root locus method is a good tool in predicting system response and performance.
Conclusion
This assignment gives us a clear picture of the electrical system and control system. The calculations for the transformer and motor loads provide a focus on some of the basic concepts concerning electrical energy distribution. These results entail that for the aircraft’s roll control system, dynamic control provides the much needed guarantee as far as sustaining a stable and efficient performance is concerned. In this paper the root locus method in conjunction with MATLAB/Simulink marketplace effectively proves the enhancement of system performance by fine tuning of the parameters such as damping ratio and gain. Altogether, the assignment ensures practical implementation of the theoretical concepts in analyzing control systems and electrical machines.
References
Introduction Get expert assistance with our well-researched content. Assignment Helper ensure originality, accuracy, and...View and Download
Introduction to Burberry's Marketing Strategy Assignment Marketing is one of the most important factors for any company,...View and Download
Introduction: Mastering People Management for Organisational Growth The Managing People at Tesco Assignment explores the...View and Download
Introduction - Cross-Cultural Management and Leadership Challenges Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for...View and Download
Introduction The goal of this project is to show the design, implementation and testing of a sequential digital circuit to...View and Download
Introduction - Principles & Practices of Marketing Assignment Sample Marketing Principles refers to techniques and...View and Download
