+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
5CO02 Evidence-Based Practice emphasizes making informed, effective decisions by rigorously applying tested evidence and critical analysis within organizational and HR contexts. This assignment explores methodologies and tools that improve decision quality and enhance organizational outcomes, ensuring fairness, efficiency, and innovation. For students seeking support, Assignment Helper UK for students offers expert guidance to excel in this complex subject.
5CO02 Evidence-Based Practice involves integrating the best available research, professional expertise, and stakeholder values to guide decisions. This approach improves HR strategies by reducing bias, increasing transparency, and focusing on data-driven talent management, engagement, and retention. Challenges include costs and limited evidence availability.
Evidence-based practice is making decisions with the explicit, conscientious, as well as judicious use of the accessible evidence from the range of sources, which enhances the likelihood of outcomes (Benevene and Buonomo, 2020). People professionals play a crucial role in making workplace decisions as well as need to analyse the work to impact organizational outcomes for the better. Evidence-based practice assists in making more efficient decisions by selecting trustworthy solutions, reliable and less dependent on the outdated received fads and quick fixes. This is about improving the decision-making by using well-researched, clear as well and evidence-based justification in certain ways.
Evidence-based practice is the systematic use of the available best research with best expertise together with values to guide decision-making and improve outcomes. It promotes a culture of informed decision-making within the organization. It is about developing as well as fostering the best practice and critically considering the real data and evidence regarding the challenges using subjective opinions (Falletta and Combs, 2020). Evidence-based practice (EBP) signifies the systematic procedure in which decisions are made using the available evidence accessible.
The evidence-based practice has a positive impact on the organization, which influences the range of aspects of the strategy and operations. Decisions based upon evidence reduce biases and enhance fairness which leads to more efficient HR practices. This results in better talent management as well as employee relations which influence organizational efficiency. By using evidence to analyse as well as handle employees’ requirements, organizations can develop more efficient engagement strategies. This leads to high employee satisfaction, enhances productivity as well as reduces turnover.
Evidence based approach lead to efficient retention, recruitment as well as development strategies. This makes sure the organization retains and attracts the top talent which is significant for a competitive edge (McCartney et al, 2021). However, adopting evidence-based practice is quite costly as it requires significant resources such as time, money and expertise. In order for an organisation to implement evidence-based practice, it needs to invest in training staff , acquiring access to research databases, evaluating and integrating the evidence required to practice. This is a challenge to organisations with limited budgets.
In addition, in some cases, there is limited or outdated evidence especially in fields where research is sparse. This makes it hard for the organisation to find applicable evidence to support the decision-making process.
Evidence based practice has various approaches like;
Critical thinking which enhances decision making since it encourages individuals to analyze data and information objectively and evaluate its relevance and reliability. This enables them to make informed decisions based on evidence rather than assumption.
However, critical thinking is time wasting as it requires time and effort to obtain critical thinking skills, practicing analysing information, evaluating different data arguments. This is a challenge in environments where quick decisions are often required.
Rationale model approach helps in making structured decisions as it provides a structured approach by drawing analogies to previous successful cases and principles. This helps in organizing thoughts and systematically evaluating available options.
The downside of rationale approach is that there is confirmation bias since there is a risk of selectively choosing analogies that support a desired outcome while disregarding those that may challenge the decision and this may lead to potential errors in judgement.
How evidence based practice used:
In an organization facing high absence rates, critical thinking can be used to identify the root cause instead of assuming reasons such as falling sick. This may involve analysing data to identify patterns and potential causes of absenteeism. For example, examining employee feedback, health records as well as work distribution.
In an organisation experiencing shortage of skilled employees, the rationale model can be used in analogical reasoning where HR managers look at past instances where the organisation addressed shortages in skills successfully. They can draw analogies and examples from those situations to address current challenges, identifying recruitment and skill development initiatives.
SWOT analysis comprises strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. This is a framework for matching organizational programmes, goals and capabilities to the atmosphere in which it operates. Strengths are positive intangible and tangible attributes which are considered as internal to the firm and are within the organizational control. Weaknesses are internal factors which are not in the control of organization that distract from the company’s capability to attain desired objectives. Opportunities are external attractive factors which represent the organization to develop and exist. Threats include external factors which are beyond the organizational control that can place the organization operation or mission at risk (Kulik and Perry, 2023). For instance, in people professional strengths and weaknesses are related with the people skills, internal HR procedures as well as workforce capabilities. Threats and opportunities tend to revolve around external labour market conditions, advancement in HR technology as well as regulatory changes.
SWOT analysis helps organisations obtain a comprehensive assessment of compliance as it begins by identifying internal strengths of the organisation related to current compliance practices. For example an organisation may have robust internal policies and procedures in place that ensure compliance to existing legislation rules.
In terms of weaknesses, SWOT analysis enables an organisation identify its gaps and limitations in terms of compliance due to following outdated process or lack of resources for regular updates. On the downside, it can lead to subjectivity in interpretation of legislative impacts since assessments can be influenced by individual perspectives and biases which potentially leads to incomplete and biased conclusions.
Interviews play a vital role in the procedure of understanding the human experiences as well as behaviours. These conversations are personal which uncover the individual perspectives, experience as well as emotions..
In terms of legislation, interviews allow for a deep exploration of complex organisation issues . They provide room for interviewees such as stakeholders, employees to provide detailed examples and contextual insights that quantitative methods may miss out in capturing. For example, interviews capture how new legislation impacts organisation operations and the specific challenges faced by individuals, different departments and where implementation gaps exist.
However, interviews have limited generalizability as findings from interviews may not represent the entire organisation as some responses are based on individual perspectives. For example, a manager’s view on a legislative impact maybe positive and may differ significantly from those of frontline employees who experience daily compliance tasks and perceive legislative impacts negatively.
Critical thinking is referred to as a discipline of skilfully and rigorously using experience, information, reasoning and observation to guide actions, decisions as well as beliefs. Critical thinking poses a set of key characteristics which helps in question information as well as own thinking. Being able to analyse the information is the most significant aspect of critical thinking. This signifies gathering the information as well as interpreting it to evaluate the information (Ybema et al, 2020).
It involves a set of principles and skills that enable individuals to objectively analyse, evaluate and interpret information to reach reasoned conclusions. One of the fundamental principles is objective and rational thinking which aims to minimize the influence of bias.
Rational thinking involves using logical reasoning and sound judgment to evaluate arguments and make informed decisions. It focuses on understanding underlying reasons and evidence supporting claims rather than based on one’s claims.
Contextual understanding is another principle of critical thinking and it considers the broader context in which information is presented and decisions made. It involves recognizing how structural forces, background information and external influences impact the interpretation and validity of arguments,
Principle to apply to own ideas
Intellectual humility: This involves recognizing the limits of my own knowledge and ideas and expertise that is learn to actively distinguish what one knows from what one doesn’t know. It encourages a willingness to learn from others, acknowledging mistakes and remaining open to improvement.
I can apply intellectual humility to my own ideas by accepting feedback both positive and negative , admitting when you don’t know something or missed out a viewpoint , evidence and seeking opportunity for learning from others. This helps in refining my ideas and expanding understanding.
Applying to others ideas
Objectivity: This requires approaching other people’s ideas without personal bias or emotional attachment. It involves evaluating arguments based on merit and considering evidence and logical thinking rather than personal judgement and points.
When evaluating ideas from other individuals, be objective and focus on the strength of their evidence and logical reasoning plus validity of their conclusion. Avoid dismissing other people’s ideas without a strong logical disagreement or based on personal opinions.
The decision-making process is the series of the steps individuals take to analyse the best alternative to handle specific issues.
Rationale decision-making: This model of decision-making uses logical steps to choose the best solution. Rational decision-making involves a structured approach where decisions are made through logical analysis and objective evaluation of information (Smith, 2022). This process typically includes problem identification, information gathering, and evaluation of alternatives to select the option that best aligns with the decision-maker's goals (Johnson & Lee, 2021). Intent reference in this context means aligning decisions with broader strategic objectives, ensuring that choices support long-term aims rather than just immediate outcomes (Brown, 2023).
Steps include:
Identifying the problem/ decision to be made: This is the first step and it involves clearly defining the problem or decision that needs to be addressed. It sets the foundation for decision making process. This helps avoid addressing symptom since it addresses the root cause.
Gathering relevant information: this requires gathering comprehensive and relevant information to the problem. It may involve data collection, research and consultation with experts. This enables decision makers make informed assessments and consider all factors before coming up with a solution.
Identifying alternatives: here, decision makers identify possible alternatives to address the problem. This helps decision maker’s increase the likelihood of identifying innovative solutions and selecting most suitable solution.
Evaluating alternatives: Each identified alternative is evaluated based on predetermined criteria such as feasibility and cost effectiveness. This enables decision makers to effectively assess strength and weakness of each alternative and also in selecting the best alternative.
Making the decision: here, decision makers choose an option that offers highest probability of achieving desired outcomes based on the analysis conducted.
Implementing the decision: this involves putting the chosen decision into action. It involves developing an action plan, allocating resources. This ensures decision is executed effectively and efficiently.
Monitoring and evaluating the decision: decision makers monitor outcomes to ensure and assess the effectiveness of the decision. This involves comparing actual results with expected outcomes and making any necessary adjustments.
Vroom-Yetton decision model: This is a critical process to make the decision tree which allows leaders to make the specific decisions. While taking decisions it is significant to have the procedure which includes adequate stakeholders. Team commitment enhances the quality of the decisions and is likely to offer the successful result faster. Time constraints include more space to research in option and include others which assist in boosting the quality of the decisions (SELVARAJ and Santhi, 2023).
Autocratic: leader makes decision alone without consulting others.
Consultative: has two parts that is;
C1, here, leader gathers information from individuals one on one and makes the decision alone.
C2, leader shares problem with individuals one on one and solicits what they think and makes the decision alone.
Group: this has three parts which are,
G1,where the leader delegates decision making to the group and takes control over the final decision.
G3,where the leader shares information with the group , facilitates group discussion and makes decision alone.
G2 where leader shares problem with the group, gathers there ideas and makes decision alone.
How it ensure effective outcomes:
Tailoring decision making styles, this helps leaders select the most appropriate decision making style based on situational factors such as time constraints and commitment from team members. For example, complex decisions may benefit from participative styles such as consultative and group discussions so as to gain various ideas from team members while routine decisions can benefit from autocratic since they don’t require discussion.
Enhancing team commitment and enabling team members buy the idea: involving team members in the decision making process increases their commitment and buying the final decision. Team members are most likely to support and implement decisions where they feel their voices are heard and valued.
Ethical decision making provides a bedrock which successful leaders build in their organization, promote integrity, trust as well as long term sustainability. When people professionals make ethical decisions demonstrate their commitment to integrity as well as gain trust of customer, employees and stakeholders.
Utilitarianism signifies an ethical theory which determines the rights by emphasizing on outcomes. It is summarized as the greatest good for the greatest number. This holds as a most ethical choice which favours the greatest number. However, this theory does not predict the future consequences of the actions.
Decisions based on the utilitarianism principle focus on the benefit for the majority of stakeholders and employees. HR professionals implement a diversity and inclusion environment which provides employees to feel respected and accepted despite their differences. This helps in building trust among management and employees (Cullen et al, 2022). This creates a supportive and welcoming workplace which positively influences employee morale.
On the other hand, Utilitarianism has a short term focus and this might encourage decisions that prioritise immediate benefits for the majority which neglects long term sustainability and the wellbeing of minority groups within the organisation.
Deontological ethics is an action which is considered ethically better because of some traits. This act is morally obligatory in spite of the consequences for human welfare. This offers a clear structure for making ethical decisions on the basis of established principles. For instance, Organization needs to establish practices and policies which promote equality, fairness as well as diversity (Gurusinghe et al, 2021)..
On the downside, deontology ethics cause conflict of duties and rules making it hard and challenging to determine the best outcome. This leads to difficulty in decision making as leaders are confused about what to use.
Financial performance: ROI
Return on investment assists in evaluating the efficiency of practice, programs and initiatives aim to optimize the workforce as well as enhance organizational performance. Embracing an ROI is significant for the HR professionals to analyse their strategic value from stakeholders. This allows organizations to take informed decisions, drive sustainable success as well as optimize resource allocation (Benevene et al, 2021).
ROI is easily comparable amongst various investments and organisation projects regardless of the scale of operation since it is expressed as a percentage and it is a standardized measure of performance. This helps in evaluating and ranking investment opportunities based on their performance and profitability.
On the downside, ROI ignores potential investment risks as it measures profitability and doesn’t account for the risk associated with the investment. For example, a high ROI may reflect at times a high risk on the investment and this does not come with the calculation.
Non-financial performance: employee engagement surveys
These are designed to assess and measure the engagement and motivation within employees to perform their best. This tool is used by the organization to measure emotional satisfaction and commitment of workers. This helps in assessing the way workers feel about their team, work and overall company. Anonymity motivates workers to offer honest feedback with no fear of repercussions. These insights enable management to make informed decisions. Engagement survey responses rate enhance employees to feel that their feedback is valued, better engagement survey questions handle the range of aspects of the work environment which provide job satisfaction to leadership efficiency. Engaged employees are passionate regarding their work, encouraged to enhance productivity as well as align with organizational objectives and values (Cantarelli et al, 2020).
Employee engagement surveys also have a downside of limited action ability that is they reveal engagement and motivation levels of employees but don’t provide specific solutions to address issues negatively affecting employees.
Strategic HR plays a significant role in changing visions into actions. Strategic HR puts emphasis on crafting the recruitment and selection procedure which identifies candidates with specific skills which create the engaging employee experience which promotes loyalty as well as reduces turnover (Ferrara et al, 2022). Setting clear expectations, offering regular feedbacks, coaching and rewarding high performance are significant elements.
People practices also drive innovation and adaptability within the organisation. They foster an environment that promotes innovation and new ideas through creating processes that support generation of new ideas and collaborating them to the existing ideas and this enables organisations to respond to market change and emerging technology. For example they promote a culture that values creativity and provide platforms for employees to contribute ideas such as innovation workshops or idea sharing platforms which stimulate new solutions and improvements. (Amabile, 1996)
Employee performance metric: This is a key to track the way employees carry out their job. HR professionals must have methods to measure the efficiency as well as productivity of the employees. Monitoring employees’ performance helps in benefiting both employees and organization (Vulpen, 2024). Efficient performance management motivates the employees, promotes accountability as well as drives in a performance oriented culture.
Employee turnover rate: This is a significant workforce management metric which offer insight in employees’ satisfaction and engagement. High turnover rates can indicate issues with the organization management practices, culture as well as employee satisfaction. By measuring performance, companies can recognize employees at the risk of leaving as well as offer target support to assist them in enhancing their engagement as well as performance.
Conclusion
By summing up, it has been assessed that decisions based on solid evidence reduce biases and enhance fairness which leads to efficient HR practices. This results in better employee relations as well as talent management which directly influences organizational efficiency. The key opportunities of leveraging the HR analytics have the ability to recognize as well as handle workforce trends. By evaluating data on employee’s engagement, performance metrics as well as turnover rates can identify the trends and patterns which influence their staff as well as business operations.
Interpreting employee performance and feedback data aligns with 5CO02 Evidence-Based Practice principles, promoting fair reward systems and improving manager-employee relations. Recommendations include conducting monthly reviews and motivating employees through equitable incentives, all supported by systematic data analysis to ensure continual organizational improvement.
Table 1:
First quarter
| Name of departments | Total employees | Outstanding | In % | meet the individual KP) | In % | Not quite there yet | In % | Under performing | In % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
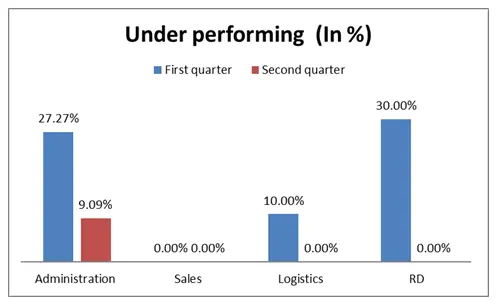
| Administration | 11 | 2 | 18.18% | 2 | 18.18% | 3 | 27.27% | 3 | 27.27% |
| Sales | 13 | 0 | 0.00% | 13 | 100.00% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
| Logistics | 20 | 4 | 20.00% | 8 | 40.00% | 6 | 30.00% | 2 | 10.00% |
| RD | 10 | 3 | 30.00% | 3 | 30.00% | 1 | 10.00% | 3 | 30.00% |
Second quarter
| Name of departments | Total employees | Outstanding | In % | meet the individual KP) | In % | Not quite there yet | In % | Under performing | In % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administration | 11 | 1 | 9.09% | 4 | 36.36% | 4 | 36.36% | 1 | 9.09% |
| Sales | 13 | 0 | 0.00% | 13 | 100.00% | 0 | 0.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
| Logistics | 20 | 5 | 25.00% | 9 | 45.00% | 4 | 20.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
| RD | 10 | 5 | 50.00% | 3 | 30.00% | 1 | 10.00% | 0 | 0.00% |
Table 1.2: Bonus
| Team | Employee Name | Salary | Bonus payment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administration | Robin Bird | £31,500.00 | £1,260.00 |
| Saffron Finch | £24,000.00 | £1,920.00 | |
| Logistic | Ruth Sixsmith | £23,750.00 | £950.00 |
| Wendy Boot | £23,750.00 | £950.00 | |
| Sally Rigbye | £23,750.00 | £950.00 | |
| Jean Livesey | £26,000.00 | £1,040.00 | |
| Julie Chisnall | £19,500.00 | £1,560.00 | |
| Rick Lovall | £19,500.00 | £780.00 | |
| Gill Jamieson | £19,500.00 | £1,560.00 | |
| RD | Ethan Brar | £32,500.00 | £2,600.00 |
| Harrison Briggs | £32,500.00 | £1,300.00 | |
| Steve Owens | £29,500.00 | £1,180.00 | |
| Tasha Graham | £29,500.00 | £2,360.00 | |
| Jennifer Frost | £29,500.00 | £2,360.00 | |
| Total | £20770 |
From the table 1.1, it is clear that within quarter 1, the performance was low and till quarter 2 the performance slightly increased. This simply means that the working of the company is improving after the first quarter. According to the department, all the departments have shown an increase in outstanding performance as compared to the previous quarter.
Referring the table 1.2, it can be stated that there are a total of 14 employees who have availed of the bonus out of a total of 54 employees. According to the criteria people falling in the category of outstanding will be getting the bonus and according to this, only 14 people availed the benefit of the bonus. From these 14 as well some people earned a bonus in only quarter 1 and some in quarter 2 only. But out of these 14, 6 employees were those who earned bonus on both the quarters. This implies the performance of the employees is increasing which is good for the company and its growth.
Data from Table 2
_68a84a4d04460.webp)
With the analysis of the line managers' view, it is clear that the majority of the managers feel confident during performance appraisal. Also, the majority of them stated that they are not good at providing feedback and agree with the set performance targets.
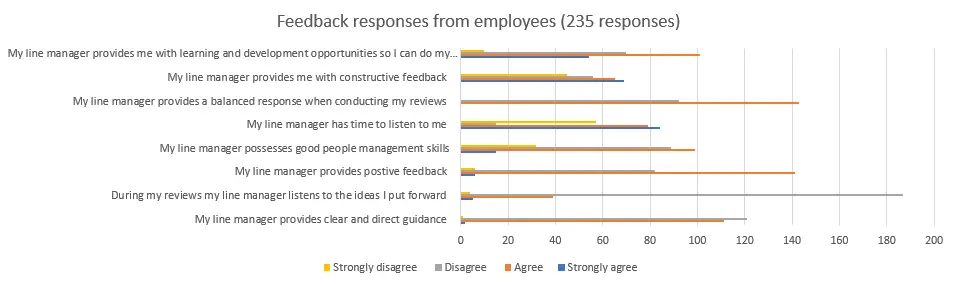
From the responses of the employees, it is clear that the majority of the employees disagree that the line manager provides clear guidance. Also maximum of them agree that the line manager provides positive feedback. Also, it was agreed that the line manager is providing good learning development opportunities for better growth of employees.
Different graphs
Comparing outstanding between both quarters
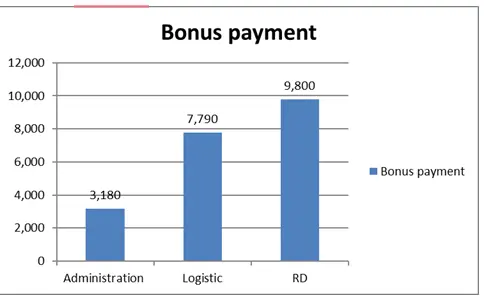
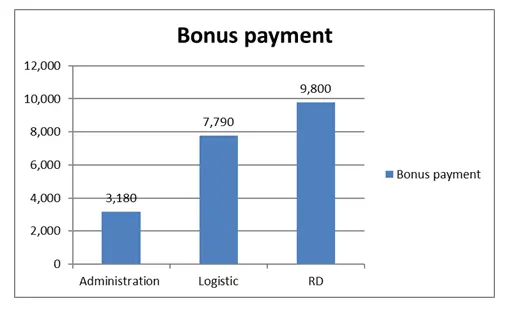
With the help of the above charts, it is clear that RD it the department which is having the highest payment for the bonus. After that comes the logistics and administration department. With this it can be stated that, when some motivation is provided to the employees then the working capability is increased and they are motivated to work well. Only the sales department is the one which is not having any of the outstanding performance and company need to try to improve it well. In case they will also be motivated to perform well then it will be assistive to the company in managing and improving the overall performance.
Table 2
Further, with Table 2, it is clear that there is a friendly relationship present between the manager and the employees. This is due to the reason that both the managers and the employees have provided positive feedback to one another (Staniec and Kalińska-Kula, 2021). This simply means that the overall working is improved and better.
By the analysis of the two tables the following recommendation is provided to the company which are as follows-
References
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Books and Journals
Online
Bibliography
1.0 Introduction to Math And English Attainment In Primary School Dissertation 1.1 Background Comparing education-related...View and Download
Introduction: TEM403 Understanding the Tourism and Event Sectors Tourism industry is termed to the activities based on the...View and Download
Introduction to the Swiss Banking Industry's Approach to Climate Change Assignment Climate change has been regarded as most...View and Download
1. Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking Online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction to Writing as a Professional Assignment The book which is chosen and will be reviewed in this assignment...View and Download
1. Introduction - Epidemiology of Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases Assignment Sample Tuberculosis (TB) is an...View and Download
