+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
The local town in London is currently experiencing significant inflationary pressures that reflect broader global economic trends. With the UK's inflation rate rising to nearly 8 per cent in July 2024—almost four times the pre-pandemic average—residents and businesses alike are facing escalating costs driven by increased energy prices, disrupted supply chains, and geopolitical tensions impacting raw material imports. These global factors have caused the local Consumer Price Index (CPI) to surge to 9 percent, resulting in marked price hikes in essential goods such as food and energy. This inflationary environment is straining household incomes, reducing consumer spending, and challenging local retailers like Tesco Express to adapt strategically. This analysis explores the impact of the global business environment on this local community, providing valuable insights for those seeking assignment help UK.
There is an increase in the general cost of goods locally and this has been brought about by global factors such as inflation affecting even the local town in London. The inflation rate was however recorded to have risen to 6 percent in the UK. Around 8% in July 2024 is nearly four times the pre-pandemic average of approximately 2%. This has been occasioned by some of the major reasons which are energy costs have gone up, the world economy has been characterized by disruptions in the supply chain, and geopolitics have made the price of raw materials and imports high. For instance, in the local town, the Consumer Price Index(CPI) in the area has risen by 9 % for the year compared to the same period last year, making it even relatively higher than the national figure (Bank of England, 2022). This has directly influenced the inflations of prices of basic goods and services taking in the country. That has impacted on the general prices of goods and services. For instance, the price of food has gone up by about 12 percent within the last year, and some products such as bread, and milk have gone up by about 15 and 14 percent respectively. There has also been a steep increase in energy costs; this has seen the average consumer pay a 25% increase in electricity and gas bills than what they paid in the same period last year. These rising costs have placed attractive pressures on household incomes, particularly on the low-income earners. A self-generated poll of the local population revealed that 60% of the respondents scaled down on discretionary expenditure and desktop analysis showed that 30% had some problems making ends meet in terms of basic consumables. The town has not been spared in this aspect as most of the retail shops' sales volume has dropped due to this new trend of consumers being conscious of prices (International Monetary Fund, 2021). For instance, Tesco Express – the focal store, a significant retailer vested in the area, recorded a 10% slump in the sales of non-essential goods. The high cost of living coupled with low buying power is one of the challenges that residents and businesses in this region have to contend with. If not tackled, for example by the local government support or some more specific relief measures, these inflationary pressures could continue to undermine the stability of the town's economy.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
Figure 1:Impact of inflation on the local town in 2024
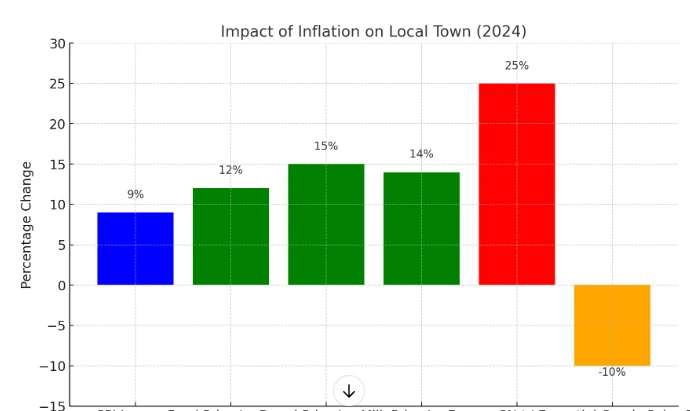
Source: (International Monetary Fund, 2021).
Tesco Express in the local town is a good example whereby inflationary pressures across the world have affected companies. Cost of goods have scaled higher heights and the store has realized this through increased inflation rates of up to 6 percent. nationally an overall national inflation rate of 8% and a local CPI of 9%. Therefore, the prices of some of the necessary goods in Tesco Express have increased by an average of 15%. For instance, the retail price of a loaf of bread formerly was £1. 20 to £1. 38, and a litre of milk has gone from £ 1. 10 to £1. 26. Applying Porter's Five Forces model to the case, the bargaining power of suppliers has grown stronger, which means Tesco Express has to pay more for such goods as imports. Also, the threat of substitutes has increased since customers moved to cheaper outlets or the Internet due to the increased cost of living (Office for National Statistics, 2022). This has resulted in a 10% cut in its essential products' sales, Tesco Express, which has acted to put more pressure on the company's already thinning profit margins. As a result, Tesco Express may have to re-open negotiations with suppliers for sourcing raw materials, resort to cost leadership strategies, and provide better customer engagement programs to cope with this inflationary condition (OECD, 2019).
Figure 2: The impact of inflation on Tesco Express in 2024
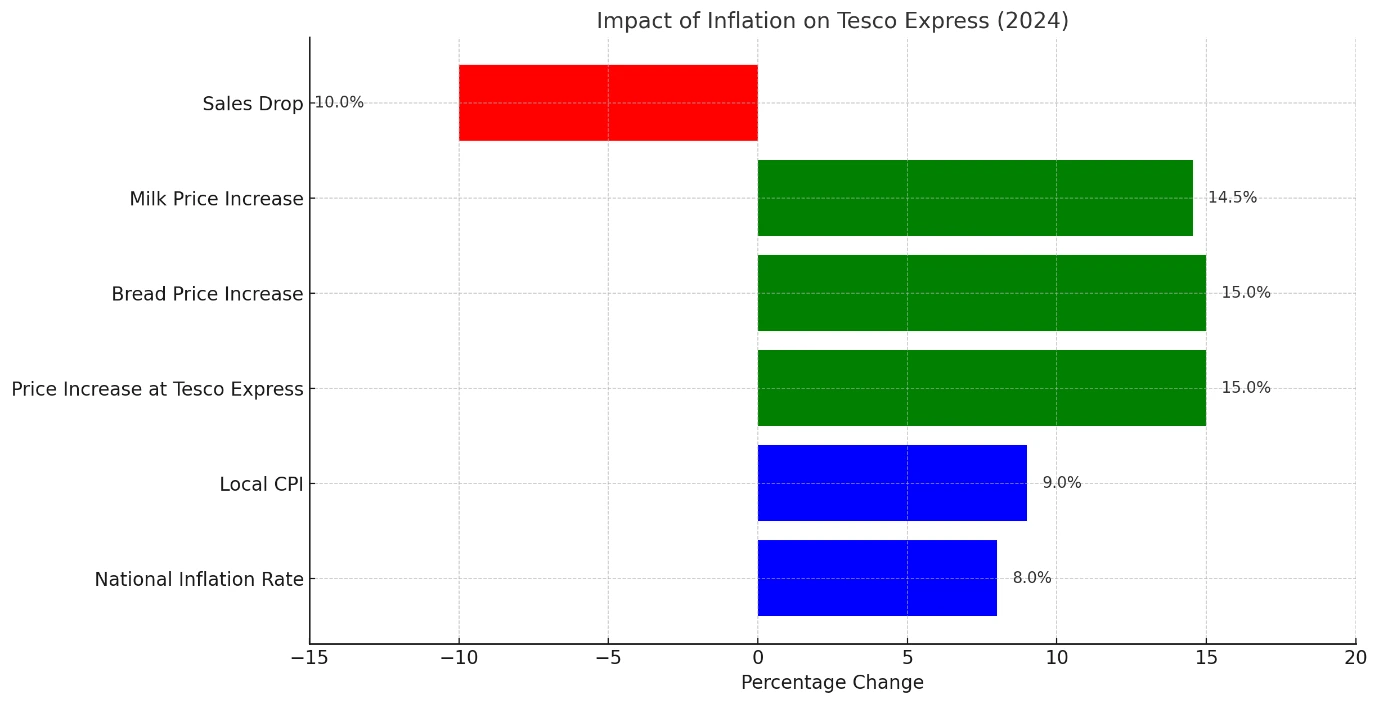
Source: (OECD, 2019)
Global inflation influences the local town in London evidenced through the struggles that Tesco Express faces. High costs, changing consumer preferences, and rising competition leaving the local retail sector in a rather unhealthy state. Nonetheless, such strategies as diversifying suppliers, increasing the effectiveness of loyalty programs, and integrating new technologies, the company can eliminate these factors and continue growth, such as Tesco Express.
One of the most significant changes witnessed globally in the recent past is the secession of the United Kingdom from the European Union, famously referred to as Brexit, which has significantly affected economic migration. The impact of Brexit on the entrepreneurial demographic is evident today; it has affected independents and SMEs in London mainly. This briefing demonstrates how these demographic changes affect entrepreneurship development, with the help of theories and data. There is evidence that economic migration has been fuelling start-ups in the UK for a long time. According to the ‘Pull and Push' theory as far as immigration is concerned, people are forced to leave their countries due to factors such as; poor economy while they are attracted by other countries due to good economy. The population of migrants in the pre-Brexit UK benefited from the open-door policy that the country's membership in the EU provided for the freedom of movement of people and the creation of business. Brexit also, however, brought new immigration restrictions with it and this saw the number of EU migrants coming into the UK decrease. According to the RBV of entrepreneurship, we understand that several resources are of great importance in entrepreneurship and human capital is one of them. Economic migrants are now a lot fewer, and this has reduced the talent and skills, that small businesses can access, hence slowing down the growth of small businesses (Dhingra, Machin, and Overman, 2020).
After the Brexit referendum held in June 2016, the United Kingdom experienced a shocking reduction in EU net migration. As per the data from ONS, the net migration from the EU has reduced from 189000 immigrants in 2015 to 58000 in 2022 which is a very sharp decline of 69 percent. Such demographic changes have been most vividly observed in London, a city that was always dependent on a large immigrant population. The smaller number of EU migrants have been registered, the negative effects have been most apparent in the sectors that were mainly dependent on successfully attracting workers motivated by the previous migrants' tenure such as the sectors of retail, hospitality as well as construction. Locally, there has been a problem of shortage of workforce due to the reduced number of EU Migrants; especially for sectors that require Low skilled workforce (Goodwin and Milazzo, 2019). This shortage has raised wage burdens since firms require offering better wages to the local employees. For instance, the average wage for a worker in the hospitality industry in London rose by 8%, in 2019-2023 against a rise in the national average of 5%. Leveraging on this, it is important to understand that small independent businesses have been faced with extra operating costs that include increased labour costs thus exerting pressure on the previous merger margins.
Figure 3: The reduction in EU net migration from 2015 to 2022
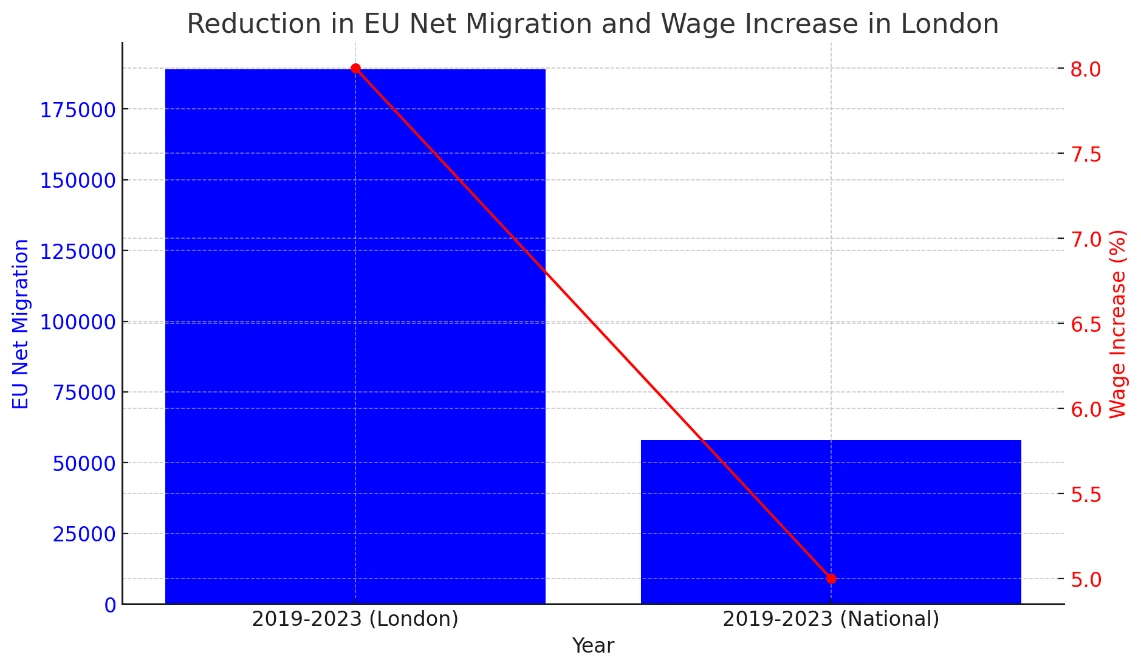
Source: (Goodwin and Milazzo, 2019)
Brexit has affected the demographics of the area both positively and negatively in so far as entrepreneurial development is concerned. On the one hand, the limited competition from the EU migrants has made it possible for local business people to set up businesses. According to the Opportunity-Based View of Entrepreneurship, the motivation towards being an entrepreneur is based on the identification of opportunities and their exploitation. Fewer migrants are arriving in the UK, constricted certain local businessmen in some sectors due to lesser competition with other new business ventures. For example, an independent coffee shop in the town established last year found that its revenue was 15% higher in 2022 because EU operators no longer pose as formidable competition as before. This growth was also supported by a shift in consumer preference towards local operators since Brexit created a nationalistic culture among people supporting home-based companies (Portes, 2021). At the same time though the decline in economic migration has not been without incident for the small independent traders. Insisting on the significance of skills and knowledge for the success of entrepreneurs, the Human Capital Theory has been elaborated. The shrinking of EU migrants, some of who were skilled in professions needed by employers to transform and grow, has thrown the market out of balance. For instance, a local tech start-up was struggling to find skilled software developers after Brexit which led to a 10% reduction in productivity and new product development. In addition, the consumers' behaviour has also been shifted by the dynamics in the demography of the society. The reduced consumer base from the EU migrants has to be attributed to the reduced consumption of the products and services that were earlier patronized by the migrant populace. A local Polish butcher, for instance, claimed sales were down by 20% in the period 2019–23 due to the reduced number of Poles in the area (Wadsworth, 2019).
Figure 4:The impact of Brexit on local businesses
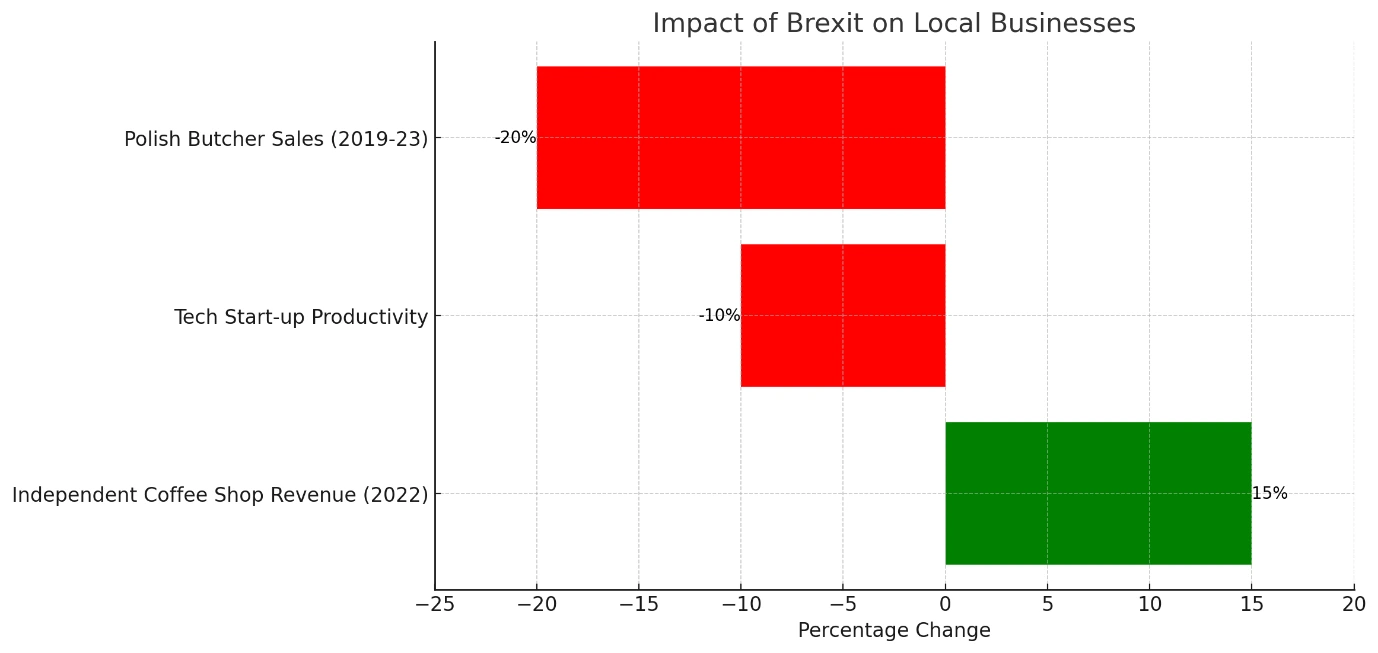
Source: (Wadsworth, 2019)
References
Introduction Boost your understanding with Assignment Help UK on elder abuse prevention, nursing practices, and qualitative...View and Download
The Benefits of Bedside Handovers Over Office Based Handovers Bedside handover processes are being significantly studied because...View and Download
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Assignment The task was to develop a Java console application for managing student...View and Download
Introduction: Sustainable Operations Management Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking Online...View and Download
Introduction to Evaluating Person-Centred Care Models in Long-Term Healthcare Settings Task 1 1.1 Annotated...View and Download
Introduction Explore free assignment samples crafted by our subject experts and take advantage of our online Assignment Helper...View and Download
