+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Cells are the fundamental units of life, forming the basis of all living organisms. They carry out essential functions such as energy production, protein synthesis, and reproduction, which are vital for the survival of organisms. Understanding the structure and function of different types of cells is crucial for studying biology and medicine. For students who wants proper guidance on these concepts, assignment help in UK can provide valuable support in explaining complex topics clearly and effectively. This assignment explores the characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, their organelles, cellular processes, and applications in medicine.
AC 1.1: Compare the structure and function of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells
| Feature | Bactrim (Prokaryotic) | Plant Cell (Eukaryotic) | Animal Cell (Eukaryotic) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent, DNA in Cytoplasm | Present, membrane-bound | Present, membrane-bound |
| Cell Membrane | Present | Present | Present |
| Cell wall | Present (Peptidoglycan) | Present (cellulose) | Absent |
| Organelles | No membrane- bound organelles | Membrane - bound organelles | Membrane -bound organelles |
| Ribosomes | Present (Smaller size) | Present (Larger size) | Present (Larger size) |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present | Present |
| Chloroplasts | Absent | Present (for photosynthesis) | Absent |
| Shape | Typically Spherical or rod-shaped | Rectangular, rigid | Irregular, flexible |
| Size | Generally smaller (1-10 µm) | Larger (10-100 µm) | Larger (10-30 µm) |
| The function | Reproduction, Digestion, The production of energy, Metabolism, Protein synthesis, Respiration | Energy production, Homeostasis, and cell structure support the plant-cell, Cell- to cell interaction, Protection, food production | Maintain homeostasis, regulate cell metabolism, and replication, form networks in organisms, produce energy |
Table 1: Comparing bacteria, plant, and animal cells
AC 1.2: Describe the subcellular structure of eukaryotic cells
The organelle is a small part of a cell and like all cells there are many with various functions to allow for the survival and functionality of the cell (Sies et al. 2022). Therefore, there are three important organelles, which include mitochondria, ribosome and nucleus. Below is a list of all the structures illustrated as well as how they are directly related to their functions;
Mitochondria (Energy Production)
The organelle frequently referred to as the “powerhouse” of the cell is characterized to be the mitochondria. These are of the bean shape, and contain two membrane layers. For instance, this inner membrane has folds known as cristae in order to expand the area where biochemical occurrences are able to take place. Aerobic respiration, the process of producing ATP, the cellular transport molecule is produced through one of the several organelles in cells, known as mitochondria (Hameed et al. 2021). Released through metabolic breakdown of food, nutrients like glucose, in the mitochondria are changed into ATP which drives all macromolecular synthesis, muscle contractions, and active transport against electricity gradients through biological membranes.
Ribosomes (Protein Synthesis)
Ribosomes are small RNA and protein structures which are present in the cytoplasm and in some cases, located close to the endoplasmic reticulum known as rough endoplasmic reticulum. Another important role of ribosomes is translation in which a molecule of messenger RNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids to build proteins required for structure, function, and regulation of a cell. Since ribosomes are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, then special attention should be given to the fact that ribosomes are of significant importance for sustaining cellular processes.
Nucleus (Cell Control Center)
Nucleus is considered as the control center of the cell and it is usually situated in middle of the eukaryotic cell. It contains a nuclear membranes which is a double membrane which serves to regulate transport of molecules in the nucleus and out of it. The nucleus holds the chromatin which is responsible for storing the genetic details that is required for the new formation or reproduction of cells and the working of cells (Le Mercier et al. 2022). The nucleolus is a part of cell nucleus, which is involved in the production of ribosomal RNA that forms the molecule tagged as ribosome. The nucleus controls gene and protein as well as other molecules synthesis related to the cellular activities.
AC 1.3: Explain the function of each organelle of eukaryotic cells.
Erythrocyte: Red Blood Cell
Erythrocyte or red blood cell (RBC’s) stands as one of the most specialized cells of the body. It is said to mainly be for the “transportation of oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs”(Fefilova et al. 2022). For this purpose, it is imperative that such a cell is designed to have a structure that enables it to work.
Structure and function
The erythrocyte is a biconcave disc shape to provide the largest surface area for the exchange of gases. It enable oxygen and carbon dioxide to cross through the cell membrane more easily.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
For example, erythrocytes lack nucleus and other cell organelles to allow for quarter of cell volume for hemoglobin the protein that has ability to bind to oxygen. This absence also make the cell adaptable since it can pass through the narrowest capillaries without any issue.
Erythrocytes contains in its cytoplasm, hemoglobin the protein which binds to oxygen in the lungs and releases it in the tissues with low rate of oxygenation. This is because it has the capacity to transport a great deal of oxygen as compared to its size.
The cell membrane is very elastic and permeable which enables a change of shape when needed for instance, when erythrocytes must pass through narrow blood vessels in order to continue delivering oxygen to other parts of the body.
Such structural adaptations facilitate the performance of this role in oxygen transport by erythrocytes effectively and efficiently.
AC 2.1: Explain the regulation of the movement of substances by the cell membrane.
_6933d0c701e4f.webp)
Figure 1: Plasma membrane diagram label (A-E)
A: Transmembrane protein
B: Phospholipid Head
C: Channel Potein
D: Cholesterol
E: Periperal Protein
The following substances pass through
Phospholipid Head (pass between phospholipids)
Phospholipid Head (pass between phospholipids)
Transmembrane protein (via assisted transport)
Transmembrane protein (via active transport)
Channel Protein (through aquaporin’s)
Channel Protein (through specific ion channels)
Explanation of cell membrane structure and functions
The plasma membrane is a semi permeable barrier that controls movement of molecules form one place to another with a view of maintaining a steady state (Gralnick and Bond, 2023). It will transport ions and small proteins by forming a phosphollipin layer with cholesterol included in the middle.
A: Transmembrane protein
It has a helical structure that spans the membrane and helps to transport ions across the membrane and in signal transduction.
B: Phospholipid Head
There is hydrophilic group which faces outside and interacts with water.
C: Channel Potein
These forms bridges that allow for passive transport of ions and molecules to happen
D: Cholesterol
This also ensures that the membrane does not get rigid.
E: Periperal Protein
It attached to the membrane for structural support or cell signaling.
AC 2.2: Explain how animal cells use nutrients to promote cellular functions.
Transport mechanisms: Comparison of water vs oxygen movement
This explains that the water in the body moves across the alveoli membrane through osmosis since they possess a polar nature passing through the aquaporin channel proteins (Wu et al. 2023). The oxygen is a small moleculae that is nonpolar, free to pass through the phospholipid bilayer through the process of diffusion from an area of high concentration to the area of low concentration.
Na+/K+ transport vs neurotransmitter release
Na⁺/K⁺ ions are transported through sodium-potassium pump and to transport Na⁺ out and K⁺ in, the ATP is needed as an energy source for transporting ions across the membrane so as to maintain the resting membrane potential (Szymoniuk et al. 2022). While neurotransmitters, these molecules are released through a process called exocytosis which implies that they are transported in the synaptic cleft through fusing with the membrane leading to the release of the neurotransmitters into the gap.
AC 2.3: Describe protein synthesis
Stages 1,2,4,6 in enzyme secretion
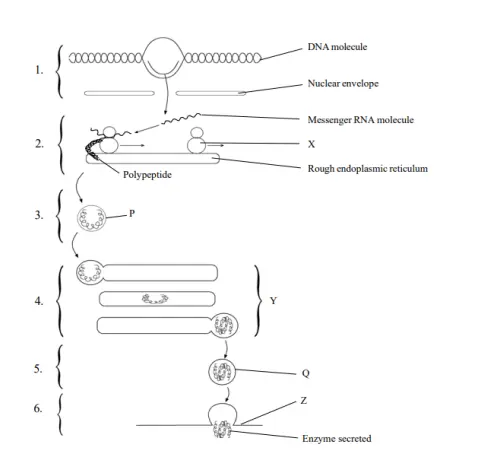
Figure 2: Enzyme Secretion
Identification of structures X, Y, and Z and their function
X (Rough ER)
Synthesis and initial folding of proteins.
Y (Golgi Apparactus)
Functions in modifying, sorting off and packaging of proteins.
Z (Secretory Vescile)
It is involved in the transportation of proteins to the membrane and secreting them. These organelles are interdependent in their roles within the secretory pathway to properly process and secrete proteins.
Comparison of vesicles P and Q
P (Transport Vesicles)
Plasma membrane proteins that transports opportune proteins from the rough ER to the Golgi apparatus where they are not substantially modified.
Q (Secretory Vesicles)
It is used to transport fully processed proteins for their secretion.Both the types of vesicles are also very much involved in the transport of proteins in the cell (Ferrand et al. 2024).
Role of peptide
(i) Peptide synthetase
Peptide synthetase can also be described as the combination of enzymes that is involved in the process of formation of specific peptide bonds during translation stage when amino acids are joined, which provides a proper chain formation in the polypeptide assembly that leads to the synthesis of functional proteins in response to the cellular activities.
(ii) Transfer RNA in polypeptide synthesis:
tRNA is the carrier molecule that brings a specific amino acid to the ribosome during translation is going on (Chen et al. 2023). Each tRNA will have an anticodon that will have to match to a certain codon of the mRNA. In this manner, only the right sequence of amino acids is brought into the assembling polypeptide chain.
AC 2.4: Explain the role of nucleic acids in transcription and translation.
ATP production and respiration
Stages A, B, and C in ATP production
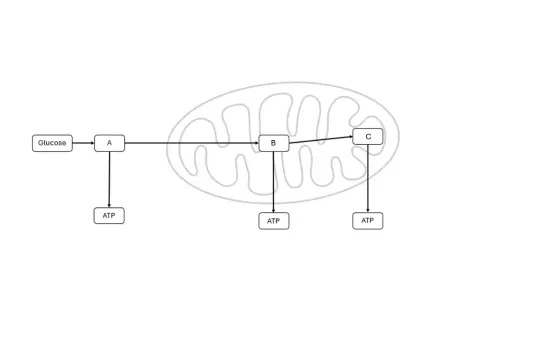
Figure 3: Stages of cellular respiration
A (glycolysis)
B (krebes cycle)
C (Electron transport chain)
Each stage contributes to cellular respiration
A (glycolysis): Occurs in cytoplasm matrix where glucose is divided into two pyruvates for generating two ATP and NADH.
B (Krebs cycle): it is situated at the matrix of mitochondria. It also generates NADH and FADH2, and two ATP are made in the process.
C (Electron transport chain):This residing in the inner Mitochondria’s membrane constructs, establish through chemiosmosis 34 ATP.
AC 3.2 Describe the stages of mitosis, including interphase.
The stages of mitosis
Interphase
The cell makes for division by growing, replicate the DNA.
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes. The formation of spindle fibers starts while the nuclear membrane disintegrates.
Metaphase
Chromosomes also position themselves along the equator of the cell, by the centromere region being connected to spindle fibers.
Anaphase
The two homologous chromosomes split and move towards the two poles of the cell as the centromere of spindle attached to fibers shorten.
Telophase
Chromosomes become less condensed, the nuclear membranes reappear and the spindle fibres disappear.
Cytokinesis
Division occurs in the cytoplasm and results in formation of two similar daughter cells.
The stages of meiosis
A. Meiosis I
Prophase I
Chromosomes begin to thicken and sisters align at the metaphase plate while homologous chromosomes form chiasmata.
Metaphase I
The homologous pairs are located at the equator and connected to the spindle fibers.
Anaphase I
The homologous chromosomes separate and move towards the opposite poles.
Telophase I
Two haploid cells are formed that are half the size of the original sized chromosomes.
B.Meiosis II
Prophase II
Formation of new spindle fibres.Chromosomes re-condense.
Metaphase II
Chromosomes align at the equator.
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids separate.
Telophase II
Four non sister haploid cells are formed which are genetically very distinct.
AC 3.2 Explain how genetic information is preserved and passed to daughter cells during mitosis
Purpose and Function
Mitosis:Mitosis is a process of vegetative or asexual type of cell division that forms two identical daughter cells required for growth, repair or maintenance (Strømme and Mork, 2021). It makes certain that each new cell has a replica of the genes in the parent cell only.
Meiosis:It takes place in gamete production of sperms and ova and is the process of halving genetic materials for the continuity of each succeeding generations.
Numbers of divisions and outcomes
Mitosis: It consiosts of one or a single division process where diploid (2n) cells are formed and are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Meiosis:It is the meiosis is divided into two categories. As these divisions are completed, the four cells are haploid(n) and genetically different due to recombination and independent assortment (Guo et al. 2022).
Genetic variation
Mitosis: Thirty three chromosomes in the somatic cell are evenly distributed in the daughter cell and on separating, no new variation of genetic material is added in the daughter cell through mitosis. In terms of appearance, it is literally the mirror image of the parent.
Meiosis: increase the genetic diversity through Meiosis which has crossing over; prophase of the first division and independent assortment; metaphase of the first division. As a result, variation of offfspring is achieved.
Genetic preservation in mitosis
In mitosis phase, DNA reproduces itself in a very accurate manner in Interphase so as to make sure that the resulting cell is an exact replica of the original cell (Tateishi-Karimata and Sugimoto, 2021). This makes certain that there is order in cell division and hence avert distortions that originate from mutations so that organisms can grow and replace aberrant cells appropriately and effectively without compromising on the lineage.
AC 3.1 Explain the role of stem cells from the embryo in developing new tissues
4.1 Stem Cells Used in Medicine: Spinal Cord Injury Repair
That is the reason for the damaged nerve cells bring about paralysis, since nerve cells have a negligible capacity for regeneration. There is hope in stem cell treatment which involves the use of pluripotent stem cells meant for replacing the damaged nerve tissue and recuperation of normal function (Kalous and Aleshkina, 2023). Neural stem cells or mesenchymal stem cells are introduced to the region affected by a spinal cord injury with the purpose of restoring their efficiency, reducing inflammation and growing neurons. These seem to have been achieved in the studies and trials where patients who lost their ability to move and feel were able to recover. But, there are still challenges that have to be surmounted, however, stem cell therapy provides hope for future treatment for spinal injury that showed the possibility of a new way of healing.
4.2 Potential future application of stem cells
Stem cell research is a powerful potential for regenerative medicine to proceed into infinity. Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, and heart diseases have possibly seen their treatments as analysts have discovered different treatment approaches (Meitinger et al. 2024). Tissue-healing and stem cell therapies are said to change the face of organ transplant. Gene editing using stem cells is being considered for cure of genetic diseases.
However, it is ethical, especially when dealing with embryonic stem cells, since it raises issues regarding the consent from the embryos and their status as human beings, the regulations make sure that the research is responsible and doesn’t cross the road of science into the realm of unethical (Zarepour et al. 2022). Despite the challenges mentioned above, stem cell science has offered prospects to eradicate diseases that are hitherto incurable, this painting a picture of future medical advancement possibilities.
Conclusion
Understanding the structure and function of cells is fundamental to the study of biology and medicine. From distinguishing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells to exploring organelles, protein synthesis, and the role of stem cells, this assignment highlights how cellular processes sustain life and contribute to medical advancements. The knowledge gained through this exploration provides a strong foundation for further studies in genetics, physiology, and biotechnology. Overall, mastering these concepts is essential for academic success and for appreciating the complexity and adaptability of living organisms.
References
Introduction Sociological imagination refers to the framework for understanding social reality while emphasis over personal...View and Download
Introduction to Evidence-Based Practice In Nursing Assignment Sample Contemporary nursing aims to present a review of the...View and Download
Introduction - Mn5067 Portfolio Assessment Assignment Sample Efficient leadership promotes positive behavior which can...View and Download
Task 1 Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking online Assignment...View and Download
Introduction: Digital Transformation in the Retail Industry Digital transformation refers to the changes made in the existing...View and Download
Introduction to the History Of London Assignment Q.1 Choose at least TWO resources from the list below and critique their...View and Download
