+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that organizes the software based on ideas of objects. It enables efficient arrangement and reuse or programs through the use of objects that contain data as well as behaviors. This report focuses on the realization of the main concepts of OOP using classes and Objects in Java using a case scenario of generic programming.
The first part is dedicated to binary operations on the string, parse strings to Java, conversion to numeric and palindrome. The second section deals with Object-Oriented Design and provides the reader with a clear understanding of classes, objects, and generic classes, concepts frequently covered in assignment help in UK for better understanding of practical programming applications, which serve to enhance the flexibility and maintainability of a software. Using Java API, exceptions, and text manipulation in this text, experienced and prospective program developers understand the significance of OOP. These principles enable writing clean code, writing scalable code, code that has sustainable software qualities, and maintainable code, therefore establishing software sustainability best practices.
This section introduces the foundational concepts of Object-Oriented Programming and how they are applied to the case scenario. It provides a structured approach to designing software using classes, objects, and their relationships, highlighting how OOP principles improve modularity, maintainability, and clarity in program development.
This section presents a Java program to process only binary strings built from characters ‘0’ and ‘1’ with the maximum length of 64 characters. The program reads a binary string, starts from the second character, remodel it in the same order as the first one and returns true if the first string is a palindrome. If the string is palindrome it will return both the bit representation of the string and the actual decimal value of it (GeeksforGeeks, 2024). If not, not only it displays the binary and decimal representation of the given string and the mirror image string but also the reversed string. This implementation makes use of Java string methods as well as numerical conversion and Core OOP principles such as encapsulation and modularity.
OOD is a core concept in software engineering that brings about the use of objects in the organization of programs to create efficiency. It is important to note here that the three main idea that constitute Object-oriented development include classes, objects, and generic classes. A class is a template or a blueprint of objects with precisely defined attributes and their behavior. An object is an occurrence of a class with defined attributes holding particular values, and it can execute actions through relying on/executing the class’s methods. It makes it easier to organize and reuse data and due to the use of more constants than variables the program is more efficient.
One of the biggest improvements the OOD had seen has been the development of generic classes which enhance coding since it can accommodate most data types (Programiz, 2025). A generic class is a class defined to have same class multiple times but the class operate with different data type but not dangerous to type safety. This makes it unnecessary to have different classes of the type just because of their kind thereby eliminating code replication for maintainability.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
For example, in Java, a generic class was designed to encompasses different types of data at one single necessary structure. The use of type parameters in the generic class makes data strong typed while at the same time is more flexible. This leads to more flexible and repeats fewer type-related errors during the run-time of the programs.
To sum up, all of the principles of OOD like encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism bring better modularity, maintainability and efficiency to software systems (Somashekara et al. 2024). Information hiding protects information from being modified directly, and abstraction allows programming new codes to add onto existing features. Polymorphism helps a method to be in a position to handle more than one type of data. If these concepts are applied into java programming, then more reliable, reusable and efficient programs that conform to standard are developed by the developers of the system resulting in an organized system.
References
This section provides an overview of how Object-Oriented Analysis uses UML diagrams to model system interactions. By defining actors, use cases, and their relationships, developers can visualize system functionality and requirements clearly, which aids in planning, designing, and implementing software effectively.
A3.1 Fundamental Concepts of Actor and Use Case
In OOA, actors and use cases are the critical elements of Use case diagram that depict a broader version of how a system interfaces with the user.
An actor is therefore a human or an external system that uses the system. As for actor roles, there can be initiators – actors that begin the interaction and reactive – actors that respond to the actions of the system. Booch, Rumbaugh and Jacobson assert that actors define roles not persons in order to attain abstraction and generalization in modeling.
In more detail,Use case is a description of, a feature or an interaction of the system with an actor. To the simple-minded, it describes a set of steps that bring about a worthwhile goal. Use cases are about user goals and not about the implementation of a system and hence should be used in identifying requirements and system design phase.
A3.2 Identified Actors
As for the actors, the following are found in the given scenario:
A3.3 Use Case Diagram
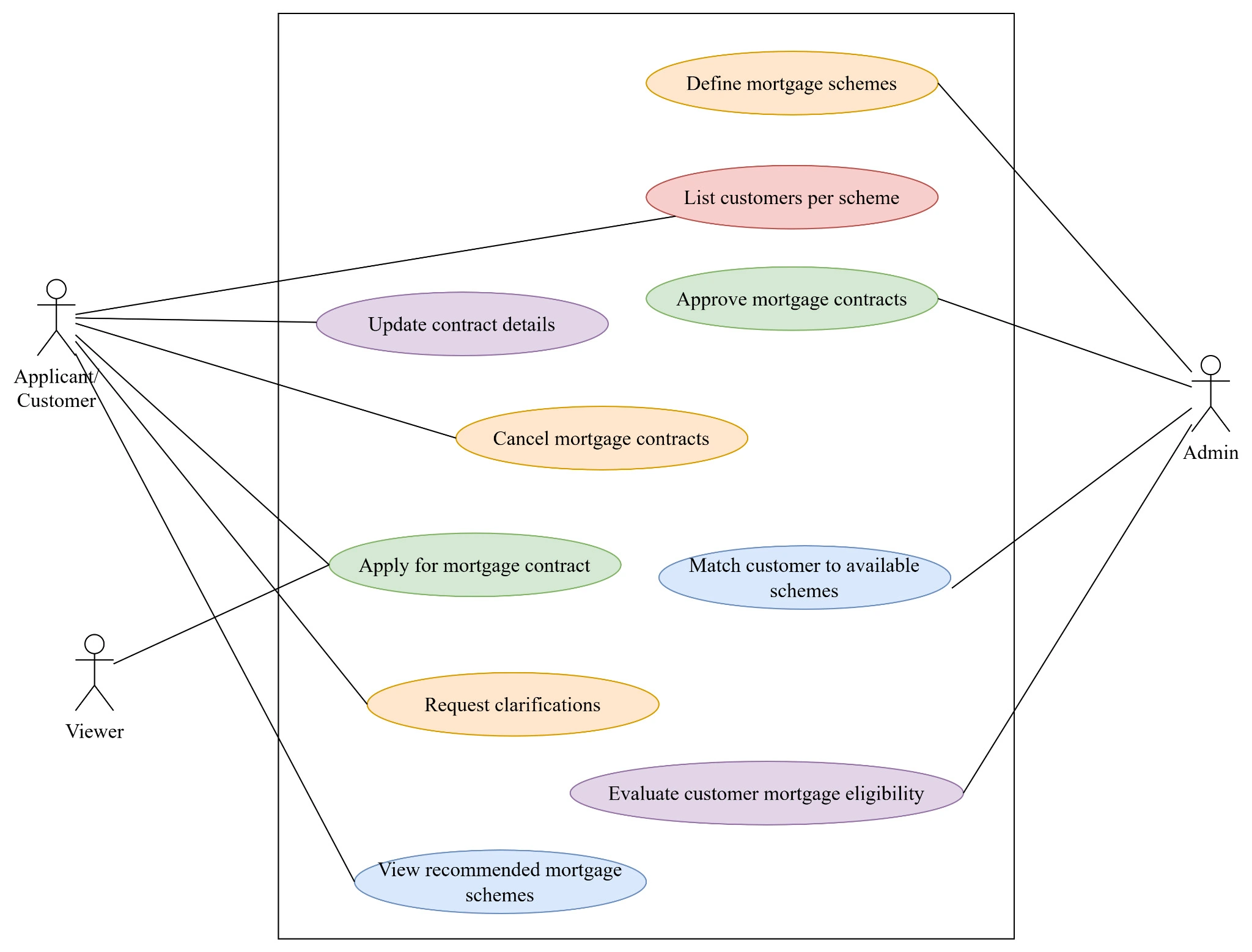
Figure 1: Use Case Diagram
Such a breakdown also helps to provide clarity in the organization of interactions between different systems and also follows good practice where UML modeling is concerned.
References
This section explains how algorithms and logical reasoning are applied in object-oriented analysis to model complex system behaviors. It highlights how class diagrams, relationships, and object interactions help developers understand system structure and ensure accurate, efficient, and maintainable software design.
A4.1 Class Diagram and Relationships
Class diagram in OOA is specifically used to depict the static view of the system, showing the classes, attributes, methods, and the relations between them. These diagrams assist the developers in comprehending the design of a system, how the systems interfaces and interacts, and various limitation measures which must be observed.
In mediating the processes of the mortgage system scenario, the emerged primary classes are as follows:
A4.2 Identified Sets of Objects and Complex Relationships
Sets of Objects
A set is an organized collection of items of a certain category. The objects that we categorize based on the given aforesaid scenario are as follows:
Complex Relationships
Many-to-Many Relationship: Applicants and Mortgage Schemes
Symbolically, they can be expressed as Applicant_set and Scheme_set which holds a relation with each other.
Application ⊆ Applicant_Set × Scheme_SetApplication
In the case of the symbol Application, where each tuple (A_i, S_j) means that A_i has applied to be enlisted in S_j.
Many-to-Many Relationship: Risk and Compliance Officers and Customers
This can be explained mathematically as follows:
Supervision ⊆ RCO_Set × Customer_Set
where each tuple (RCO_x, C_y) ∈ Supervision means that RCO_x is the responsible for the customer C_y.
A4.3 Logical Expressions Representing Relationships
To represent these relations the following notations are used: set notation and logical statements
Applicant to Mortgage Scheme Relationship (Many-to-Many)
∀Ai∈Applicant_Set,∃Sj∈Scheme_Set:(Ai,Sj)∈Application
This precisely means that for any given applicant, there must be a mortgage scheme that the person can qualify for.
Customer to RCO Relationship (Many-to-Many)
∀Cy∈Customer_Set,∃RCOx∈RCO_Set:(RCOx,Cy)∈Supervision
This states that each customer must have at least one Rating of Credit Officer supervising over their mortgage contract.
System Matching Customers to Schemes
∀Cq∈Customer_Set,∃Sk∈Scheme_Set:(Cq,Sk)∈Match
This stipulates that the process of selection of mortgage schemes that clients qualify for, is done automatically and every customer is required to be matched to at least one suitable scheme.
Approval Process Between RCO and MM
∀Cy∈Customer_Set,∃RCOx,MMw:(RCOx,Cy)∈Supervision∧(MMw,Cy)∈Approval
This implies that any mortgage contract has to go through the process of examination by an RCO as well as approval by the Mortgage Manager.
References
This section focuses on the practical application of OOP principles through testing. It demonstrates how unit testing verifies that each part of the system works as intended, ensuring reliability, correctness, and robustness in software development.
Use Case Diagram
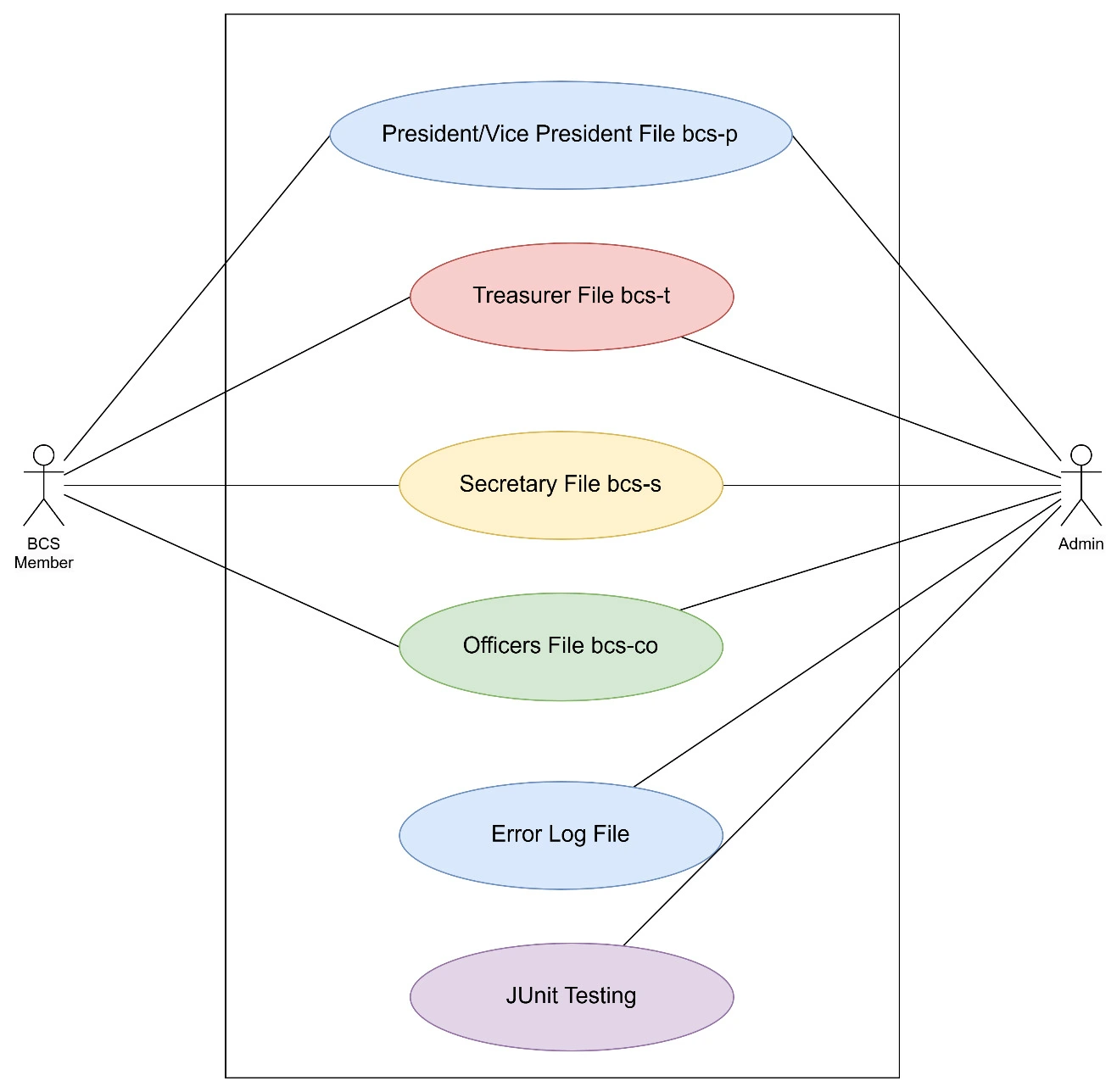
Figure 2: Use Case Diagram
This diagram illustrates the type of relationship that PiSocExecs has together with the actors or users. BCS Members offer personal information, which PiSocExecs processes. As a result, its students’ records are divided into separate files according to their roles. Incase the above UoB numbers are invalid, the system writes them into an Error Log File. The records are managed by the admins and the processes are properly coordinated. The first assert type ensured by JUnit Testing is to check if separateExecs() function runs as per its designed operational plan.
This is structural diagram of PiSocExecs system in which, represents different classes and their relationship.The core class of PiSocExecs is responsible to manage the record of all students. FileHandler deals with opening and pathing when it comes to the text files. It also contains ExceptionHandler that checks proper format of UoB numbers and log the errors. Statistics collections and analyzes data. The Automated JUnitTests tests the separateExecs() method for the class to check whether it is functioning correctly or not.
References
Introduction to Managing Food and Beverage Operations Assignment Sample ACTIVITY 1 TASK 1 (LO1) P1: Different types of...View and Download
Introduction - Business Project Assessment Sample In the dynamic business environment, numerous challenges are faced by the...View and Download
Introduction - Unit 3 Theories, Principle and Models in Education and Training Make your assignments stand out with our...View and Download
Introduction to Psychological Disorders Mental Health Assignment The main aim of the study will be based on the several...View and Download
Chapter 1: Introduction : Workplace Culture-A Case Study Of ASDA Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts...View and Download
Assignment 1: Explain the role of marketing and how it interrelates with other functional units of an organisation Enhance your...View and Download
