+44 75754 30035 help@rapidassignmenthelp.co.uk
offer
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
🎁Special Offer 🎁 Discounts - Up to 55% OFF!
Struggling with complex operations topics? Get Help with Assignment from professionals who simplify concepts in Manufacturing and Service Operational Management. Whether it’s theories, Industry 4.0 integration, or strategy development, our experts provide tailored support to ensure clarity, accuracy, and academic excellence in every submission. Let’s streamline your success.
The study of Manufacturing and Service Operation Management (MSOM) plays a crucial role in engineering management. It involves the planning, execution, and regulation of processes that transform raw inputs into final goods or services. Efficient management of both manufacturing and service operations helps organizations achieve operational excellence, meet customer expectations, and maintain a competitive edge.
The Primary Aim of this study is to conduct a thorough analysis of the fundamental concepts, tactics, and obstacles in the field of MSOM, and also construct a framework that may effectively improve operational efficiency and enhance customer satisfaction. The purpose of this research is to analyse the theories and concepts present in MSOM, strategies, and challenges for a better framework which could lead to improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The research objectives comprise of - investigating the existing MSOM techniques, determining the challenges in the field of production/service management, assessing the methods of process improvement, and suggesting the novel solutions to the topical MSOM issues.
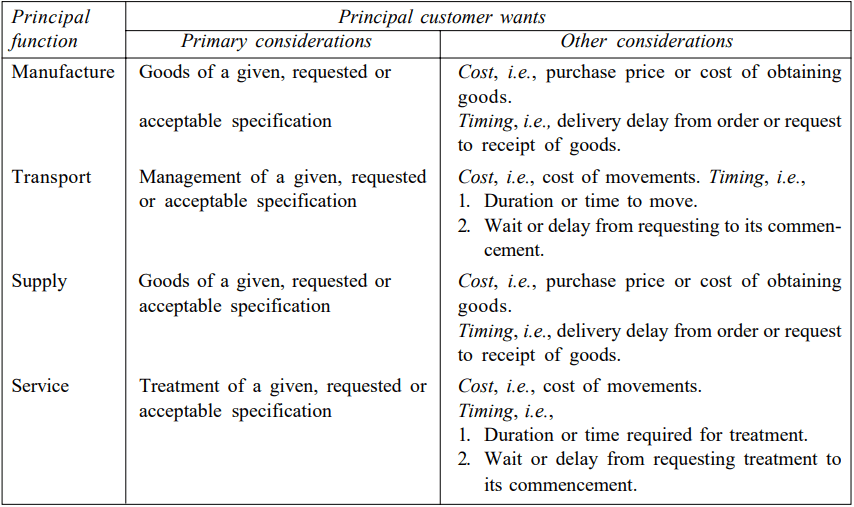
This section explores the fundamentals of manufacturing operations and production systems, emphasizing the importance of planning, coordination, and control in achieving efficient production.
It highlights various production types, the significance of customer satisfaction, and the challenges globalization poses for operations managers in aligning processes with global market demands.
According to Patil (2022), the utilization of the assembling capabilities is of principal importance in the domain of authoritative administration, as it contains the cycle by which data sources are changed over into wanted yields, thus expanding the ease of use of the eventual outcome. According to the author, production may be defined as the process of generating tangible things and intangible services (Patil, 2022). Also from the study of Kumar and Suresh, 2006 the different types of production systems, such as WorkShop, Batch, Mass, along Continuously Manufacturing, possess distinct features that are tailored to meet particular objectives. Production management encompasses the systematic coordination and oversight of many operations related to production, including but not limited to organizing, directing, planning, and regulating.
_compressed[1].png)
(Source: Kumar and Suresh, 2006)
Its essential goal is to guarantee the conveyance of items or administrations that satisfy foreordained guidelines of amount, standard, idealness, and cost-viability. The achievement of optimal operations management involves the careful consideration and balancing of both client satisfaction and usage of resource goals.
(Source: Kumar and Suresh, 2006)
The phenomenon of globalization presents an additional layer of complexity for operations managers, as they are required to adopt a global perspective in order to effectively coordinate their goods and strategies with varied markets (Patil, 2022). Within this particular context, the domain of manufacturing and operations management includes a range of tasks, including but not limited to plant setting, plant arrangement, development of products and processes, planning production, quality assurance, inventory control, and maintenance management. These roles jointly contribute to the optimization and efficacy of the company's manufacturing processes. [Referred to Appendix 2]
According to Olsen and Tomlin, 2020. The idea of Industry 4.0 embodies a fresh era of manufacturing powered by the combination of cyber and physical systems. The current revolution is facilitated by several technologies such as additive manufacturing (commonly known as three-dimensional manufacturing), the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain technology, sophisticated robots, and artificial intelligence (AI). The aforementioned technologies possess the capacity to alter conventional operational trade-offs, hence augmenting attributes such as adaptability, efficiency, and excellence, while concurrently diminishing expenses. One example of a technology that provides distinct benefits is additive manufacturing. This method allows for the creation of intricate forms and internal structures, facilitating the speedy development of prototypes and decreasing initial manufacturing expenses.
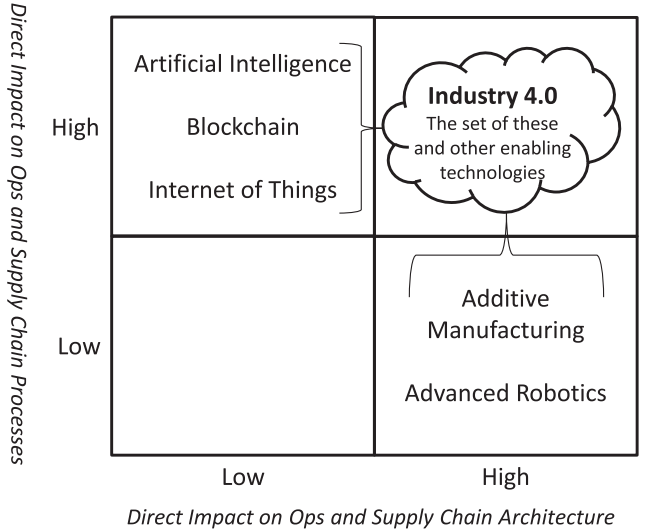
(Source: Olsen and Tomlin, 2020)
The use of blockchain technology guarantees the establishment of a safe and transparent system for storing data. This technological advancement has brought about a significant transformation in the oversight of supply chains by facilitating the provision of comprehensive product histories and allowing the execution of smart contracts (Olsen and Tomlin, 2020). The incorporation of advanced robotics, especially cooperative robots, is becoming predominant across different areas, for example, manufacturing and horticulture because of its improved moderateness and flexibility. These technologies provide prospects for inventive operational techniques, such as regionally dispersed low-volume production and assembly-free manufacturing.
According to Terra et al. 2021, their study examines the difficulties associated with the integration of "Industry 4.0 Practices" with "World-Class Manufacturing" (WCM) within the framework of increasing manufacturing processes and the intricate monitoring of data. The research, which employed a semi-structured questionnaire to collect data from 15 prominent multinational corporations spanning five nations and three continents, demonstrates that the synchronization of a company's strategic objectives with Industry 4.0 and World Class Manufacturing (WCM) practices enhances productivity by means of production surveillance, analytical tools, and the cultivation of an organizational culture that prioritizes process enhancement. The significance of human resources is recognized as pivotal in the process of integration.
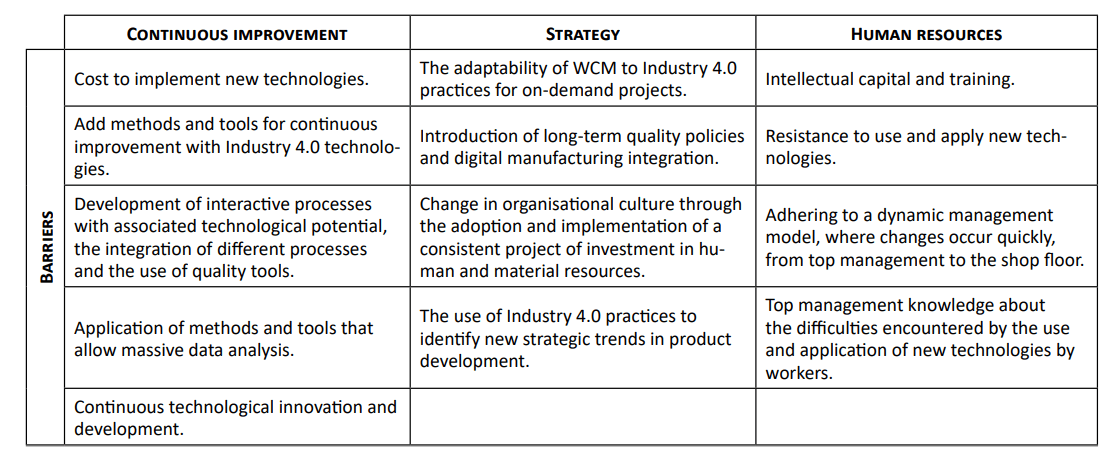
(Source: Terra et al. 2021)
Nevertheless, the research features huge deterrents to progression, for example, the monetary ramifications of implementing technology, limited understanding of practical methodologies and devices, lacking accessibility of gifted staff, and worker hesitance towards newly implemented procedures. The rapid pace of growth in Industry 4.0 outpaces the rate at which continuous improvement techniques are implemented.
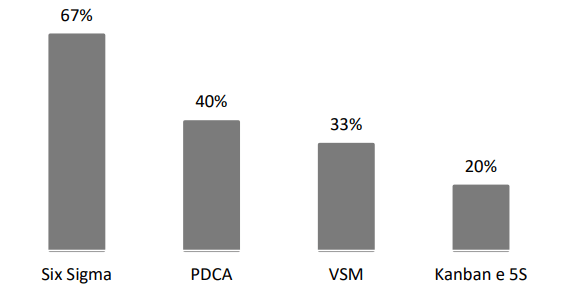
(Source: Terra et al. 2021)
Consequently, there is a need for dedicated research on the practices of World Class Manufacturing (WCM) and Industry 4.0. The study highlights the need to implement strategic modifications in production procedures to successfully integrate both world-class production (WCM) and Industry 4.0 technologies. The incorporation of Industry 4.0 principles into the World Class Manufacturing (WCM) approach necessitates the reevaluation of strategies, adoption of emerging technology, and development of a proficient workforce. This research highlights the significance of aligning human resources, technology improvements, and organizational strategies in order to facilitate an easy transition between Industry 4.0 and WCM, hence improving efficiency and competitiveness at a worldwide level.
According to Mehmood, 2021, in the competency model, different kinds of acknowledgments, and abilities with various skills are required for the fleet with the distribution of management in e-commerce related sector to maintain different successful shift of various materials between several organizations in the aspect of the management of supply chain logistics to gain high levels of dependability with significant cost-effectiveness. This research assessment tried to figure out the collaboration and the effect of the competencies of IT and different practices that connected with fleet management to gain effective service delivery (Mehmood, 2021). With the help of methodology, the section of this research paper followed a descriptive design. A dataset with diverse insights based on some real-world information is used here for the betterment of this research assessment.
Figure 4: 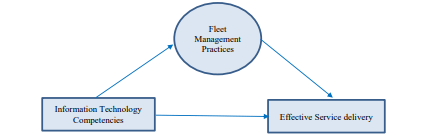
(Source: Mehmood, 2021)
The significant outcome of this assessment highlighted the relevant connections with the effective service delivery context by assessing different outcomes with different hypothesis assessments. Researchers also proposed some recommendations related to the competencies of information technology with different multi-dimensional aspects which should be improved based on aligning the latest innovations to smoothen fleet management.
According to Wand, et al. 2022, researchers investigated different kinds of journal papers with scholarly items to signify the issues related to email engagement and its relevant effects on consumers and the significant dependability aspects connected with numerous service providers with retailers. Researchers used various kinds of literary sources to connect the significant assessment to develop customer retention. Researchers concentrated on various empirical studies related to the engagement of consumers in the aspect of e-mailing services (Wand, et al. 2022). To conduct the relevant outcome, researchers analyzed different field experiments on the insights of a large group of US car wash chains that introduced a tiered subscription system that connected with consumers several RFID-related technologies to monitor numerous events and functions related to subscription services. Researchers also introduced survival assessment with different-in-differences procedures to calculate the relevant impacts on email engagement. Through assessing various procedures, researchers discovered that engagement of the subscriber increases based on a specific period. By assessing various contexts related to lifetime value with subscriber aspect with basic level subscribers, researchers recommended some specific strategies by providing email engagement to connect the aspect of profitable subscription aspect. Researchers also highlighted the importance of subscription service providers with an adaptation approach to improve e-mail engagement contexts.
In the aspect of manufacturing and service operation management, different theories regarding integrative theories, and bureaucratic theories with different operational theories are relevant here. The Bureaucratic Theory will focus on different connections with coordination between various key variables between organized sectors. The functional theory will explain the importance of collaboration with various operational areas related to the business with operation management. In the context of the operational management aspect, different theories will be very effective in the aspect of connecting different departments. Different types of models related to physical with schematic and mathematical models will be very relevant due to connecting different factors like maps of routings, and networks based on specific events.
The literature examined offers a thorough examination of manufacturing procedures, management of production, and the transformational effects of Industry 4.0 methods. According to Patil (2022) along with Kumar & Suresh (2006), production may be defined as the systematic transformation of various inputs into tangible commodities and services. The field of operations management is of utmost importance in achieving efficient production via the careful monitoring of consumer happiness and resource allocation. The phenomena of globalization introduces intricacy, necessitating a global outlook in the field of operations management. According to Olsen and Tomlin (2020), Industry 4.0 signifies a paradigm shift in the manufacturing sector, characterized by the convergence of digital and physical structures. Technological advancements like added substance manufacturing, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and artificial intelligence (AI) add to the upgrade of adaptability, proficiency, and cost-adequacy. The issues related with the integration of Industry 4.0 with World-Class Manufacturing (WCM) are highlighted by Terra et al. (2021), who stress the criticality of fitting vital objectives, HR, and technological forward leaps. Regardless of the expected benefits, there are provokes that should be thought of. These difficulties include financial ramifications, limited comprehension, and reluctance to change. The process of addressing these disparities necessitates the implementation of deliberate adjustments, integration of nascent technology, and cultivation of a proficient labor force, underscoring the need for more investigation in this domain.
The study's research design integrates a combination of both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Qualitative research is centered on the study of resources and data via observation and perception, while quantitative research yields quantifiable findings and statistical analysis depending on the research conducted (Battesini et al. 2021). The selection of a study design is based on the positivist ideology, which prioritizes the generation of statistical findings via the application of logical reasoning to existing data.
|
Qualitative Analysis |
|
Quantitative Analysis |

Figure 4: Research Design
(Source: Self-Created)
This research about Manufacturing and Service Operation Management aims to overcome the built-in limitations of qualitative and quantitative assessments by using a combined approach. By incorporating and combining both methodologies, the study seeks to improve the robustness and validity of its results (Hashemi-Petroodi et al. 2020). The present study aims to establish the credibility of data obtained from primary and secondary sources by means of a meticulous assessment procedure. The amalgamation of both quantitative and qualitative information will provide a strong basis for deriving significant results within this realm of study.
This study adopts a positivist philosophy, which emphasizes the verification and evaluation of theoretical assertions and research questions formulated for the research. The selection of a research philosophy has significant importance within the field of Manufacturing and Service Operation Management, as it serves as a guiding principle for conducting a study in alignment with its predetermined strategic goals (Kirongo, and Odoyo, 2020). The study endeavors to adhere to the principles of positivism, with a focus on offering quantitative explanations. Specifically, it tries to explore the purchasing habits and decision-making procedures that are impacted by intense advertising methods. Adhering to this philosophical approach guarantees that the results are based on empirical facts and quantifiable data, thus promoting a thorough comprehension of the study context. This methodology facilitates the examination of certain domains within consumer behavior, guaranteeing a methodical evaluation of the impacts of advertising tactics (Hürlimann and Hürlimann, 2019). The research philosophy plays a fundamental role in establishing the framework for research methodologies, tactics, and procedures, hence enhancing the overall quality and knowledge base of studies conducted in the fields of Industrial and Services Management of Operations
This Research approach is based on deductive approach. The selection of a research strategy plays a critical role in influencing the examination and interpretation of data within the field of Manufacturing and Service Operation Management. Two basic techniques, ly the inductive and deductive approaches, are often used. The deductive method is predicated upon the use of established theories, which serve as a framework for directing the study towards predetermined conclusions that are informed by pre-existing information (Mehrad and Zangeneh, 2019). On the other hand, the inductive technique involves the exploration of novel material, which subsequently results in the development of original hypotheses and perspectives. The choice of methodology is firmly created with the fundamental examination idea. This exploration upholds the positivist philosophy, which contends for the utilization of the consistent technique (Taherdoost, 2022). By utilizing pre-existing data, this methodology empowers a systematic examination, empowering the creation of results that efficiently tackle the review requests. Subsequently, the logical methodology is viewed as the most suitable for this review, since it works with a systematic and theory-based investigation of issues connected with Manufacturing and Service Operation Management.
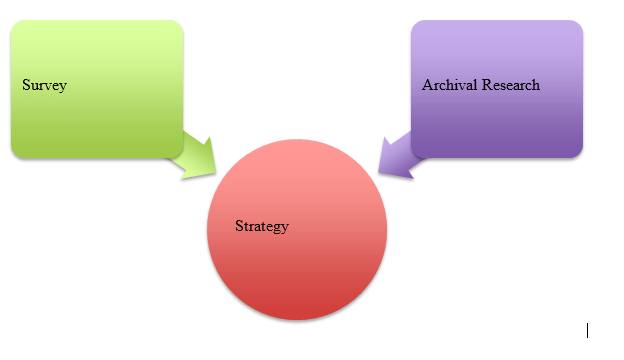
This research paper follows archival research strategy as research strategy. The system of examination utilized in this study is steady with the positivist ideology, which focuses on the social affair of quantifiable and prior information that is appropriate to the subject area.
|
Strategy |
|
Survey |
|
Archival Research |
Figure 5: Research Strategy
(Source: Self-created)
The collection of essential information includes the utilization of reviews collected by surveys, working with the methodical collection of information directly from people engaged with the review (Battesini et al. 2021). This procedure ensures the foundation of the review's premise on existing information, while empowering the assessment of a great many perspectives (Duffner et al. 2021). Besides, the utilization of secondary information gathering includes the execution of the authentic exploration procedure, which includes the assessment of prior documents and literature.
Data gathering is of most extreme significance in the domain of Manufacturing and Administration Operation Management as it empowers a far reaching understanding of intricate operational characteristics. In this review, an efficient data-collecting approach will be utilized, including the utilization of Google Forms to plan and administer organized questions. There will be 20 respondents that will be conducting this survey and will be conducted using the google forms. The polls will be painstakingly created to gather subjective inputs from the people who have aptitude in the sector, experts, and partners (Kumar et al. 2020). The subjective procedure seeks to explore in-depth the emotional encounters, perspectives, and discernments pertaining to administration and creation exercises.
After the finish of the data-collecting stage, the gathered responses will be exposed to investigation using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). The Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) is a robust software application often used for the analysis of quantitative data (Çınar et al. 2020). However, in this context, it will be employed for the purpose of interpreting qualitative data. The identification of recurring themes, trends, and qualitative linkages within the obtained data will be accomplished via the use of qualitative coding and theme analysis techniques.
The maintenance of research ethics is of utmost importance while undertaking the administration of survey questionnaires within the realm of Manufacturing and Service Operation Management. The privacy and anonymity of participants will be rigorously maintained, ensuring that their replies are combined and de-identified throughout the analytic process (Lee, 2021). The researchers will ensure that informed permission is acquired from participants, clearly stating the objectives of the questionnaire and emphasizing the voluntary aspect of their involvement. Participants will get the guarantee that their replies will only be used for the purpose of conducting research. The study procedure will adhere to ethical principles and standards, ensuring the protection of participants' privacy and dignity.
This section is dedicated to the examination of possible outcomes of the survey questions directed to 20 peoples related with manufacturing and service operational management concepts in order to answer the core research questions designed for this study. The analysis focuses on the responses that illustrate the perceptions regarding present day MSOM strategies, barrier in production and service operations, present process reengineering techniques, crucial problems, the levels of satisfaction with existing processes, procedural bottlenecks, prospects for digitalization, areas that need improvement and effective management paradigms. These key findings are then examined in the light of general MSOM theory and models, pointing out crucial gaps and problems. Furthermore, actionable recommendations generated from the breakdown are given as advice for enhancing operational effectiveness and customer satisfaction. The other research areas are also identified to support the findings on a wide range. This analysis and discussion makes a minimal yet significant contribution to knowledge in the MSOM.
It can be expected that the results will reveal that the majority of the participants are knowledgeable about the modern MSOM methods to some degree. They think that there is still work to do in overcoming problems such as the inefficiency of the processes and the supply chain issues. The participants are also thought the current streamlining techniques are not very effective. Quality control, costs and customer satisfaction will significantly emerge as key challenges, though the satisfaction levels with present practices may differ. Bottlenecks in process are sometimes, but sometimes, even frequent (Atasu et al., 2020). The use of digital technologies integration is generally viewed as advantageous for efficiency enhancement. Improvement effort should be concentrated on production planning and scheduling, supply chain management, and service delivery. Respondents seem to be ready to apply new methods of systematic management. Lean management and Six Sigma approaches seem to be the most popular ones presently when it comes to enhancing customer satisfaction.
An inspection of the answer choices provides some interesting possible insights that may come out. Even though most participants were somewhat familiar with current MSOM, many still disputed the usefulness of the changes and expressed discontent with today’s approaches. It shows that there is a worrying gap between theory and practise as it can be found after survey. Similarly, if most people view digitization in a positive way but not all are willing to adopt it, organisational inertia may be the reason that tech is not integrated (Zhou et al., 2022). One other thing that can be a surprise is that while quality control and customer satisfaction are thought to be higher priority than cost control, there is a huge chance that perspective might change after the results. If supply chain disruptions are referred to as the major limitation, the still-undervalued impacts of events such as the pandemic would be highlighted. Any such thought-provoking conclusions should be emphasised on their potentiality to instigate the changes by rectifying them clearly.
Get assistance from our PROFESSIONAL ASSIGNMENT WRITERS to receive 100% assured AI-free and high-quality documents on time, ensuring an A+ grade in all subjects.
The expected survey outcomes are directly related to the primary research questions that are developing MSOM foundations, identifying the challenges, improvement methods, and new solutions. The responses will specifically point out the shortage of proper digitalization and process blockages as a fundamental problem of the companies, when they are aimed at the efficient management of production and service operations. The other is quality control and cost control that forms a part of the core issues which are critical for choosing the areas that need innovation. Outcomes are about determining if existing streamlining methods are effective and presentation of how satisfied the users are. Responses that comprise patterns of improvement areas, roadblocks like supply chain weaknesses, approaches that offer strategic ways, also come into light to provide critical insights to enrich the MSOM frameworks using emerging technologies and philosophies for operational excellence and customer centricity. What is essential to note here is that any counterintuitive results may draw attention of the scientists and engineers to promising areas for new research and unprecedented applications which, in turn, could be used to establish a new standard or best practices for the future.
Some important inferences are made from the findings that were expected. A lack of parity between theories and practical effectiveness emphasises that the MSOM principles do not transfer into success, which should be a sign for their reconsideration. Organisations appear quite reluctant to embrace a digital culture indeed; digital campaigns should be propagated accordingly. Basing too much on cost and productivity may depreciate the virtue of "customer centricity" thereby necessitating the need for more "quality/satisfaction" metrics to be considered whilst making decisions. The presence of legacy processes and technologies within supply chains constitutes a major risk when times are uncertain. Lean, Six Sigma and agile all have their merits, but how they ought to be addressed may depend on suitability (Singh and Rathi., 2019). Parts from each could be blended together into a single framework. Similar to the individual findings, the overall themes centre on people, process and technology - these focus areas form a holistic foundation for an MSOM transformation strategy geared towards engagement, enablement and experience.
The basic concepts of supply chain management consist of production planning, inventory control, supply chain harmonisation, quality assurance, process design, customer relationship management, productivity metrics and technology integration. Evidence from the survey will offer an authentic assessment as to where current performance is found wanting with regard to these several specific dimensions - be it through operational and quality lapses, digitization gaps, no customer-centeredness or legacy supply chain vulnerabilities. Further, accessories to the issues concerning the barriers for skills, laws as well as sustainability have marked correlation with abilities facing MSOM that are comprising personnel readiness, administrative loads and environmental requirements (Brown et al., 2018). Additionally, it is evident that the customer-centric approach is becoming a dominant trend through the underlining of customer-oriented strategy approaches such as Service Design Thinking. As such, the identified findings should be studied for their feasibility under re-defined MSOM basic tenets in terms of people, process and technology aspects. Then new integrated frameworks can rework, accordingly, the old systems with new demands like digitalization, customizability and robustness.
Some of the data gaps and vulnerabilities are likely to be emphasised by the survey results. This means that the existing streamlining processes, which could be seen as ineffective, point to a shortcoming of translating manufacturing systems organisation principles into manufacturing floor practices. Talent shortages that represent barriers, as well as skill gaps, are challenges that the curriculum reforms should take into account. Reliant on old technologies by many firms is an evidence of how important it is to embrace digitalization. Although customer dissatisfaction and quality problems show that there are still technological gaps between the customer’s experience and the process, state of the art MSOM solutions have improved the situation. Over dependence of supply chains on some areas demonstrates lack of coverage and risk management in concerned operations. Compliance constraints relating to regulation draw attention to the policy gap, where the latter does not take into account the right proportion of supervision and ease of doing business. Through these gaps lies the big issue of change inertia which is one of the main consequences of insular thinking, self-preservation instincts and legacy mindsets.
The study is of a broad significance both in the MSOM theory and practice. It underlines the possibility of disconnection among implementers and the concepts, pointing out the need to restructure academic programs towards a process rather than philosophical instructions for the purposes of transferring the knowledge gained into real-world skills and a shift of values and culture in the industry. Moreover, customer parameters pervade throughout insights that therefore put their point of view first could be crucial to up their services, adjust processes and improve their technologies. The supply chain risks highlight the requirement of developing secure and transparent networks via open data standards, predictive systems and near-shoring. Legacy processes should take advantage of automation and analytics to be efficient without seeing jobs lost to adopt a hybrid human-machine type of methodology. Force behind compliance and sustainability is innovation to generate ideas like product tracking based on blockchain and circular production models (Lohmer and Lasch., 2020). Companies have to move away from marginal enhancements directed to costs or quality factors unbundled and embrace integrated solutions based on customer, employee, and ecosystem value creation in order to holistically transform MSOM.
The findings on expected survey results highlight a very important disconnect between the MSOM theory and the current practices as well as clearly exposing the areas of improvement in terms of process excellence, customer centricity, risk mitigation and technology infusion. Equally the insights are highlighting human, process and technical dimensions for bringing organisational effectiveness. There are limitations in the study due to the sampling size and methodological constraints, however, the results provide the foundation for a more detailed analysis, audits, value stream studies, maturity analysis, and integrated modelling to progress the MSOM frameworks. The study revolved around cultural change and customer centricity, supply chain stabilisation, process automation and human craftsmanship, and sustainability innovation. This multi-faceted approach can bring out the best of MSOM and design future-ready operations.
5.1 Conclusions
This study conducted a comprehensive analysis of Manufacturing and Service Operational Management (MSOM) in the field of Engineering Management, including both qualitative and quantitative research methodologies. The participants exhibited differing degrees of expertise with MSOM, with notable issues included market competitiveness, regulatory compliance, resource limitations, and technological obstacles. The present tactics used in the field of MSOM have garnered a varied range of evaluations, underscoring the need for enhancements in operational effectiveness, client satisfaction, quality management, and inventory chain management. The research findings demonstrated a significant association between individuals' views towards the integration of digital technology and their inclination to embrace innovative MSOM strategies. The assessments of novel MSOM approaches were shown to be barely impacted by satisfaction with established practices. The results underscore the intricate characteristics of MSOM issues, underscoring the need for tailored approaches to achieve successful resolutions.
5.2 Recommendations
Reference List
Articles
Books
Website
Introduction - Reflective Writing Struggling to meet deadlines? Rapid Assignment Help provides fast, reliable, and affordable...View and Download
Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking the Assignment Help from Rapid...View and Download
1.0 Introduction Get free samples written by our Top-Notch subject experts for taking help from our assignment helper. The...View and Download
Introduction to Business Finance Assignment Ratio analysis refers to the study of line items that appear in a company’s...View and Download
Introduction Achieve your academic dreams with expert Assignment Help that guarantees top grades and timely...View and Download
Introduction to Unit 15 Hospitality Marketing Essentials Marketing may be defined as a process, activity and set...View and Download